
The length of carbon-carbon single bond of the compounds
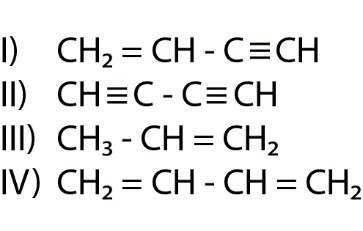
is expected to increase in the order
(A) Ⅲ > Ⅱ > Ⅰ > Ⅳ
(B)Ⅰ > Ⅲ > Ⅱ > Ⅳ
(C) Ⅲ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅱ
(D)Ⅱ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅲ
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: The length of the carbon-carbon single bond depends upon the hybridization of the carbon atom. The hybridization of the carbon contains S and P characters. More will be the p percentage, more will be the length of the carbon-carbon single bond.
Complete step by step solution:
For comparing the length of the carbon-carbon single bond, we need to check the hybridization of the carbons bonded via single bonds in each option.
In $ sp $ , $ 50\% $ S and $ 50\% $ P character is there.
In $ s{p^2} $ , $ 33.33\% $ S and $ 66.66\% $ P character is there.
In $ s{p^3} $ , $ 25\% $ S and $ 75\% $ P character is there.
Checking each option separately,
(Ⅰ)
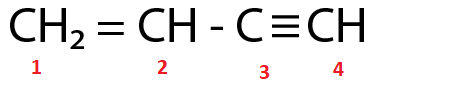
$ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ and $ sp $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅱ)
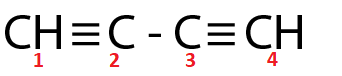
Both $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ sp $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅲ)
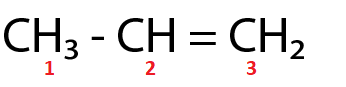
$ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ are $ s{p^3} $ and $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅳ)
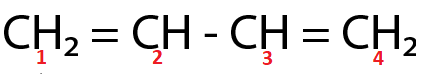 $ \because $
$ \because $
Here, both $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.
Now, we know as the p character increases, the bond length of the carbon-carbon single bond increases.
Combining the percentage p character of the carbon-carbon single bond,
For the molecule in option (Ⅰ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 66.66\% + 50\% = 116.66\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ and $ sp $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule in option (Ⅱ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 50\% + 50\% = 100\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ sp $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule in option (Ⅲ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 75\% + 66.66\% = 141.66\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ are $ s{p^3} $ and $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule present in option (Ⅳ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 66.66\% + 66.66\% = 133.32\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.)
Now, we can easily compare on the basis of combined percentage p character.
The molecule in option (Ⅲ) will have the longest carbon-carbon single bond length followed by (Ⅳ),
(Ⅰ) and (Ⅱ).
Therefore, the correct order will be Ⅲ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅱ
So, the correct option will be option C: Ⅲ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅱ.
Additional information:
A carbon-carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. Single bond is the most common form: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon-carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms.
Note:
The carbon-carbon single bond length is directly proportional to the combined percentage of p of both the carbon atoms bonded via single bond and inversely proportional to the combined percentage of s of both the carbon atoms bonded via single bond.
As the combined percentage of p increases, bond length of carbon-carbon single bond increases.
Complete step by step solution:
For comparing the length of the carbon-carbon single bond, we need to check the hybridization of the carbons bonded via single bonds in each option.
In $ sp $ , $ 50\% $ S and $ 50\% $ P character is there.
In $ s{p^2} $ , $ 33.33\% $ S and $ 66.66\% $ P character is there.
In $ s{p^3} $ , $ 25\% $ S and $ 75\% $ P character is there.
Checking each option separately,
(Ⅰ)
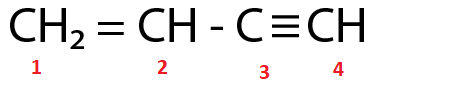
$ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ and $ sp $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅱ)
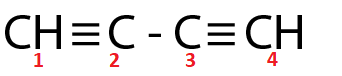
Both $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ sp $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅲ)
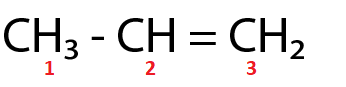
$ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ are $ s{p^3} $ and $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.
(Ⅳ)
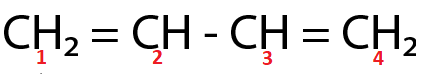
Here, both $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.
Now, we know as the p character increases, the bond length of the carbon-carbon single bond increases.
Combining the percentage p character of the carbon-carbon single bond,
For the molecule in option (Ⅰ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 66.66\% + 50\% = 116.66\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ and $ sp $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule in option (Ⅱ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 50\% + 50\% = 100\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ sp $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule in option (Ⅲ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 75\% + 66.66\% = 141.66\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_1} $ and $ {C_2} $ are $ s{p^3} $ and $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.)
For the molecule present in option (Ⅳ),
Total p percentage of carbons bonded via single bond = $ 66.66\% + 66.66\% = 133.32\% $
( $ \because $ $ {C_2} $ and $ {C_3} $ are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized respectively.)
Now, we can easily compare on the basis of combined percentage p character.
The molecule in option (Ⅲ) will have the longest carbon-carbon single bond length followed by (Ⅳ),
(Ⅰ) and (Ⅱ).
Therefore, the correct order will be Ⅲ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅱ
So, the correct option will be option C: Ⅲ > Ⅳ > Ⅰ > Ⅱ.
Additional information:
A carbon-carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. Single bond is the most common form: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon-carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms.
Note:
The carbon-carbon single bond length is directly proportional to the combined percentage of p of both the carbon atoms bonded via single bond and inversely proportional to the combined percentage of s of both the carbon atoms bonded via single bond.
As the combined percentage of p increases, bond length of carbon-carbon single bond increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




