
The maximum volume of the right circular cone having slant height 3m is
$\begin{align}
& \left( A \right)3\sqrt{3}\pi \\
& \left( B \right)6\pi \\
& \left( C \right)2\sqrt{3}\pi \\
& \left( D \right)\dfrac{4}{3}\pi \\
\end{align}$
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: We start solving this problem by considering the height and radius of a cone as h and r respectively. Then, we use the Pythagoras theorem to write ‘r’ in terms of h. Then we use the formula for volume of cone $Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$, and later substitute the value of r in it. Then we differentiate the volume and equate it to zero to find the condition for maximum volume and substitute in the volume formula to find the maximum volume of the cone. We use the following formulas while solving the question, $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n\times {{x}^{n-1}}$ and Pythagoras theorem, ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We were given that the slant height of the cone is 3m.
So, let us consider the height of the cone as h and the radius of the base of the cone as r.
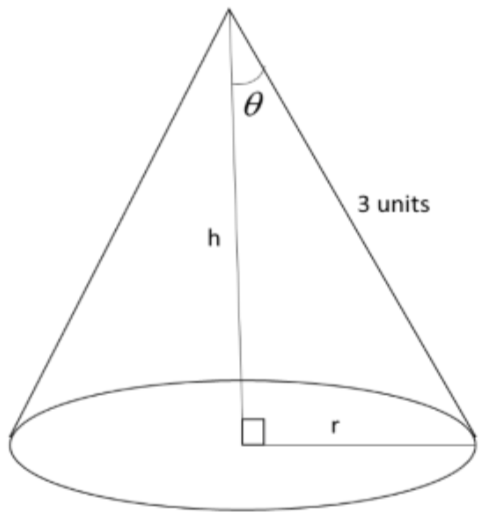
As the cone is right circular
Using Pythagoras Theorem, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}={{3}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=9-{{h}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us consider the formula for the volume of cone of height h and radius r,
$Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Using this formula, we get volume of our cone as
\[V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, let us substitute above attained value of r in the volume,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-{{h}^{2}} \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us use the optimization techniques. When a function $f\left( x \right)$ is at its extremum, that is maximum or minimum if its derivative is zero, that is ${f}'\left( x \right)=0$.
So, let us differentiate volume with respective to h.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{dh}\left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us equate it to zero.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 9-3{{h}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{h}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=3 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3},-\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we need to find which of them is the condition is for maximum.
The condition for maximum is double derivative of the function should be negative.
As \[\dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right)\], let us differentiate it with h to find the double derivative.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( -3\times 2h \right)=-2\pi h \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us substitute the values obtained in the double derivative of volume.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=\sqrt{3}}}=-2\pi \left( \sqrt{3} \right)<0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=-\sqrt{3}}}=-2\pi \left( -\sqrt{3} \right)>0\]
As the double derivative is negative when \[h=\sqrt{3}\]. It is the value for which the volume is maximum.
Now, let us substitute the above value in the formula for volume. Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9\left( \sqrt{3} \right)-{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9\sqrt{3}-3\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 6\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi \left( 2\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=2\sqrt{3}\pi \\
\end{align}\]
Hence maximum volume of cone is \[2\sqrt{3}\pi \] cubic units. Hence answer is Option C.
Note: We can also solve this problem by writing r and h in terms of angle $\theta $ as, $r=3\sin \theta $ and $h=3\cos \theta $.
Now let us substitute the above values in the formula for volume of cone.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{\left( 3\sin \theta \right)}^{2}}\left( 3\cos \theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times 9{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \times 3\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow V=9\pi {{\sin }^{2}}\theta \cos \theta \\
\end{align}\]
Later we differentiate the above volume with respective to $\theta $ and equate it to zero to find the condition for maximum volume and later we substitute the condition in the volume formula to find the maximum volume as we did in the solution part above.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We were given that the slant height of the cone is 3m.
So, let us consider the height of the cone as h and the radius of the base of the cone as r.

As the cone is right circular
Using Pythagoras Theorem, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}={{3}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}=9-{{h}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us consider the formula for the volume of cone of height h and radius r,
$Volume=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Using this formula, we get volume of our cone as
\[V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h\]
Now, let us substitute above attained value of r in the volume,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-{{h}^{2}} \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let us use the optimization techniques. When a function $f\left( x \right)$ is at its extremum, that is maximum or minimum if its derivative is zero, that is ${f}'\left( x \right)=0$.
So, let us differentiate volume with respective to h.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \dfrac{d}{dh}\left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us equate it to zero.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 9-3{{h}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{h}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=3 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\sqrt{3},-\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we need to find which of them is the condition is for maximum.
The condition for maximum is double derivative of the function should be negative.
As \[\dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right)\], let us differentiate it with h to find the double derivative.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9-3{{h}^{2}} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( -3\times 2h \right)=-2\pi h \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us substitute the values obtained in the double derivative of volume.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=\sqrt{3}}}=-2\pi \left( \sqrt{3} \right)<0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=-\sqrt{3}}}=-2\pi \left( -\sqrt{3} \right)>0\]
As the double derivative is negative when \[h=\sqrt{3}\]. It is the value for which the volume is maximum.
Now, let us substitute the above value in the formula for volume. Then, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9h-{{h}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9\left( \sqrt{3} \right)-{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{3}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 9\sqrt{3}-3\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( 6\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi \left( 2\sqrt{3} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=2\sqrt{3}\pi \\
\end{align}\]
Hence maximum volume of cone is \[2\sqrt{3}\pi \] cubic units. Hence answer is Option C.
Note: We can also solve this problem by writing r and h in terms of angle $\theta $ as, $r=3\sin \theta $ and $h=3\cos \theta $.
Now let us substitute the above values in the formula for volume of cone.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{\left( 3\sin \theta \right)}^{2}}\left( 3\cos \theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \times 9{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \times 3\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow V=9\pi {{\sin }^{2}}\theta \cos \theta \\
\end{align}\]
Later we differentiate the above volume with respective to $\theta $ and equate it to zero to find the condition for maximum volume and later we substitute the condition in the volume formula to find the maximum volume as we did in the solution part above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




