
The main function of lenticels is
(a) Transpiration
(b) Guttation
(c) Gaseous exchange
(d) Translation
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: A lenticel is a porous tissue composed of cells in the periderm of secondarily thickened organs with wide intercellular spaces and the bark of woody stems and roots of dicotyledonous flowering plants.
Complete answer:
- It acts as a pore, providing a path through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gases, for the direct exchange of gases between the internal tissues and the atmosphere.
- The name lenticel is derived from its (lens-like) lenticular form.
- Lenticels facilitate the gas exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor in plant bodies that produce secondary growth.
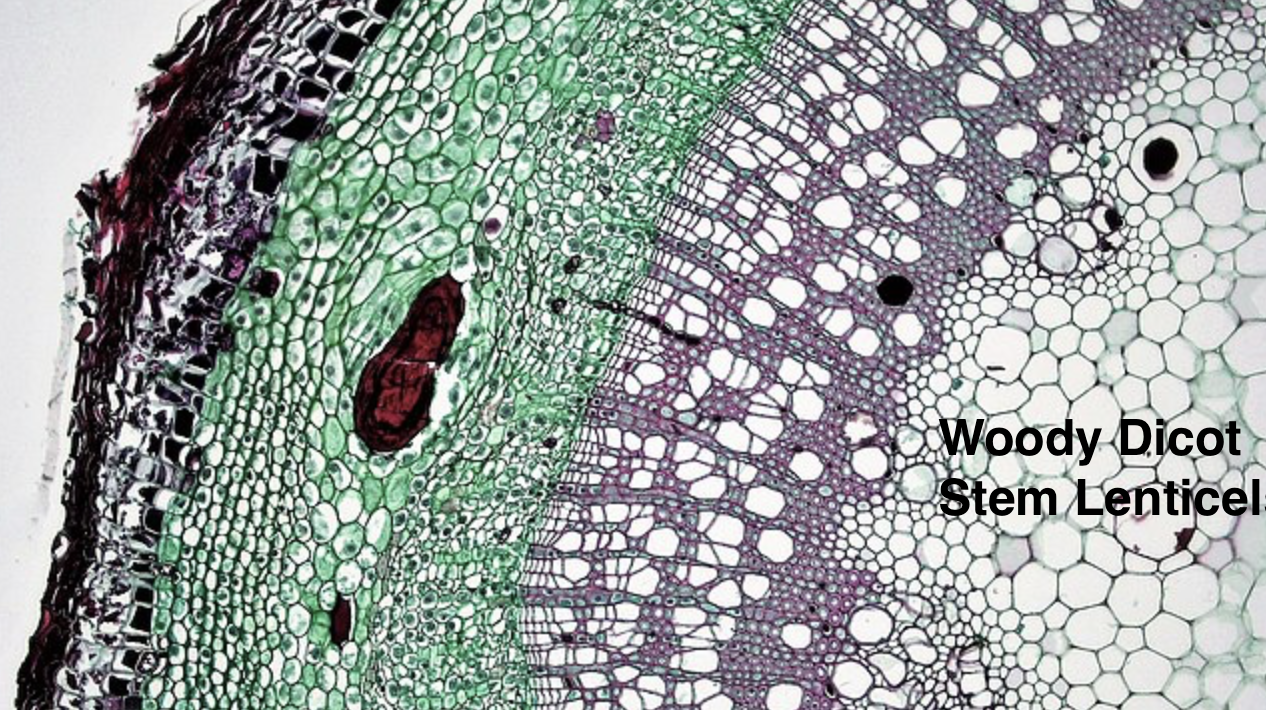
- During primary growth prior to the production of the first periderm, lenticel formation typically begins beneath stomatal complexes.
Additional information:
- The development of lenticels tends to be directly related to the growth and strength of the shoot and the tissue hydrose, which refers to the inner moisture.
- As mature lenticel growth continues throughout the new periderm stems and roots, lenticels are found on stems and roots as raised circular, oval, or elongated regions.
- Lenticels usually occur in woody plants as rough, cork-like structures on young branches.
- Underneath them, a number of large intercellular spaces between cells are produced by porous tissue.
- Different organisms may have specialized systems in which lenticels can be found in oxygen- deficient environments, rendering respiration a regular task.
- For example, lenticels occur on pneumatophores (specialized roots) in a common mangrove species, where the parenchyma cells that bind to the structure of the aerenchyma increase in size and go through cell division.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Gaseous exchange’.
Note:
- Lenticels in grapes are located on the pedicels and serve as a temperature feature.
- If they are blocked, it can result in hypoxia and successive accumulation of ethanol and lead to cell death.
- One of the features used in tree identification is the shape of lenticels.
Complete answer:
- It acts as a pore, providing a path through the bark, which is otherwise impermeable to gases, for the direct exchange of gases between the internal tissues and the atmosphere.
- The name lenticel is derived from its (lens-like) lenticular form.
- Lenticels facilitate the gas exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor in plant bodies that produce secondary growth.

- During primary growth prior to the production of the first periderm, lenticel formation typically begins beneath stomatal complexes.
Additional information:
- The development of lenticels tends to be directly related to the growth and strength of the shoot and the tissue hydrose, which refers to the inner moisture.
- As mature lenticel growth continues throughout the new periderm stems and roots, lenticels are found on stems and roots as raised circular, oval, or elongated regions.
- Lenticels usually occur in woody plants as rough, cork-like structures on young branches.
- Underneath them, a number of large intercellular spaces between cells are produced by porous tissue.
- Different organisms may have specialized systems in which lenticels can be found in oxygen- deficient environments, rendering respiration a regular task.
- For example, lenticels occur on pneumatophores (specialized roots) in a common mangrove species, where the parenchyma cells that bind to the structure of the aerenchyma increase in size and go through cell division.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Gaseous exchange’.
Note:
- Lenticels in grapes are located on the pedicels and serve as a temperature feature.
- If they are blocked, it can result in hypoxia and successive accumulation of ethanol and lead to cell death.
- One of the features used in tree identification is the shape of lenticels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




