
The IUPAC name of:
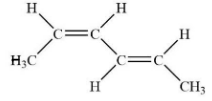
(A) $\left( E \right),\left( E \right) - 2,4 - hexadiene$
(B) $\left( Z \right),\left( Z \right) - 2,4 - hexadiene$
(C) $\left( E \right),\left( Z \right) - 3,5 - hexadiene$
(D) $\left( Z \right),\left( E \right) - 2,4 - hexadiene$

Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint:Stereoisomers are those isomers that possess the same relationship between the substituent’s atoms but having different arrangements of atoms in the space. So, we can say that the relationship between two molecules above is that of diastereomers. So, we can say that diastereomers are the stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other.
These two molecules have different physical properties – different boiling points, melting points, reactivity, spectral characteristics and so on.
Complete answer:In organic chemistry nomenclature, “cis” is used to the isomer which has two identical groups (e.g. the two chlorines in 1,2-dichlorocyclopentane) are present in the similar direction from the plane of the ring, and trans to the isomer which has groups in opposite directions. We can use the priority system developed by Cahn, Ingold, and Prelog which is explained as;
1. Each carbon in the pi bond is attached to two substituents. For each carbon, these two groups are given priority (1 or 2) according to the atomic numbers of the atom directly attached to the carbon. (e.g. Cl > F)
2. If both substituents with priority 1 are on the same side of the pi bond, the bond is given the naming Z (short for German Zusammen, means “together”).
3. If both substituents priority 1 are on the two-opposite side of the pi bond, the bond is given the naming E (short for German Entgegen, means “opposite”).
So, Z is same as “cis” and E is same as “trans”.
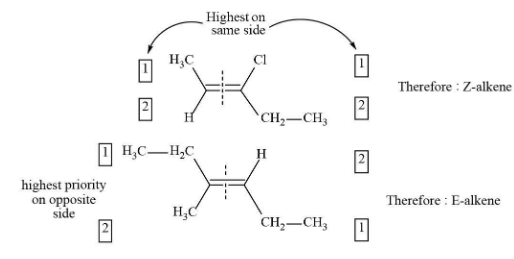
So, in our question methyl is given high priority over hydrogen atom.
So, one double bond will be in cis i.e. Z isomer and another double bond will be in trans i.e. E isomer. There are six carbons in the molecule and there two double bonds at second and fourth position.
So correct naming of this compound will be $\left( Z \right),\left( E \right) - 2,4 - hexadiene$
Hence, option (D), is the correct option.
Note:For any molecules in alkene showing cis-trans isomerism each carbon is must be bonded to two different groups, and that the two carbons must have one substituent common.
These two molecules have different physical properties – different boiling points, melting points, reactivity, spectral characteristics and so on.
Complete answer:In organic chemistry nomenclature, “cis” is used to the isomer which has two identical groups (e.g. the two chlorines in 1,2-dichlorocyclopentane) are present in the similar direction from the plane of the ring, and trans to the isomer which has groups in opposite directions. We can use the priority system developed by Cahn, Ingold, and Prelog which is explained as;
1. Each carbon in the pi bond is attached to two substituents. For each carbon, these two groups are given priority (1 or 2) according to the atomic numbers of the atom directly attached to the carbon. (e.g. Cl > F)
2. If both substituents with priority 1 are on the same side of the pi bond, the bond is given the naming Z (short for German Zusammen, means “together”).
3. If both substituents priority 1 are on the two-opposite side of the pi bond, the bond is given the naming E (short for German Entgegen, means “opposite”).
So, Z is same as “cis” and E is same as “trans”.

So, in our question methyl is given high priority over hydrogen atom.
So, one double bond will be in cis i.e. Z isomer and another double bond will be in trans i.e. E isomer. There are six carbons in the molecule and there two double bonds at second and fourth position.
So correct naming of this compound will be $\left( Z \right),\left( E \right) - 2,4 - hexadiene$
Hence, option (D), is the correct option.
Note:For any molecules in alkene showing cis-trans isomerism each carbon is must be bonded to two different groups, and that the two carbons must have one substituent common.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




