
The long and short arms of the chromosome are designated as respectively.
A. p and q arms
B. q and p arms
C. m and p arms
D. i and s arms
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation.
Complete answer: Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a significant role in genetic diversity. Each eukaryotic chromosome consists of a long linear DNA molecule associated with proteins, forming a compact complex of proteins and DNA called chromatin. Chromatin contains the vast majority of the DNA of an organism, but a small amount of inherited maternally can be found in the mitochondria. Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience to talk about gene loci. Most important is the distinction between chromosome region p and chromosome region q. These are virtual regions that exist in all chromosomes. During cell division, the molecules that compose chromosomes (DNA and proteins) undergo chromatin condensation that forms a compact and small complex called a chromatid. The complexes containing the duplicated DNA molecules, the sister chromatids, are attached by the centromere. The centromere divides each chromosome into two regions: the smaller one, which is the p region, and the bigger one, the q region. The sister chromatids will be distributed to each daughter cell at the end of the cell division.
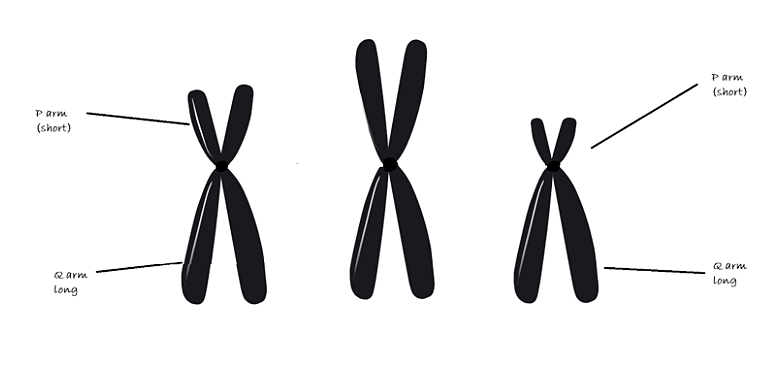
Hence, the correct option is (B)-q and p arms.
Note: The p region is represented in the shorter arm of the chromosome while the q region is in the larger arm. At either end of a chromosome is a telomere, a cap of DNA that protects the rest of the chromosome from damage. The areas of the p and q regions close to the telomeres are the subtelomeres or subtelomeric regions. The areas closer to the centromere are the pericentromeric regions.
Complete answer: Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a significant role in genetic diversity. Each eukaryotic chromosome consists of a long linear DNA molecule associated with proteins, forming a compact complex of proteins and DNA called chromatin. Chromatin contains the vast majority of the DNA of an organism, but a small amount of inherited maternally can be found in the mitochondria. Several chromosome regions have been defined by convenience to talk about gene loci. Most important is the distinction between chromosome region p and chromosome region q. These are virtual regions that exist in all chromosomes. During cell division, the molecules that compose chromosomes (DNA and proteins) undergo chromatin condensation that forms a compact and small complex called a chromatid. The complexes containing the duplicated DNA molecules, the sister chromatids, are attached by the centromere. The centromere divides each chromosome into two regions: the smaller one, which is the p region, and the bigger one, the q region. The sister chromatids will be distributed to each daughter cell at the end of the cell division.

Hence, the correct option is (B)-q and p arms.
Note: The p region is represented in the shorter arm of the chromosome while the q region is in the larger arm. At either end of a chromosome is a telomere, a cap of DNA that protects the rest of the chromosome from damage. The areas of the p and q regions close to the telomeres are the subtelomeres or subtelomeric regions. The areas closer to the centromere are the pericentromeric regions.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




