
The length of a tangent from point A at a distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. What is the radius of the circle?
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. 4 cm}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. 5 cm}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. 3 cm}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. 9 cm}} \\
$

Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by drawing the figure according to the problem statement and then using the concept that the angle made between the tangent to any circle and the radius line (joining the point of contact of the tangent to the circle and the centre of the circle) is always equal to ${90^0}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
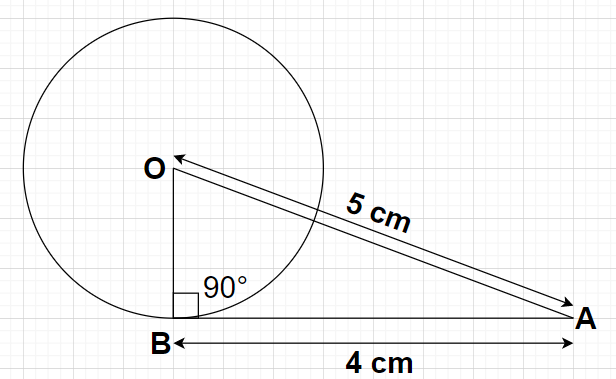
Let us suppose a circle with radius OB whose centre is at point O. Consider point A at a distance of 5 cm from the centre of the circle O as shown in the figure. Here, AB is the tangent drawn from point A to the given circle where point B is the point at which tangent touches the circle.
Given, Length of the tangent AB = 4 cm
OA = 5 cm
As we know that the angle made between the tangent to any circle and the radius line (joining the point of contact of the tangent to the circle and the centre of the circle) is always equal to ${90^0}$.
For the given circle, angle between AB and OB is equal to ${90^0}$ i.e., $\angle {\text{OBA}} = {90^0}$
So, the triangle ABO is a right angled triangle.
In any right angled triangle according to Pythagoras Theorem, we can write
\[{\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Using Pythagoras Theorem in right angled triangle ABO, we have
\[
{\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{4}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 25 = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + 16 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} = 25 - 16 = 9 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{OB}} = \pm \sqrt 9 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{OB}} = \pm 3 \\
\]
Since, OB represents the length of a side of the triangle which will always be positive. So, OB = -3 is neglected.
Radius of the circle = 0B = 3 cm
Therefore, the radius of the given circle is 3 cm.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note- In any right angled triangle, the side opposite to the right angle is known as hypotenuse, the side opposite to the considered angle is known as perpendicular and the remaining side is known as base. Here, in the right angled triangle ABO, OA is the hypotenuse and if angle A is considered, the perpendicular will be OB and the base will be AB.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us suppose a circle with radius OB whose centre is at point O. Consider point A at a distance of 5 cm from the centre of the circle O as shown in the figure. Here, AB is the tangent drawn from point A to the given circle where point B is the point at which tangent touches the circle.
Given, Length of the tangent AB = 4 cm
OA = 5 cm
As we know that the angle made between the tangent to any circle and the radius line (joining the point of contact of the tangent to the circle and the centre of the circle) is always equal to ${90^0}$.
For the given circle, angle between AB and OB is equal to ${90^0}$ i.e., $\angle {\text{OBA}} = {90^0}$
So, the triangle ABO is a right angled triangle.
In any right angled triangle according to Pythagoras Theorem, we can write
\[{\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Using Pythagoras Theorem in right angled triangle ABO, we have
\[
{\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{4}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 25 = {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} + 16 \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2} = 25 - 16 = 9 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{OB}} = \pm \sqrt 9 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{OB}} = \pm 3 \\
\]
Since, OB represents the length of a side of the triangle which will always be positive. So, OB = -3 is neglected.
Radius of the circle = 0B = 3 cm
Therefore, the radius of the given circle is 3 cm.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note- In any right angled triangle, the side opposite to the right angle is known as hypotenuse, the side opposite to the considered angle is known as perpendicular and the remaining side is known as base. Here, in the right angled triangle ABO, OA is the hypotenuse and if angle A is considered, the perpendicular will be OB and the base will be AB.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




