
The image formed by a convex mirror is always:
A. erect, virtual, large.
B. erect, virtual, diminished.
C. upright, virtual.
D. none of the above.
Answer
614.4k+ views
Hint: We need to know the principle of image forming of a convex mirror to solve this problem. The convex mirror is a spherical mirror in which light reflects on the convex surface (or bubbles out of the air).
Complete step-by-step solution -
Image is an optical illusion that is created when a mirror reflects light rays coming from an object.
We know that the image you can get on a screen is called a true image. The image not obtainable on a screen is called a virtual image.
The rules of obtaining images formed by a convex mirror are:
Rule 1. A beam of light parallel to a convex mirror 's main axis tends to come from its focus after mirror reflection.
Rule 2. A ray of light going towards the center of curvature of a convex mirror is reflected back along the same path.
Rule 3. A ray of light going towards the focus of the convex mirror becomes parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
Rule 4. A ray of light which is incident at the pole of a convex mirror is reflected back making the same angle with the principal axis.
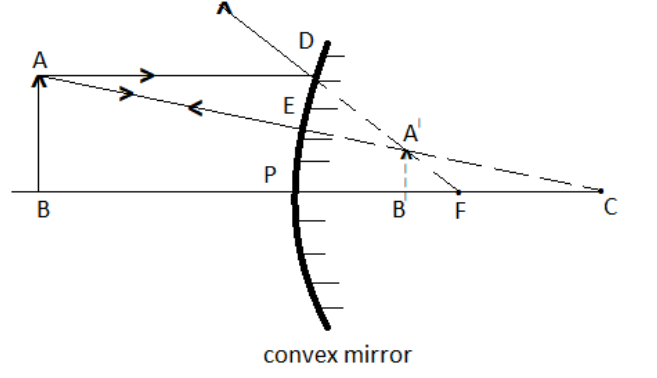
Whatever the position of the object in front of a convex mirror in a convex mirror, the image formed by a convex mirror is always behind the mirror, it is virtual, erect, and smaller than the object itself. (Or shrunk).
In the figure below, the formation of an image by a convex mirror is shown when the object is placed anywhere between the pole of the mirror and infinity.
The image created by a convex mirror is thus always virtual, erect, and diminished.
So choice (B) is the correct one.
Note: If we ask questions of this kind, we must first note that the image formed behind the mirror is always virtual and erect and that the image formed in front of the mirror is always real and inverted. We should realize that a convex mirror still shapes behind the mirror images. We will be getting the answer through this.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Image is an optical illusion that is created when a mirror reflects light rays coming from an object.
We know that the image you can get on a screen is called a true image. The image not obtainable on a screen is called a virtual image.
The rules of obtaining images formed by a convex mirror are:
Rule 1. A beam of light parallel to a convex mirror 's main axis tends to come from its focus after mirror reflection.
Rule 2. A ray of light going towards the center of curvature of a convex mirror is reflected back along the same path.
Rule 3. A ray of light going towards the focus of the convex mirror becomes parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
Rule 4. A ray of light which is incident at the pole of a convex mirror is reflected back making the same angle with the principal axis.
Whatever the position of the object in front of a convex mirror in a convex mirror, the image formed by a convex mirror is always behind the mirror, it is virtual, erect, and smaller than the object itself. (Or shrunk).
In the figure below, the formation of an image by a convex mirror is shown when the object is placed anywhere between the pole of the mirror and infinity.
The image created by a convex mirror is thus always virtual, erect, and diminished.
So choice (B) is the correct one.

Note: If we ask questions of this kind, we must first note that the image formed behind the mirror is always virtual and erect and that the image formed in front of the mirror is always real and inverted. We should realize that a convex mirror still shapes behind the mirror images. We will be getting the answer through this.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Draw a diagram to show how hypermetropia is correc class 10 physics CBSE




