
The ion that is not univalent is
A. Ammonium
B. Sodium
C. Bicarbonate
D. Sulphite
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: We can define valency as the total of electrons which are gained or lost by an atom to control the steadiness for getting the electronic configuration of the noble gas which is adjacent to the element. We can conclude the valency using the octet rule, with the help of a periodic table and also based on the chemical formula.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say valency is the capability of atoms of a single element to react and join with a particular number of atoms of another element.
Based on the valency, we can classify ions as,
1,Univalent: Ions that contain one charge. Example: Cesium cation
2.Bivalent: Ions that contain two charges. Example: Magnesium cation
3.Trivalent: Ions that contain three charges. Example: Aluminum cation
4.Polyvalent: Ions that contain many variable charges. Example: Iron (Seen as +2 and +3 ions.
From the above explanation, we saw that univalent means ion that contains a single charge. Let us now identify the ion that is not univalent.
Ammonium is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (A) is incorrect.
Sodium is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (B) is incorrect.
Bicarbonate is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (C) is incorrect.
Sulphite is an example of bivalent ion as it contains ${\text{ - 2}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (D) is correct. We can draw the structure of sulphite as,
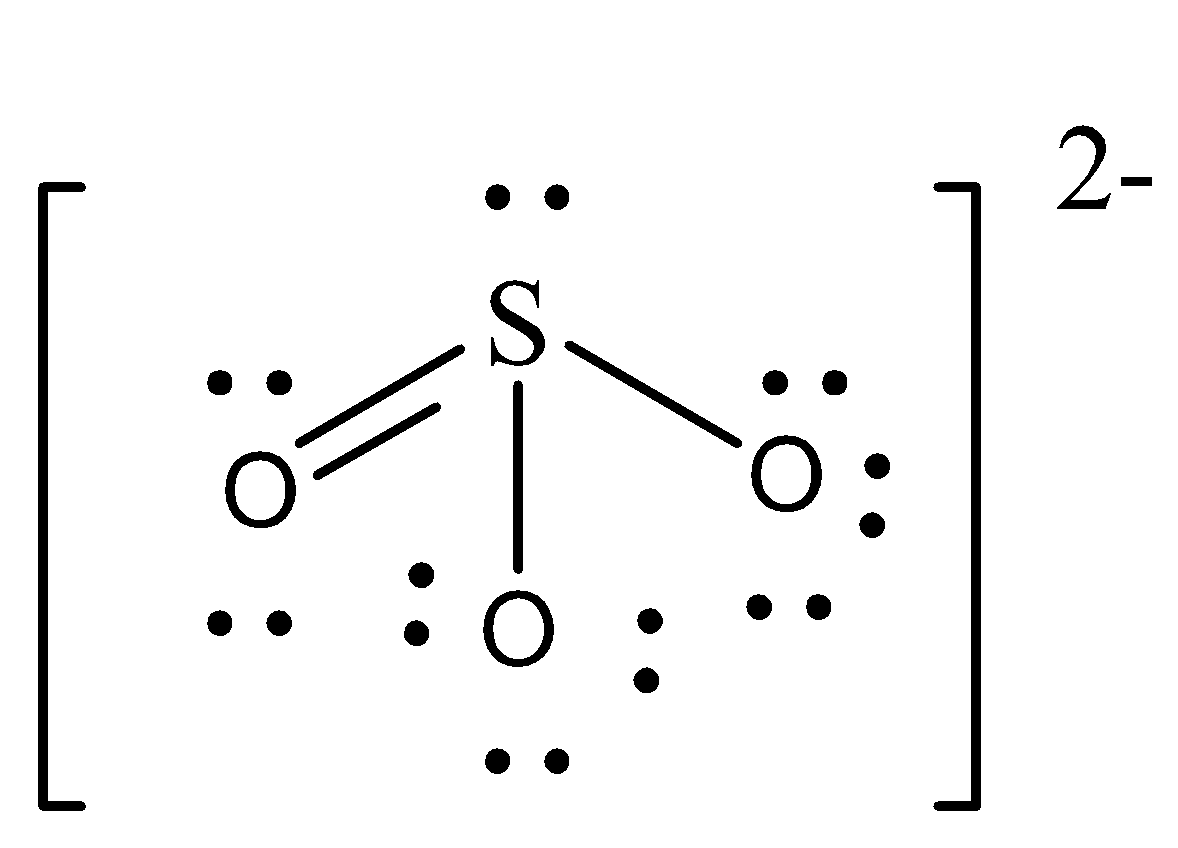
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We have to remember that the difference between the octet and the total of valence electrons would also give the valency of an element. We know that the valency is the total of electrons that is required to finish its octet. We know that the octet rule says that the valence shell of an atom is filled with eight electrons then the atom is said to be most stable.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say valency is the capability of atoms of a single element to react and join with a particular number of atoms of another element.
Based on the valency, we can classify ions as,
1,Univalent: Ions that contain one charge. Example: Cesium cation
2.Bivalent: Ions that contain two charges. Example: Magnesium cation
3.Trivalent: Ions that contain three charges. Example: Aluminum cation
4.Polyvalent: Ions that contain many variable charges. Example: Iron (Seen as +2 and +3 ions.
From the above explanation, we saw that univalent means ion that contains a single charge. Let us now identify the ion that is not univalent.
Ammonium is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (A) is incorrect.
Sodium is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (B) is incorrect.
Bicarbonate is an example of an univalent ion that contains ${\text{ + 1}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (C) is incorrect.
Sulphite is an example of bivalent ion as it contains ${\text{ - 2}}$ charge. Therefore, the option (D) is correct. We can draw the structure of sulphite as,

So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We have to remember that the difference between the octet and the total of valence electrons would also give the valency of an element. We know that the valency is the total of electrons that is required to finish its octet. We know that the octet rule says that the valence shell of an atom is filled with eight electrons then the atom is said to be most stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




