
The line\[y=mx+c\] will be a tangent to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]if\[c=\pm a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\]. The equation of any tangent to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]can be considered as \[y=mx+a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\]and the co-ordinates of the points of contact are \[\left( \pm \dfrac{am}{\sqrt{{{1}^{{}}}+{{m}^{2}}}},\mp \dfrac{a}{\sqrt{{{1}^{{}}}+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)\] and the length of the tangent from the point \[P\left( {{x}_{1}}+{{y}_{1}} \right)\] to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] is \[\sqrt{{{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}+c}\].
The equation of tangent to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y=0\] from the point \[P\left( 1,-2 \right)\]is
(a) \[y-2x-5=0\]
(b) \[x+2y+5=0\]
(c) \[x-2y=0\]
(d) \[y-3x=0\]
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint:First, before proceeding for this, we must know the equation of circle is given by where (h, k) is centre and r is radius as ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$. Then, we must draw the figure that illustrates the condition and get the idea of the question more clearly. Then, by using the equation of straight line where N is slope and $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$is the point where line passes is given by $y-{{y}_{1}}=N\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$and the condition of perpendicular lines, we get the required result.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to find the equation of tangent to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y=0\] from the point \[P\left( 1,-2 \right)\].
So, before proceeding for this, we must know the equation of circle is given by where (h, k) is centre and r is radius as:
${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
So, by using the completing the square and adding and subtracting 4 and 1, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y+4-4+1-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y+{{2}^{2}}-4+{{1}^{2}}-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+1 \right)}^{2}}=5 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+1 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, by comparing we get the centre as (-2, -1) and radius as $\sqrt{5}$.
Now, we must draw the figure that illustrates the condition and get the idea of the question more clearly as:
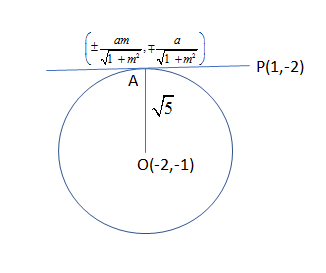
Then, by using the equation of straight line where N is slope and $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$is the point where line passes is given by:
$y-{{y}_{1}}=N\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Now, we also know the formula for the slope of any line N is given by:
$N=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$
So, by using this formula to get the slope of the line OA as:
$\begin{align}
& N=\dfrac{\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}-\left( -1 \right)}{\dfrac{am}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}-\left( -2 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}}{\dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, by using another condition of the lines that are perpendicular as OA and AP as tangent always makes an angle of ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
So, for the two lines when perpendicular the slope of the line AP is negative reciprocal of slope M of OA as:
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{-1}{N} \\
& \Rightarrow M=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow M=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, by using the equation of straight line for line AP with above calculated slope and point P, we get:
$\begin{align}
& y-{{y}_{1}}=M\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-\left( -2 \right)=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)\left( x-1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \Rightarrow y-\left( -2 \right)=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)x+\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, by comparing the above equation of tangent from the equation of tangent given in the question as \[y=mx+a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\], we get:
$\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)=m$
Then, by substituting the value of a as $\sqrt{5}$ as calculated above and compared to the equation in the question as \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\], we get:
$\begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)=m \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \right)=m\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}=m\sqrt{5}+m\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}=m\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow m=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, by substituting the value of m as 2 and a as $\sqrt{5}$ in the given expression of tangent in the question as \[y=mx+a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\], we get:
\[\begin{align}
& y=2x+\sqrt{5}\sqrt{1+{{2}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+\sqrt{5}\times \sqrt{5} \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+5 \\
& \Rightarrow y-2x-5=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the equation of the tangent as \[y-2x-5=0\].
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Note:
Now, to solve these types of questions we need to know some of the basics of the equation of the circle and equation of the straight line to proceed easily. So, the required equation of the circle and straight-line are as:
Equation of circle is given by ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$where (h, k) as centre.
Equation of the line is given by $y-{{y}_{1}}=N\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$where N is slope.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to find the equation of tangent to the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y=0\] from the point \[P\left( 1,-2 \right)\].
So, before proceeding for this, we must know the equation of circle is given by where (h, k) is centre and r is radius as:
${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
So, by using the completing the square and adding and subtracting 4 and 1, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y+4-4+1-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+4x+2y+{{2}^{2}}-4+{{1}^{2}}-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+1 \right)}^{2}}=5 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x+2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+1 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, by comparing we get the centre as (-2, -1) and radius as $\sqrt{5}$.
Now, we must draw the figure that illustrates the condition and get the idea of the question more clearly as:

Then, by using the equation of straight line where N is slope and $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$is the point where line passes is given by:
$y-{{y}_{1}}=N\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Now, we also know the formula for the slope of any line N is given by:
$N=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$
So, by using this formula to get the slope of the line OA as:
$\begin{align}
& N=\dfrac{\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}-\left( -1 \right)}{\dfrac{am}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}-\left( -2 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}}{\dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow N=\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \\
\end{align}$
Then, by using another condition of the lines that are perpendicular as OA and AP as tangent always makes an angle of ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
So, for the two lines when perpendicular the slope of the line AP is negative reciprocal of slope M of OA as:
$\begin{align}
& M=\dfrac{-1}{N} \\
& \Rightarrow M=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow M=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, by using the equation of straight line for line AP with above calculated slope and point P, we get:
$\begin{align}
& y-{{y}_{1}}=M\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-\left( -2 \right)=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)\left( x-1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \Rightarrow y-\left( -2 \right)=-\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)x+\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, by comparing the above equation of tangent from the equation of tangent given in the question as \[y=mx+a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\], we get:
$\left( \dfrac{am+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{a+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)=m$
Then, by substituting the value of a as $\sqrt{5}$ as calculated above and compared to the equation in the question as \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\], we get:
$\begin{align}
& \left( \dfrac{\sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}} \right)=m \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \right)=m\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{5}m+2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}=m\sqrt{5}+m\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}=m\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow m=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, by substituting the value of m as 2 and a as $\sqrt{5}$ in the given expression of tangent in the question as \[y=mx+a\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\], we get:
\[\begin{align}
& y=2x+\sqrt{5}\sqrt{1+{{2}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+\sqrt{5}\times \sqrt{5} \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+5 \\
& \Rightarrow y-2x-5=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, we get the equation of the tangent as \[y-2x-5=0\].
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Note:
Now, to solve these types of questions we need to know some of the basics of the equation of the circle and equation of the straight line to proceed easily. So, the required equation of the circle and straight-line are as:
Equation of circle is given by ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$where (h, k) as centre.
Equation of the line is given by $y-{{y}_{1}}=N\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$where N is slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




