
The magnification of an image by a convex lens is positive only when the project is placed.
A. at its focus F
B. between F and 2F.
C. at 2F.
D. between F and optical centre.
E. beyond 2F.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The characteristic of a convex lens in image formation has to be known. The formation of an image by a convex lens is both virtual and real and it depends on how the object is placed. Magnification is positive for virtual images and negative for real images. The real image is inverted hence its magnification is negative.
Complete step by step solution:
The graphical representation of a virtual image in convex lens is given as,
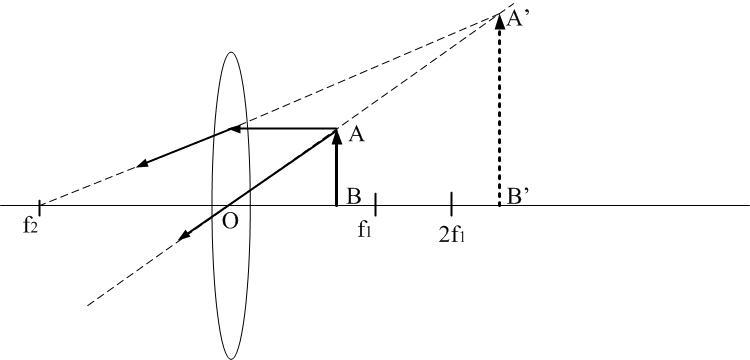
Fig.1
Fig.1 represents a convex lens where the object AB is placed in between the focus, ${f_1}$ and optical centre O. If the object is placed between optical centre and focus (between ${f_1}$ and O) then the first ray of light starting from the top of the object is parallel to the principal axis. Therefore, as per the rule, it passes through another focus after refraction through the lens. Another ray of light from the object passes through the optical centre of the lens and thus as per the rule goes straight after refraction through the lens. Thus, both the light rays diverge after refraction through the lens and do not meet. Therefore, both the refracted rays are produced backwards so that they meet at a point to form an image A’B’. This image is a virtual and magnified image. Since this virtual image is a non-inverted image, hence the magnification of such an image is positive.
Thus, the object must be between focus and optical centre to produce a positive magnification of an image.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: The students have to apply the concept of refraction in the lens and the characteristics of images formed in a convex lens. The image formed in the convex lens is positive and virtual if the object is placed between focus and optical centre and the distance of the object is less than the focal length.
Complete step by step solution:
The graphical representation of a virtual image in convex lens is given as,

Fig.1
Fig.1 represents a convex lens where the object AB is placed in between the focus, ${f_1}$ and optical centre O. If the object is placed between optical centre and focus (between ${f_1}$ and O) then the first ray of light starting from the top of the object is parallel to the principal axis. Therefore, as per the rule, it passes through another focus after refraction through the lens. Another ray of light from the object passes through the optical centre of the lens and thus as per the rule goes straight after refraction through the lens. Thus, both the light rays diverge after refraction through the lens and do not meet. Therefore, both the refracted rays are produced backwards so that they meet at a point to form an image A’B’. This image is a virtual and magnified image. Since this virtual image is a non-inverted image, hence the magnification of such an image is positive.
Thus, the object must be between focus and optical centre to produce a positive magnification of an image.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: The students have to apply the concept of refraction in the lens and the characteristics of images formed in a convex lens. The image formed in the convex lens is positive and virtual if the object is placed between focus and optical centre and the distance of the object is less than the focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




