
The heating of phenyl-methyl ethers with HI produces:
A.Benzene
B.Ethyl chlorides
C.Iodobenzene
D.Phenol
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint:Ether are basically a compound where two alkyl or aryl or one alkyl and one aryl group is bonded with oxygen. It can be formed by the dehydration of alcohols by emitting water molecules using dehydrating agents like Conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] .
Complete answer:
When ethers heated in presence of HI it dissociates into alcohol and alkyl iodide.
\[{C_2}{H_5}OH + {C_2}{H_5}OH \to {C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5}\]
In presence of acid ether can be dissociated. For example, the presence of HI, it dissociates by the following mechanism.
\[ROR'\xrightarrow{{HI}}ROH + R'I\xrightarrow{{HI}}RI + R'I\]
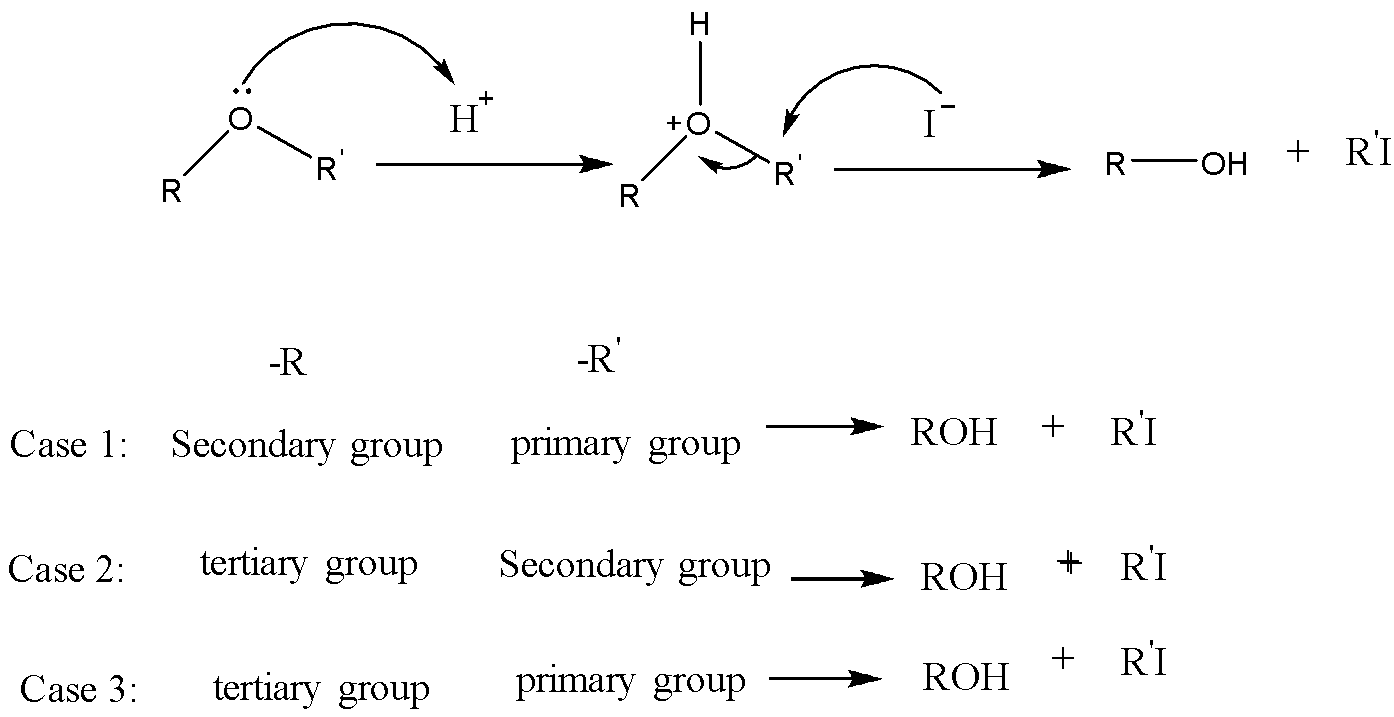
This mechanism is the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. The formation of alkyl iodide and alcohol depends upon the group attached to the oxygen. Between the secondary and Primary alkyl group, the primary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Between secondary and tertiary alkyl groups, the secondary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. And between tertiary and Primary alkyl groups, the primary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodides. In between vinyl or benzyl group and alkyl group, alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Because vinyl and benzyl groups do not participate in the \[S{N^2}\] reaction.
Now for the phenyl methyl ether in presence of HI it will dissociates in the following manner,
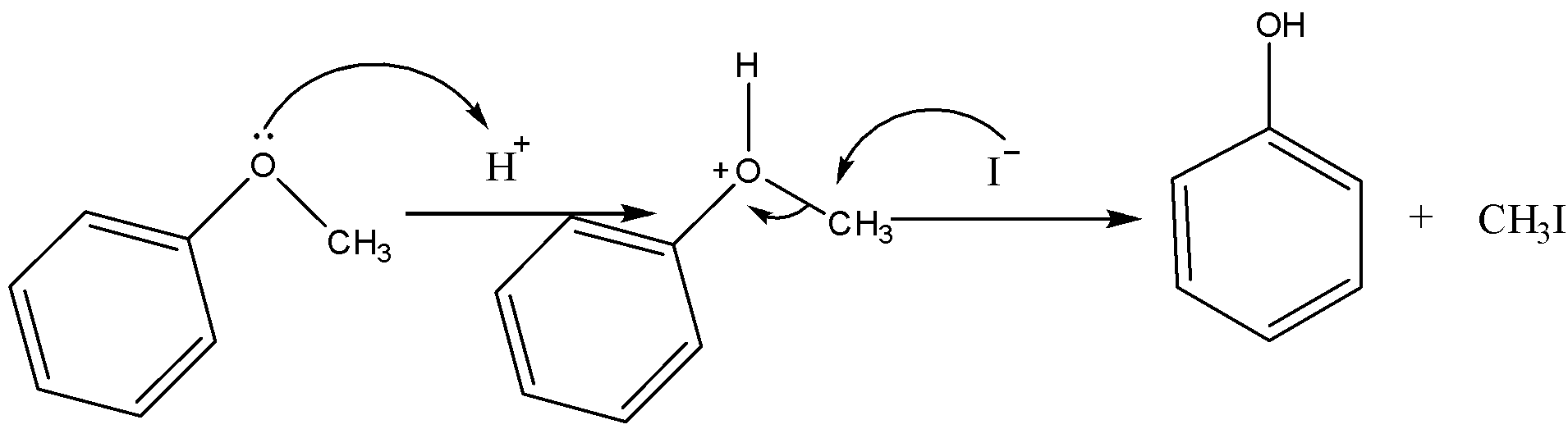
Therefore, on heating of phenyl methyl ether in presence of HI, phenol is formed.
So, the correct answer is D.
Note:
Dissociation of ether undergoes in the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. Always less bulky group will form corresponding alkyl iodide.
\[S{N^2}\] is a single step reaction in which inversion of configuration takes place while \[S{N^1}\] is a two step reaction, in first step formation of carbocation takes place and then the nucleophile attacks. In \[S{N^1}\] no inversion of configuration occurs.
Complete answer:
When ethers heated in presence of HI it dissociates into alcohol and alkyl iodide.
\[{C_2}{H_5}OH + {C_2}{H_5}OH \to {C_2}{H_5}O{C_2}{H_5}\]
In presence of acid ether can be dissociated. For example, the presence of HI, it dissociates by the following mechanism.
\[ROR'\xrightarrow{{HI}}ROH + R'I\xrightarrow{{HI}}RI + R'I\]

This mechanism is the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. The formation of alkyl iodide and alcohol depends upon the group attached to the oxygen. Between the secondary and Primary alkyl group, the primary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Between secondary and tertiary alkyl groups, the secondary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. And between tertiary and Primary alkyl groups, the primary alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodides. In between vinyl or benzyl group and alkyl group, alkyl group favors the \[S{N^2}\] attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Because vinyl and benzyl groups do not participate in the \[S{N^2}\] reaction.
Now for the phenyl methyl ether in presence of HI it will dissociates in the following manner,

Therefore, on heating of phenyl methyl ether in presence of HI, phenol is formed.
So, the correct answer is D.
Note:
Dissociation of ether undergoes in the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism. Always less bulky group will form corresponding alkyl iodide.
\[S{N^2}\] is a single step reaction in which inversion of configuration takes place while \[S{N^1}\] is a two step reaction, in first step formation of carbocation takes place and then the nucleophile attacks. In \[S{N^1}\] no inversion of configuration occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




