
The greater stability of trans-but-2-ene over cis-but-2-ene can be explained on the basis of hyperconjugation effect.
A.True
B.False
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: The concept of hyperconjugation as well as the role of steric factor in stability is to be used in this question. Hyperconjugation can be also called as no bond resonance. Compounds which are more stable have less steric hindrance.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about hyperconjugation. When the alkyl group is associated with an unsaturated area such as $-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ group, the order of inductive effect gets: reversed. This behaviour of alkyl groups is explained with the help of hyperconjugation effect. Since it was noticed for the first time by Baker & Nathan, it is also called Baker Nathan effect. Let us consider the example of propene ($C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$) in which the carbon atom of the methyl group is called $\alpha $carbon atom and the hydrogen atoms attached to are known as$\alpha $ hydrogen atoms. The $\pi $ electron pair of the double bond causes the cleavage of the C-H bond of the methyl group and the electron pair of the bond conjugates with the pi-electron pair of the double bond.
As there is no actual bond between the a-carbon atom and the positively charged hydrogen atom (or ${{H}^{+}}$), hyper-conjugation is also called no bond resonance. It is quite obvious that greater the number of $\alpha $hydrogen atoms more will be the electron releasing tendency of the alkyl group. The number of $\alpha $hydrogen atoms decreases from methyl group (three) to ethyl group (two) followed by isopropyl group (one) and finally the tertiary butyl group has no $\alpha $hydrogen atom.
Now, let us see the structures of cis and trans 3 butene:
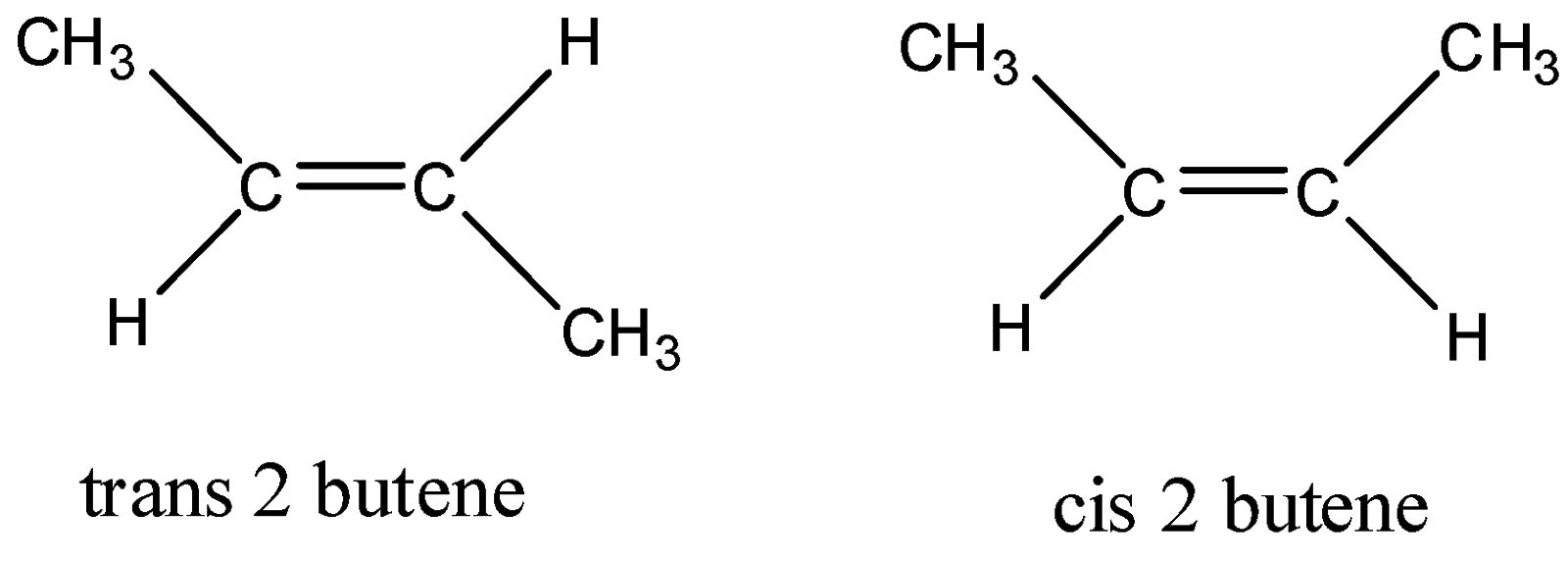
As we can see from the structures that in trans 2 butene, the steric factor is much less. Cis 2 butene has both bulky methyl groups on same side, so steric factor is more. Hence, the stability of trans 2 butene is more but it is based on the fact of stability and not hyperconjugation.
So, the answer is false.
NOTE: Hyperconjugation imparts partial double bond character to the C-C bond and hence, it shortens the bond. An $\alpha $ hydrogen along with unsaturation is required for hyperconjugation.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about hyperconjugation. When the alkyl group is associated with an unsaturated area such as $-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$ group, the order of inductive effect gets: reversed. This behaviour of alkyl groups is explained with the help of hyperconjugation effect. Since it was noticed for the first time by Baker & Nathan, it is also called Baker Nathan effect. Let us consider the example of propene ($C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$) in which the carbon atom of the methyl group is called $\alpha $carbon atom and the hydrogen atoms attached to are known as$\alpha $ hydrogen atoms. The $\pi $ electron pair of the double bond causes the cleavage of the C-H bond of the methyl group and the electron pair of the bond conjugates with the pi-electron pair of the double bond.
As there is no actual bond between the a-carbon atom and the positively charged hydrogen atom (or ${{H}^{+}}$), hyper-conjugation is also called no bond resonance. It is quite obvious that greater the number of $\alpha $hydrogen atoms more will be the electron releasing tendency of the alkyl group. The number of $\alpha $hydrogen atoms decreases from methyl group (three) to ethyl group (two) followed by isopropyl group (one) and finally the tertiary butyl group has no $\alpha $hydrogen atom.
Now, let us see the structures of cis and trans 3 butene:

As we can see from the structures that in trans 2 butene, the steric factor is much less. Cis 2 butene has both bulky methyl groups on same side, so steric factor is more. Hence, the stability of trans 2 butene is more but it is based on the fact of stability and not hyperconjugation.
So, the answer is false.
NOTE: Hyperconjugation imparts partial double bond character to the C-C bond and hence, it shortens the bond. An $\alpha $ hydrogen along with unsaturation is required for hyperconjugation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




