
The maximum peak-to-peak voltage of an AM wave is 16mV, and the minimum peak-to-peak voltage is 4mV. The modulation factor is equal to
A. 0.6
B. 0.3
C. 0.8
D. 0.25
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Modulation factor for voltage is given as \[{\mu _V} = \dfrac{{{V_{\max }} - {V_{\min }}}}{{{V_{\max }} + {V_{\min }}}}\]
It is defined by the ratio of change of amplitude in carrier wave after modulation to the amplitude of the un-modulated carrier wave.
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communications and are most commonly used for transmitting messages with a radio carrier wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier waves varies in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal.
Peak to peak voltage is the difference between the maximum positive voltage and the maximum negative voltage amplitude of a waveform. Maximum voltage is the voltage at which a device can be operated safely without causing any damages.
Complete step by step answer:
The maximum peak-to-peak voltage of an AM wave= 16mV
The minimum peak-to-peak voltage of an AM wave= 4mV
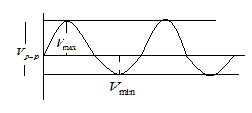
Maximum voltage is the length of the positive amplitude of a voltage-time curve calculated from the midpoint is given as
\[{V_{\max }} = \dfrac{{16}}{2} = 8mV\]
Minimum voltage is the length of the maximum negative amplitude of a voltage-time curve calculated from the midpoint is given as
\[{V_{\min }} = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2mV\]
Therefore the modulation factor for voltage will be
\[
{\mu _V} = \dfrac{{{V_{\max }} - {V_{\min }}}}{{{V_{\max }} + {V_{\min }}}} \\
= \dfrac{{8 - 2}}{{8 + 2}} \\
= \dfrac{6}{{10}} \\
= 0.6 \\
\]
Hence the modulation factor is equal to \[ = 0.6\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Students must not get confused between the peak-to-peak voltage and the maximum voltage since the peak to peak voltage is the measure of total length variation of the waveform in positive and negative y-axis whereas maximum voltage is the length from the origin axis.
It is defined by the ratio of change of amplitude in carrier wave after modulation to the amplitude of the un-modulated carrier wave.
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communications and are most commonly used for transmitting messages with a radio carrier wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier waves varies in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal.
Peak to peak voltage is the difference between the maximum positive voltage and the maximum negative voltage amplitude of a waveform. Maximum voltage is the voltage at which a device can be operated safely without causing any damages.
Complete step by step answer:
The maximum peak-to-peak voltage of an AM wave= 16mV
The minimum peak-to-peak voltage of an AM wave= 4mV

Maximum voltage is the length of the positive amplitude of a voltage-time curve calculated from the midpoint is given as
\[{V_{\max }} = \dfrac{{16}}{2} = 8mV\]
Minimum voltage is the length of the maximum negative amplitude of a voltage-time curve calculated from the midpoint is given as
\[{V_{\min }} = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2mV\]
Therefore the modulation factor for voltage will be
\[
{\mu _V} = \dfrac{{{V_{\max }} - {V_{\min }}}}{{{V_{\max }} + {V_{\min }}}} \\
= \dfrac{{8 - 2}}{{8 + 2}} \\
= \dfrac{6}{{10}} \\
= 0.6 \\
\]
Hence the modulation factor is equal to \[ = 0.6\].
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Students must not get confused between the peak-to-peak voltage and the maximum voltage since the peak to peak voltage is the measure of total length variation of the waveform in positive and negative y-axis whereas maximum voltage is the length from the origin axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




