
The measurement of voltmeter in the following circuit is:
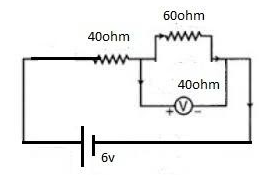
A) 2.4V
B) 3.4V
C) 4V
D) 6V

Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: To solve the above problem we will use Ohm’s Law, which tells us about the linear relationship between the voltage and current.
V=IR (V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance).
In the above circuit, we will calculate total resistance ( parallel combination of resistor of voltmeter and 60 ohm resistor into one resistor) and then the total current of the circuit
Voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the circuit or element of which we have to find the voltage.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first convert two resistors connected in parallel connection into one single resistor.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} = {R_{eq}}$ (in parallel connection ,we use the fractions of the given magnitude to calculate the equivalent resistor)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1} \times {R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$ .........1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{60 \times 40}}{{60 + 40}}$ (we have substituted the values of given resistors in the circuit)
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2400}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow 24 \\
$ (24ohm is the equivalent resistor of the parallel combination of resistors)
Let’s apply the ohm’s law in the circuit given in the question:
Now we have 40 ohm and 24 ohm resistors in series:
Therefore, Req = 40+24=64 (when resistors are connected in series their magnitudes are added)
Current in the circuit is:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
$
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{6}{{64}} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{3}{{32}} \\
$ (Substituted the values of voltage and total resistance)
Voltage across 24 ohm resistor is:
We have calculated current $I = \dfrac{3}{{32}}$ and resistor as 24ohm
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} = \dfrac{3}{{32}} \times 24$
$ \therefore {V_1} = 2.5V$
Option 1 is correct.
Note: Ammeter measures the magnitude of current flowing in the circuit and always connected in series in the circuit. Voltmeter measures the magnitude of voltage drop across the connected circuit or element and is always connected in parallel in the circuit.
V=IR (V is the voltage, I is the current and R is the resistance).
In the above circuit, we will calculate total resistance ( parallel combination of resistor of voltmeter and 60 ohm resistor into one resistor) and then the total current of the circuit
Voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the circuit or element of which we have to find the voltage.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first convert two resistors connected in parallel connection into one single resistor.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} = {R_{eq}}$ (in parallel connection ,we use the fractions of the given magnitude to calculate the equivalent resistor)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R_1} \times {R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}}$ .........1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{60 \times 40}}{{60 + 40}}$ (we have substituted the values of given resistors in the circuit)
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2400}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow 24 \\
$ (24ohm is the equivalent resistor of the parallel combination of resistors)
Let’s apply the ohm’s law in the circuit given in the question:
Now we have 40 ohm and 24 ohm resistors in series:
Therefore, Req = 40+24=64 (when resistors are connected in series their magnitudes are added)
Current in the circuit is:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
$
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{6}{{64}} \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{3}{{32}} \\
$ (Substituted the values of voltage and total resistance)
Voltage across 24 ohm resistor is:
We have calculated current $I = \dfrac{3}{{32}}$ and resistor as 24ohm
$ \Rightarrow {V_1} = \dfrac{3}{{32}} \times 24$
$ \therefore {V_1} = 2.5V$
Option 1 is correct.
Note: Ammeter measures the magnitude of current flowing in the circuit and always connected in series in the circuit. Voltmeter measures the magnitude of voltage drop across the connected circuit or element and is always connected in parallel in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




