
The IUPAC name of the compound is:
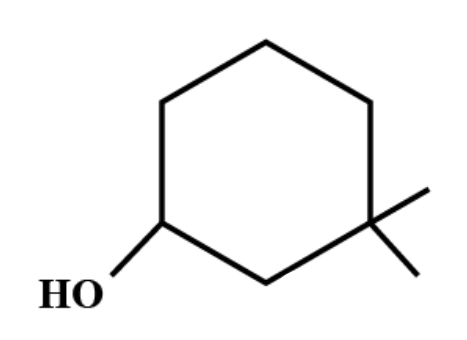
(A) $ 3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexanol. $
(B) $ 1,1-dimethyl-3-hydroxy\text{ }cyclohexane. $
(C) $ 3,3-dimethyl-1-\text{ }hydroxy\text{ }cyclohexane. $
(D) $ 1,1-dimethyl-3-cyclohexanol. $

Answer
527.7k+ views
Hint: We know that isomers are different in physical and chemical properties but have the same number of atoms. This phenomenon is termed as isomerism. Parent carbon chain can be determined by calculating the number of carbons in the longest carbon chain. Alkanes are the hydrocarbons which have no double or triple bond in their structures.
Complete answer:
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically.

Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is $ 3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexanol. $
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but numbering and IUPAC names are different. Only count the number of each atom in both molecules to see how atoms are organized to decide whether two molecules are constitutional isomers.
Note:
Remember that Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers. Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Complete answer:
If organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having that functional group is selected. Functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
As per IUPAC rules, the first thing is to select the longest continuous chain. Then this chain is numbered and the numbering should begin from the end which is close to the substituent groups. Each substituent group has a certain assigned name whose numbering depends on the position of the carbon it has been attached to. These groups are generally arranged alphabetically.

Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is $ 3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexanol. $
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but numbering and IUPAC names are different. Only count the number of each atom in both molecules to see how atoms are organized to decide whether two molecules are constitutional isomers.
Note:
Remember that Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers. Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




