
The mass of a simple pendulum bob is 100gm.The length of the pendulum is 1m. The bob is drawn aside from the equilibrium position so that the string makes an angle of \[60{}^\circ \] with the vertical and let go. The kinetic energy of the bob while crossing its equilibrium position will be:
(A)1J
(B)0.49J
(C)0.94J
(D)1.2J
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The pendulum moves under the influence of restoring force. The tension in the string is always directed towards the centre. We can exploit the law of conservation of energy here to arrive at our solution.
Complete step by step answer:
The situation can be described in the free body diagram below;
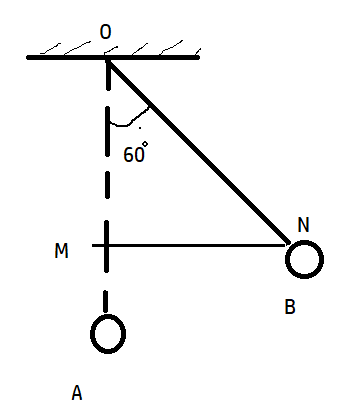
A is the equilibrium position of the pendulum and currently, it is held at B making an angle of \[60{}^\circ \]with the vertical.
m=100g
m=0.1Kg
Length of the pendulum, l=1m
When the bob is released from point B, because of restoring force it has the tendency to move towards the equilibrium position. We can use trigonometry to find out the length OM
\[\begin{align}
& \cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OM}{ON} \\
& 0.5=\dfrac{OM}{1} \\
& OM=0.5m \\
\end{align}\]
Now potential energy at point B is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{U}_{B}}=mg{{l}_{1}} \\
& =mg \\
\end{align}\]
Now potential energy at point A is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{U}_{A}}=mg{{l}_{2}} \\
& =0.5mg \\
\end{align}\]
Change in energy,
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta U={{U}_{B}}-{{U}_{A}} \\
& =mg-0.5mg \\
& =0.5mg \\
\end{align}\]
This energy is converted into kinetic energy
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{2}=0.5mg \\
& =0.5\times 0.1\times 9.8 \\
& =0.49J \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the kinetic energy of the bob at equilibrium position is 0.49J.
So, the correct option is (C)
Note:While substituting the values we have to be careful that all the units are in SI. Also, there is no external force present here, so there is no loss of energy. If some external force would have been present we would then have to consider the energy loss against that force.
Complete step by step answer:
The situation can be described in the free body diagram below;

A is the equilibrium position of the pendulum and currently, it is held at B making an angle of \[60{}^\circ \]with the vertical.
m=100g
m=0.1Kg
Length of the pendulum, l=1m
When the bob is released from point B, because of restoring force it has the tendency to move towards the equilibrium position. We can use trigonometry to find out the length OM
\[\begin{align}
& \cos 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OM}{ON} \\
& 0.5=\dfrac{OM}{1} \\
& OM=0.5m \\
\end{align}\]
Now potential energy at point B is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{U}_{B}}=mg{{l}_{1}} \\
& =mg \\
\end{align}\]
Now potential energy at point A is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& {{U}_{A}}=mg{{l}_{2}} \\
& =0.5mg \\
\end{align}\]
Change in energy,
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta U={{U}_{B}}-{{U}_{A}} \\
& =mg-0.5mg \\
& =0.5mg \\
\end{align}\]
This energy is converted into kinetic energy
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{2}=0.5mg \\
& =0.5\times 0.1\times 9.8 \\
& =0.49J \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the kinetic energy of the bob at equilibrium position is 0.49J.
So, the correct option is (C)
Note:While substituting the values we have to be careful that all the units are in SI. Also, there is no external force present here, so there is no loss of energy. If some external force would have been present we would then have to consider the energy loss against that force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




