
The line 2 x + 3 y = 12 meets the x-axis at A and the y-axis at B . The line through (5,5) perpendicular to AB meets the x-axis , y-axis and the line AB at C , D , E respectively . If O is the origin then the area of OCEB is ?
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint - Draw all the points on the cartesian plane including the perpendicular through (5,5) . Solve the equations of both the lines to get the intersection point and use the formula of area of the triangle to find the area of the quadrilateral .
Complete step-by-step answer:
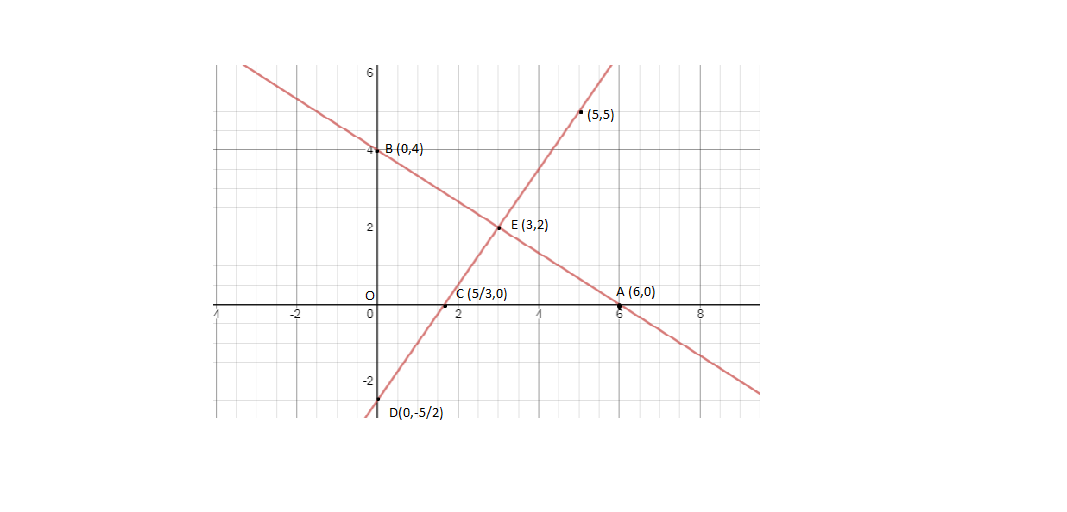
According to the question first find points A and B lying on the x and y axis respectively .
If y = 0 , x = 6 ( substituting values from 2x + 3y = 12 )
We get pt. A = (6,0)
If x = 0 , y = 4 ( substituting values from 2x + 3y = 12 )
We get pt. B = (0,4)
Finding equation of perpendicular DE ;
To find the slope of perpendicular , first find the slope of AB
i.e , ${m_{AB}}$ = $\dfrac{{ - 2}}{3}$
Therefore , slope of the perpendicular DE = $\dfrac{3}{2}$ ( since the slope of a perpendicular line is the "negative reciprocal" of the slope of the original line )
Therefore ,
y–5 = $\dfrac{3}{2}$ (x-5) ( equation of the perpendicular DE )
$ \Rightarrow $ 2y – 10 = 3x -15
$ \Rightarrow $ 2y = 3x – 5
Using the equation to find the points C , D
y = 0 , x = $\dfrac{5}{3}$ ( substituting values in the above equation of the perpendicular )
A = $\left( {\dfrac{5}{3},0} \right)$
x = 0 , y = $\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}$
B = $\left( {0,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)$
To determine E which is the intersection of the perpendicular DE and the line AB , solve the equations of both the lines
We get ,
2x + 3y = 12
Putting y = $\dfrac{{3x - 5}}{2}$ ( from the equation of the perpendicular )
$2x + 3\left( {\dfrac{{3x - 5}}{2}} \right) = 12$
4x + 9x – 15 = 24
13x = 39
x = 3
and y = 2
Therefore, E = ( 3, 2)
Now the area of the quadrilateral OCEB = area of the triangle BED - area of the triangle OCD
Area of the triangle BED = $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {4 + \dfrac{5}{2}} \right) \times 3$ = $\dfrac{{39}}{4}$ ( Since base is DB and height is 3 from the figure )
Area of the triangle OCD = $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{3}$= $\dfrac{{25}}{{12}}$ ( Since base is $\dfrac{5}{2}$and height is $\dfrac{5}{3}$ )
Therefore area of OCEB = $\dfrac{{39}}{4} - \dfrac{{25}}{{12}} = \dfrac{{92}}{{12}} = \dfrac{{23}}{3}$
Note - In such kinds of questions a firm understanding of the cartesian plane helps to simplify the question . Rather than finding the area of the quadrilateral which would be more difficult it is easier and suitable to find the areas of two triangles by the formula of area of triangle and subtracting them to find the desired area .
Complete step-by-step answer:

According to the question first find points A and B lying on the x and y axis respectively .
If y = 0 , x = 6 ( substituting values from 2x + 3y = 12 )
We get pt. A = (6,0)
If x = 0 , y = 4 ( substituting values from 2x + 3y = 12 )
We get pt. B = (0,4)
Finding equation of perpendicular DE ;
To find the slope of perpendicular , first find the slope of AB
i.e , ${m_{AB}}$ = $\dfrac{{ - 2}}{3}$
Therefore , slope of the perpendicular DE = $\dfrac{3}{2}$ ( since the slope of a perpendicular line is the "negative reciprocal" of the slope of the original line )
Therefore ,
y–5 = $\dfrac{3}{2}$ (x-5) ( equation of the perpendicular DE )
$ \Rightarrow $ 2y – 10 = 3x -15
$ \Rightarrow $ 2y = 3x – 5
Using the equation to find the points C , D
y = 0 , x = $\dfrac{5}{3}$ ( substituting values in the above equation of the perpendicular )
A = $\left( {\dfrac{5}{3},0} \right)$
x = 0 , y = $\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}$
B = $\left( {0,\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right)$
To determine E which is the intersection of the perpendicular DE and the line AB , solve the equations of both the lines
We get ,
2x + 3y = 12
Putting y = $\dfrac{{3x - 5}}{2}$ ( from the equation of the perpendicular )
$2x + 3\left( {\dfrac{{3x - 5}}{2}} \right) = 12$
4x + 9x – 15 = 24
13x = 39
x = 3
and y = 2
Therefore, E = ( 3, 2)
Now the area of the quadrilateral OCEB = area of the triangle BED - area of the triangle OCD
Area of the triangle BED = $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {4 + \dfrac{5}{2}} \right) \times 3$ = $\dfrac{{39}}{4}$ ( Since base is DB and height is 3 from the figure )
Area of the triangle OCD = $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{3}$= $\dfrac{{25}}{{12}}$ ( Since base is $\dfrac{5}{2}$and height is $\dfrac{5}{3}$ )
Therefore area of OCEB = $\dfrac{{39}}{4} - \dfrac{{25}}{{12}} = \dfrac{{92}}{{12}} = \dfrac{{23}}{3}$
Note - In such kinds of questions a firm understanding of the cartesian plane helps to simplify the question . Rather than finding the area of the quadrilateral which would be more difficult it is easier and suitable to find the areas of two triangles by the formula of area of triangle and subtracting them to find the desired area .
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




