
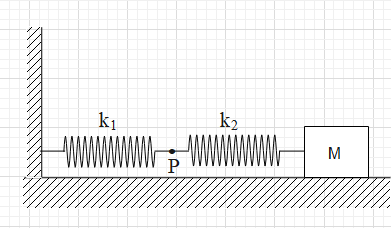
The mass M shown in the figure oscillates in simple harmonic motion with amplitude A. The amplitude of the point P is
$\text{A}\text{. }\dfrac{{{k}_{1}}A}{{{k}_{2}}}$
$\text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{{{k}_{2}}A}{{{k}_{1}}}$
$\text{C}\text{. }\dfrac{{{k}_{1}}A}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$
$\text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{{{k}_{2}}A}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: When the block oscillates, the springs will elongate in such a way that the force exerted by both is the same. Use the formula for the spring force and an expression for the extension in the left spring when the block is at the right extreme. This value will be the amplitude of point P.
Formula used:
F=-kx
Complete answer:
As we can see in the given figure, a block of mass M is attached to a combination of two springs. The springs are connected in series. It is said that the block is under simple harmonic motion with an amplitude A.
When the block is at its right extreme, the displacement of the block from the mean position is A. Let the extensions in the springs with spring constants ${{k}_{1}}$ and ${{k}_{2}}$ be ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{x}_{2}}$ respectively.
Here, ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=A$.
When the block oscillates, the springs will elongate in such a way that the force exerted by both is the same.
That means that $F={{k}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}={{k}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}$
And
${{x}_{2}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{2}}}$
But ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=A$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{2}}}=A$
$\Rightarrow F\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)=A$
$\Rightarrow F=\dfrac{A}{\left(\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}}\right)}=\dfrac{A{{k}_{1}}{{k}_{2}}}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$ …. (i).
Since the one end of the left spring is fixed, the amplitude of point P is equal to ${{x}_{1}}$.
And we know that ${{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}$
Substitute the value of F from (i).
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{A{{k}_{1}}{{k}_{2}}}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}}{{{k}_{1}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{k}_{2}}A}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
When we have a combination of spring, we define the equivalent spring constant of the combination. Let the equivalent spring constant of the combination be ${{k}_{eq}}$.
When the total extension is equal to A, $F={{k}_{eq}}A$
And we found that $\Rightarrow F=\dfrac{A}{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)}$.
This implies that ${{k}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}}$.
Formula used:
F=-kx
Complete answer:
As we can see in the given figure, a block of mass M is attached to a combination of two springs. The springs are connected in series. It is said that the block is under simple harmonic motion with an amplitude A.
When the block is at its right extreme, the displacement of the block from the mean position is A. Let the extensions in the springs with spring constants ${{k}_{1}}$ and ${{k}_{2}}$ be ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{x}_{2}}$ respectively.
Here, ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=A$.
When the block oscillates, the springs will elongate in such a way that the force exerted by both is the same.
That means that $F={{k}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}={{k}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}$
And
${{x}_{2}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{2}}}$
But ${{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}=A$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{2}}}=A$
$\Rightarrow F\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)=A$
$\Rightarrow F=\dfrac{A}{\left(\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}}\right)}=\dfrac{A{{k}_{1}}{{k}_{2}}}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$ …. (i).
Since the one end of the left spring is fixed, the amplitude of point P is equal to ${{x}_{1}}$.
And we know that ${{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{F}{{{k}_{1}}}$
Substitute the value of F from (i).
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{A{{k}_{1}}{{k}_{2}}}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}}{{{k}_{1}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{k}_{2}}A}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
When we have a combination of spring, we define the equivalent spring constant of the combination. Let the equivalent spring constant of the combination be ${{k}_{eq}}$.
When the total extension is equal to A, $F={{k}_{eq}}A$
And we found that $\Rightarrow F=\dfrac{A}{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)}$.
This implies that ${{k}_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}} \right)}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{k}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{k}_{2}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




