
The lateral area of the frustum of right circular cone is calculated using the formula
A. \[\dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi R + 2\pi r)L\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi R - 2\pi r)L\]
C. \[\dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi R + 2\pi r)\]
D. \[\dfrac{1}{3}(2\pi R + 2\pi r)L\]
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Frustum of a right circular cone is that portion of right circular cone included between the base and a section parallel to the base not passing through the vertex. And the altitude in the frustum is the perpendicular distance between the two bases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Properties of Frustum of Right Circular Cone
i. The altitude of a frustum of a right circular cone is the perpendicular distance between the two bases. It is denoted by h.
ii. All elements of a frustum of a right circular cone are equal. It is denoted by L.
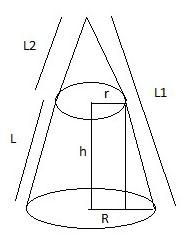
By ratio and proportion:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{R} = \dfrac{L}{{R - r}}\\
{L_1} = \dfrac{{LR}}{{R - r}}
\end{array}\]
From the figure:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{L_2} = {L_1} - L\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{RL}}{{R - r}} - L\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{RL - (R - r)L}}{{R - r}}\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{rL}}{{R - r}}
\end{array}\]
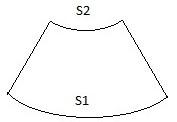
The length of arc is the circumference of the base:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{s_1} = 2\pi R\\
{s_2} = 2\pi r
\end{array}\]
From the figure:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\therefore A = \dfrac{1}{2}{s_1}{L_1} - \dfrac{1}{2}{s_2}{L_2}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi R)\left( {\dfrac{{RL}}{{R - r}}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi r)\left( {\dfrac{{rL}}{{R - r}}} \right)\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}L}}{{R - r}} - \dfrac{{\pi {r^2}L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}L - \pi {r^2}L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi \left( {{R^2} - {r^2}} \right)L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi (R + r)(R - r)L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \pi (R + r)L
\end{array}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The actual definition of the whole thing can be given as; The lateral area of the frustum of a right circular cone is equal to one-half the sum of the circumference of the bases multiplied by slant height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Properties of Frustum of Right Circular Cone
i. The altitude of a frustum of a right circular cone is the perpendicular distance between the two bases. It is denoted by h.
ii. All elements of a frustum of a right circular cone are equal. It is denoted by L.


By ratio and proportion:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\dfrac{{{L_1}}}{R} = \dfrac{L}{{R - r}}\\
{L_1} = \dfrac{{LR}}{{R - r}}
\end{array}\]
From the figure:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{L_2} = {L_1} - L\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{RL}}{{R - r}} - L\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{RL - (R - r)L}}{{R - r}}\\
{L_2} = \dfrac{{rL}}{{R - r}}
\end{array}\]
The length of arc is the circumference of the base:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{s_1} = 2\pi R\\
{s_2} = 2\pi r
\end{array}\]
From the figure:
\[\begin{array}{l}
\therefore A = \dfrac{1}{2}{s_1}{L_1} - \dfrac{1}{2}{s_2}{L_2}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi R)\left( {\dfrac{{RL}}{{R - r}}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi r)\left( {\dfrac{{rL}}{{R - r}}} \right)\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}L}}{{R - r}} - \dfrac{{\pi {r^2}L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {R^2}L - \pi {r^2}L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi \left( {{R^2} - {r^2}} \right)L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi (R + r)(R - r)L}}{{R - r}}\\
\Rightarrow A = \pi (R + r)L
\end{array}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The actual definition of the whole thing can be given as; The lateral area of the frustum of a right circular cone is equal to one-half the sum of the circumference of the bases multiplied by slant height.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




