
The IUPAC name of ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$ is,
A. Ethoxy methane
B. Methoxy ethane
C. Ethyl methyl ether
D. Methyl ethyl ether
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: We know that ether is a functional group whose structure is R-O-R, where R is an alkyl or aryl group. The two alkyl groups of the ether may be the same or different. There are two types of naming of ether, common naming and IUPAC naming.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss the IUPAC naming of ether. In IUPAC naming, ethers are considered as derivative of hydrocarbon in which an –OR or –OAr group replaces a hydrogen atom, where, Ar and R represents aryl and alkyl groups respectively. The larger R group should be considered as a parent chain and the remaining alkyl group should be considered as a prefix such as ethoxy, methoxy etc.
Now, come to the question. We have to choose the correct IUPAC name of ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$.
In ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$,
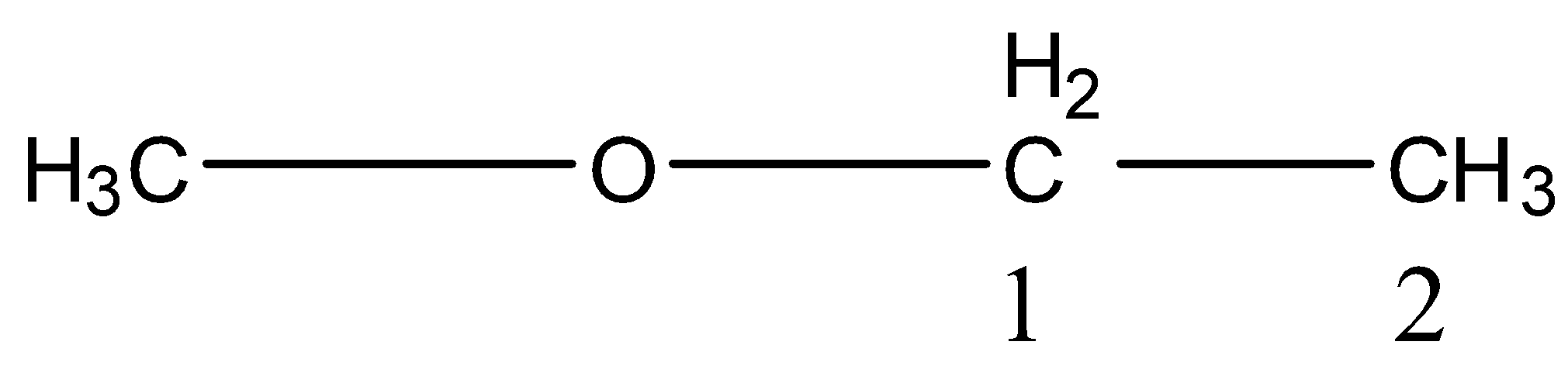
Here, the ethyl group is the parent chain and the methyl group is the substituent. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is methoxyethane
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Additional Information:
IUPAC naming is a method of naming organic compounds following a set of guidelines recommended by the international Union of Pure and Applied chemistry. The general format of naming of any organic compound is prefix + word root + suffix. The word root indicates the name of the parent chain, suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound and the prefix indicates the substituents of the compound.
Note: Common names of ethers are derived from the names of alkyl/ aryl groups written as separate words in alphabetical words followed by adding ‘ether’ at the end. For ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$, the common name is ethyl methyl ether. If the two alkyl groups of the ether are same, prefix ‘di’ is added before the name of the alkyl group, such as, the name of ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$ is dimethyl ether.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss the IUPAC naming of ether. In IUPAC naming, ethers are considered as derivative of hydrocarbon in which an –OR or –OAr group replaces a hydrogen atom, where, Ar and R represents aryl and alkyl groups respectively. The larger R group should be considered as a parent chain and the remaining alkyl group should be considered as a prefix such as ethoxy, methoxy etc.
Now, come to the question. We have to choose the correct IUPAC name of ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$.
In ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$,

Here, the ethyl group is the parent chain and the methyl group is the substituent. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is methoxyethane
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Additional Information:
IUPAC naming is a method of naming organic compounds following a set of guidelines recommended by the international Union of Pure and Applied chemistry. The general format of naming of any organic compound is prefix + word root + suffix. The word root indicates the name of the parent chain, suffix indicates the functional group present in the compound and the prefix indicates the substituents of the compound.
Note: Common names of ethers are derived from the names of alkyl/ aryl groups written as separate words in alphabetical words followed by adding ‘ether’ at the end. For ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}$, the common name is ethyl methyl ether. If the two alkyl groups of the ether are same, prefix ‘di’ is added before the name of the alkyl group, such as, the name of ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{O}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$ is dimethyl ether.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




