
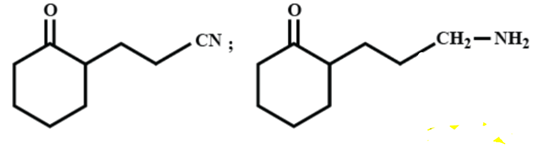
The major products A and B for the following reactions are respectively:
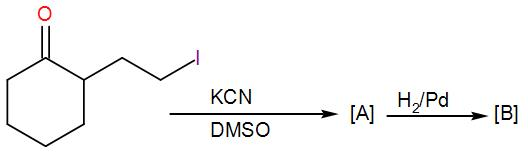
(A)
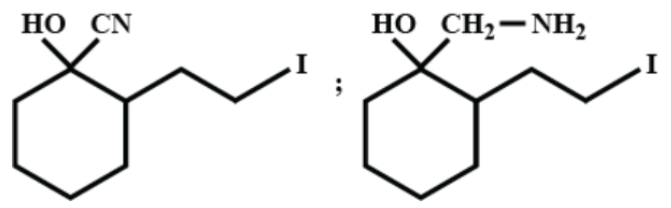
(B)
(C)
(D)





Answer
586.8k+ views
HINT: To solve this proceed stepwise and find A and then arrive at B. Remember that KCN with DMSO leads to cyanation via nucleophilic substitution bimolecular. Also remember that hydrogen and palladium together make a strong reducing agent and thus leads to reduction of the substrate.
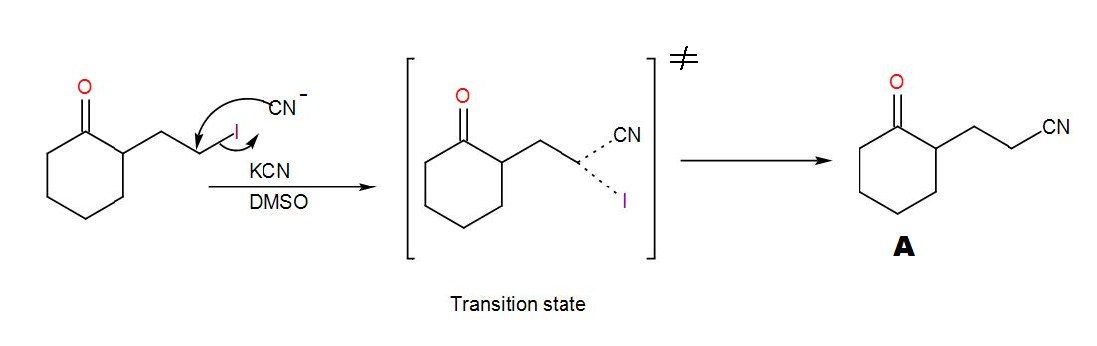
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: Here, we can see that a cyclohexanone with an alkyl halide substituent is given to us. Before seeing its reaction with KCN and DMSO, let us discuss what type of reaction these reagents are used for and which reaction mechanism is followed. KCN is potassium cyanide and DMSO is dimethyl sulfoxide. DMSO acts as a solvent here and the cyanide ion obtained from KCN acts as a nucleophile. Here, the reaction will proceed via ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism. Here, 2 stands for bi-molecular and SN stands for nucleophilic substitution as usual. This mechanism is concerted i.e. the removal of the leaving group and addition of the nucleophile takes place in a single step and the reaction passes through a transition state. We can write the reaction as-
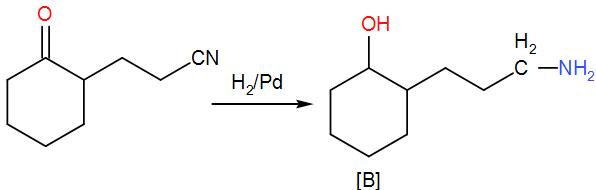
Now, when we add hydrogen and palladium to (A), reduction takes place and the ketone group is reduced to –OH giving us alcohol. As ${{H}_{2}}/Pd$ is a strong reducing agent, the cyanide group is reduced to a primary amine as well. We can write the reaction as-
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B].
NOTE: We can also use sodium cyanide or even zinc cyanide (in some cases) instead of potassium cyanide for cyanation. Here, the reaction is nucleophilic substitution as nucleophilic addition reaction is not possible here as the solvent i.e. DMSO is aprotic. Therefore, if the nucleophile attacks at the carbonyl centre, the reaction will not proceed as there is no proton in the reaction medium for the negatively charged oxygen atom here. Therefore, in an aprotic solvent like DMSO, only substitution reactions are feasible and additional reactions are not.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: Here, we can see that a cyclohexanone with an alkyl halide substituent is given to us. Before seeing its reaction with KCN and DMSO, let us discuss what type of reaction these reagents are used for and which reaction mechanism is followed. KCN is potassium cyanide and DMSO is dimethyl sulfoxide. DMSO acts as a solvent here and the cyanide ion obtained from KCN acts as a nucleophile. Here, the reaction will proceed via ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism. Here, 2 stands for bi-molecular and SN stands for nucleophilic substitution as usual. This mechanism is concerted i.e. the removal of the leaving group and addition of the nucleophile takes place in a single step and the reaction passes through a transition state. We can write the reaction as-

Now, when we add hydrogen and palladium to (A), reduction takes place and the ketone group is reduced to –OH giving us alcohol. As ${{H}_{2}}/Pd$ is a strong reducing agent, the cyanide group is reduced to a primary amine as well. We can write the reaction as-

Therefore, the correct answer is option [B].
NOTE: We can also use sodium cyanide or even zinc cyanide (in some cases) instead of potassium cyanide for cyanation. Here, the reaction is nucleophilic substitution as nucleophilic addition reaction is not possible here as the solvent i.e. DMSO is aprotic. Therefore, if the nucleophile attacks at the carbonyl centre, the reaction will not proceed as there is no proton in the reaction medium for the negatively charged oxygen atom here. Therefore, in an aprotic solvent like DMSO, only substitution reactions are feasible and additional reactions are not.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




