
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced by assuming that:
A.The heat of adsorption varies with coverage
B.The adsorbed molecules interact with each other
C.The adsorption takes place in multi-layers
D.The adsorption sites are equivalent in their stability to adsorb the particles
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: To describe the equilibrium established between the adsorbate particles and the adsorbent the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. It has some assumptions related to the adsorbate and adsorbent interaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Before moving to the answer we have to be familiar with some terms; adsorbate and adsorbent.
The substance that is adsorbed is known as adsorbate. And the substance that absorbs the other substance in it is known as adsorbent.
In simple language we can say that adsorption means sticking of solid, gaseous or liquid particles on the surface of another solid particle forming a layer on it is known as adsorption. The particles are bound on the surface of the solid by the help of adhesive forces. So, adsorption is adhesion of atoms, molecules or ions on the solid surface.
And to describe the equilibrium established between the adsorbate and adsorbent the Langmuir adsorption isotherm was introduced. Some assumptions were made for the Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
The assumptions are as follows:
Each adsorbent site can hold only one molecule and the solid can only have adsorbents present in monolayer on the surface, the energy of adsorption is equal for all the sites and there is no force of interaction between the adjacent adsorbate particles.
The temperature dependent graph related to adsorption isotherm is as follows:
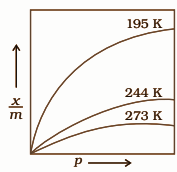
Here the mass of adsorbate is $x$ and the mass of adsorbent is $m$.
Hence from all of the above discussion we can conclude that the adsorption sites are equivalent in their stability to adsorb the particles.
So, option (D) is correct.
Note: A term familiar term similar to adsorb is adsorb which is used in our daily lives. As we understand that adsorption is sticking of particles on the surface of another matter but absorption is taking in the particles such as atoms, ions and molecules into another substance.
Complete step by step solution:
Before moving to the answer we have to be familiar with some terms; adsorbate and adsorbent.
The substance that is adsorbed is known as adsorbate. And the substance that absorbs the other substance in it is known as adsorbent.
In simple language we can say that adsorption means sticking of solid, gaseous or liquid particles on the surface of another solid particle forming a layer on it is known as adsorption. The particles are bound on the surface of the solid by the help of adhesive forces. So, adsorption is adhesion of atoms, molecules or ions on the solid surface.
And to describe the equilibrium established between the adsorbate and adsorbent the Langmuir adsorption isotherm was introduced. Some assumptions were made for the Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
The assumptions are as follows:
Each adsorbent site can hold only one molecule and the solid can only have adsorbents present in monolayer on the surface, the energy of adsorption is equal for all the sites and there is no force of interaction between the adjacent adsorbate particles.
The temperature dependent graph related to adsorption isotherm is as follows:

Here the mass of adsorbate is $x$ and the mass of adsorbent is $m$.
Hence from all of the above discussion we can conclude that the adsorption sites are equivalent in their stability to adsorb the particles.
So, option (D) is correct.
Note: A term familiar term similar to adsorb is adsorb which is used in our daily lives. As we understand that adsorption is sticking of particles on the surface of another matter but absorption is taking in the particles such as atoms, ions and molecules into another substance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




