
The line segment joining points A (2,1) and B (5,-8) is trisected at the point P and Q. P is nearer to A. If P also lies on the line 2x-y+k=0, find the value of k.
Answer
620.1k+ views
Hint: The points of trisection divide the line segment in the ratio 1:2 and 2:1. Hence P divides AB in the ratio of 1:2 and Q divides AB in the ratio of 2:1. Use section formula which states that the coordinates of the point P which divides $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ in the ratio of m:n is given by $\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)$. Hence find the coordinates of point P. Also, as point P lies on 2x-y+k, it must satisfy the equation. Hence find the value of k so that p satisfies the above equation of the line.
Complete step-by-step solution -
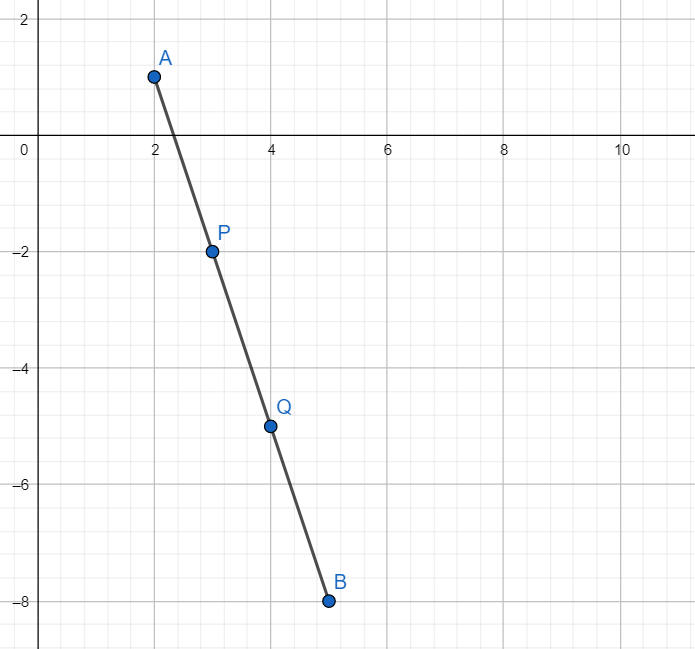
As P and Q are the points of trisection, we have
AP = PQ = QB.
Hence we have $\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AP}{2AP}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence P divides AB in the ratio of 1:2.
Similarly Q divides AB in the ratio of 2:1
Finding coordinates of P:
that the coordinates of the point P which divides $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ in the ratio of m:n is given by $\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)$
Here ${{x}_{1}}=2,{{x}_{2}}=5,{{y}_{1}}=1$ and ${{y}_{2}}=-8$ and m = 1 and n= 2
Hence we have
$P\equiv \left( \dfrac{1\times 5+2\times 2}{1+2},\dfrac{1\times \left( -8 \right)+2\times 1}{1+2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{9}{3},\dfrac{-6}{3} \right)=\left( 3,-2 \right)$
Finding coordinates of Q:
that the coordinates of the point P which divides $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ in the ratio of m:n is given by $\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)$
Here ${{x}_{1}}=2,{{x}_{2}}=5,{{y}_{1}}=1$ and ${{y}_{2}}=-8$ and m = 2 and n= 1
Hence we have
$Q\equiv \left( \dfrac{2\times 5+1\times 2}{1+2},\dfrac{2\times \left( -8 \right)+1\times 1}{1+2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{12}{3},\dfrac{-15}{3} \right)=\left( 4,-5 \right)$
Also, since P lies on 2x-y+k = 0, P must satisfy its equation.
Hence we have
2(3)-(-2)+k = 0
i.e. k =-8
Hence the value of k is -12.
Note: Alternative solution: Best method:
The ratio in which the line ax+by+c=0 divides the line segment joining points $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $-\dfrac{a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c}{a{{x}_{2}}+b{{y}_{2}}+c}$ (Remember)
Hence the ratio in which 2x-y+k = 0 divides the line segment joining A (2,1) and B (5,-8) is given by
$-\dfrac{2\left( 2 \right)-1+k}{2\left( 5 \right)-\left( -8 \right)+k}=-\dfrac{3+k}{18+k}$
Since the line 2x-y+k = 0 intersects AB at P which divides AB in the ratio 1:2, we have
$-\dfrac{3+k}{18+k}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Cross multiplying, we get
$\begin{align}
& -6-2k=18+k \\
& \Rightarrow 3k=-24 \\
& \Rightarrow k=-8 \\
\end{align}$
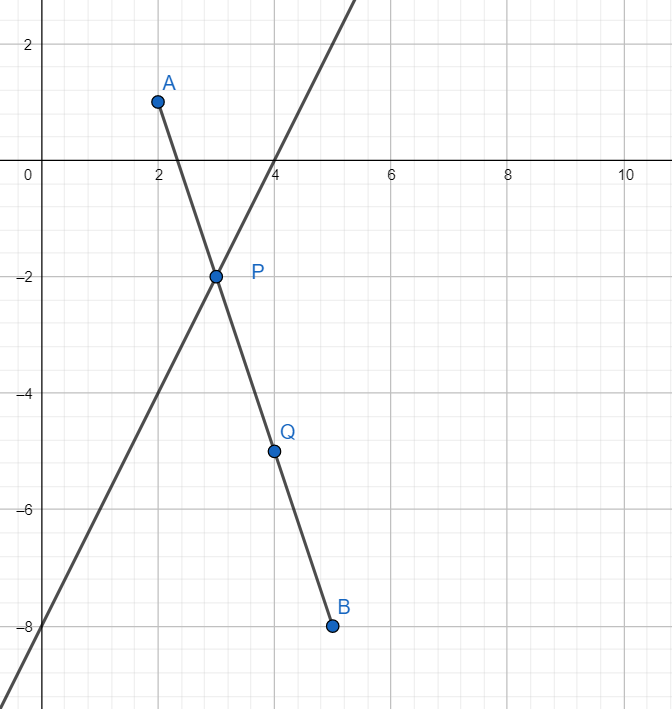
Complete step-by-step solution -

As P and Q are the points of trisection, we have
AP = PQ = QB.
Hence we have $\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AP}{2AP}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence P divides AB in the ratio of 1:2.
Similarly Q divides AB in the ratio of 2:1
Finding coordinates of P:
that the coordinates of the point P which divides $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ in the ratio of m:n is given by $\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)$
Here ${{x}_{1}}=2,{{x}_{2}}=5,{{y}_{1}}=1$ and ${{y}_{2}}=-8$ and m = 1 and n= 2
Hence we have
$P\equiv \left( \dfrac{1\times 5+2\times 2}{1+2},\dfrac{1\times \left( -8 \right)+2\times 1}{1+2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{9}{3},\dfrac{-6}{3} \right)=\left( 3,-2 \right)$
Finding coordinates of Q:
that the coordinates of the point P which divides $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ in the ratio of m:n is given by $\left( \dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n} \right)$
Here ${{x}_{1}}=2,{{x}_{2}}=5,{{y}_{1}}=1$ and ${{y}_{2}}=-8$ and m = 2 and n= 1
Hence we have
$Q\equiv \left( \dfrac{2\times 5+1\times 2}{1+2},\dfrac{2\times \left( -8 \right)+1\times 1}{1+2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{12}{3},\dfrac{-15}{3} \right)=\left( 4,-5 \right)$
Also, since P lies on 2x-y+k = 0, P must satisfy its equation.
Hence we have
2(3)-(-2)+k = 0
i.e. k =-8
Hence the value of k is -12.
Note: Alternative solution: Best method:
The ratio in which the line ax+by+c=0 divides the line segment joining points $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $-\dfrac{a{{x}_{1}}+b{{y}_{1}}+c}{a{{x}_{2}}+b{{y}_{2}}+c}$ (Remember)
Hence the ratio in which 2x-y+k = 0 divides the line segment joining A (2,1) and B (5,-8) is given by
$-\dfrac{2\left( 2 \right)-1+k}{2\left( 5 \right)-\left( -8 \right)+k}=-\dfrac{3+k}{18+k}$
Since the line 2x-y+k = 0 intersects AB at P which divides AB in the ratio 1:2, we have
$-\dfrac{3+k}{18+k}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Cross multiplying, we get
$\begin{align}
& -6-2k=18+k \\
& \Rightarrow 3k=-24 \\
& \Rightarrow k=-8 \\
\end{align}$

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




