
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
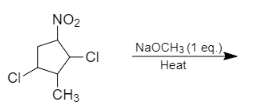

Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: Sodium methoxide having a chemical formula, $C{{H}_{3}}ONa$ is an organic compound which is formed by removing hydrogen from methanol. It is a white solid which is used as a reagent in the laboratory. It acts as a base.
Complete step-by-step answer:Sodium methoxide is used as a base in organic chemistry and is used in the synthesis of many compounds in pharmaceutical and agrichemical. It acts as a base and is employed in dehydrohalogenation and condensation reaction. It also acts as a nucleophile in the production of methyl ether. It is highly caustic and when it reacts with water it gives methanol, which is very volatile and toxic.
When \[1,3-\]dichloro\[-2-\]methyl\[-4-\]nitrocyclopentane reacts with sodium methoxide, it results in the formation of \[4-\]chloro\[-3-\]methyl\[-1-\]nitrocyclopentane\[-1-\]ene. Here, sodium methoxide acts as a base. It attacks on more acidic hydrogen and donates its electrons on the carbon. Now these electrons move to the single bond and chlorine is removed as it is a good leaving group. This results in the formation of double bonds. Acidic hydrogen is the hydrogen which is near to the nitro group which acts as an electron withdrawing group. The nitro group shows resonance effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon. Therefore, the hydrogen near the nitro group will be more acidic than the other hydrogens.
The reaction can be given as follows:
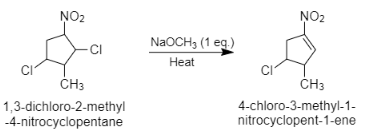
Note:It is to note that electron withdrawing group is defined as the group that has the tendency to withdraw electrons from the reaction center. In this question, the nitrogen group $(N{{O}_{2}})$ is an electron withdrawing group. It withdraws electrons from the carbon and makes it electron deficient. Therefore, the hydrogen attached to this carbon will be more acidic.
Complete step-by-step answer:Sodium methoxide is used as a base in organic chemistry and is used in the synthesis of many compounds in pharmaceutical and agrichemical. It acts as a base and is employed in dehydrohalogenation and condensation reaction. It also acts as a nucleophile in the production of methyl ether. It is highly caustic and when it reacts with water it gives methanol, which is very volatile and toxic.
When \[1,3-\]dichloro\[-2-\]methyl\[-4-\]nitrocyclopentane reacts with sodium methoxide, it results in the formation of \[4-\]chloro\[-3-\]methyl\[-1-\]nitrocyclopentane\[-1-\]ene. Here, sodium methoxide acts as a base. It attacks on more acidic hydrogen and donates its electrons on the carbon. Now these electrons move to the single bond and chlorine is removed as it is a good leaving group. This results in the formation of double bonds. Acidic hydrogen is the hydrogen which is near to the nitro group which acts as an electron withdrawing group. The nitro group shows resonance effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon. Therefore, the hydrogen near the nitro group will be more acidic than the other hydrogens.
The reaction can be given as follows:

Note:It is to note that electron withdrawing group is defined as the group that has the tendency to withdraw electrons from the reaction center. In this question, the nitrogen group $(N{{O}_{2}})$ is an electron withdrawing group. It withdraws electrons from the carbon and makes it electron deficient. Therefore, the hydrogen attached to this carbon will be more acidic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




