
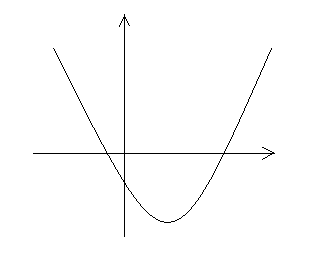
The graph of the quadratic polynomial; y = $ a{{x}^{2}} $ + bx + c is as shown in the figure. Then:
A. $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac > 0
B. b > 0
C. a < 0
D. All of these.

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Observe that the parabola is opening upwards which means that the values of y are increasing in the positive direction. What does it tell about the coefficient a of the term $ a{{x}^{2}} $ ?
Locate the position of the roots of the parabola. Are real roots real or imaginary (no real roots)? What does it tell about the value of the discriminant $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac?
Complete step-by-step answer:
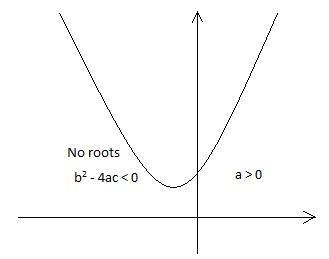
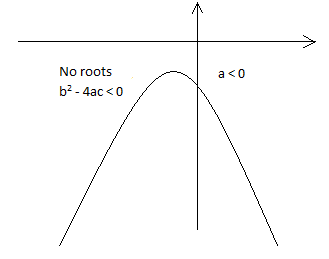
It should be observed that the value of $ {{x}^{2}} $ is always positive and greater than the terms bx and c for large magnitudes of x. Therefore, the sign of the multiplier a in the term $ a{{x}^{2}} $ , decides whether the value of y will move in the positive or negative direction for an increase in the magnitude of x in either direction. This is illustrated in the following graphs:
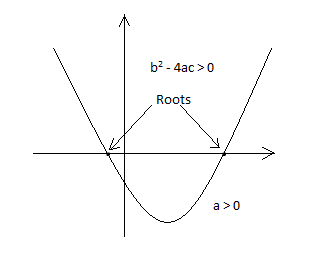
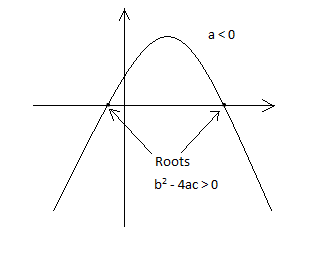
Since the given graph has two real roots and it opens upwards in the positive direction, we can conclude that a > 0 and $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac > 0 (see Note below).
The correct answer is A. $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac > 0.
Note: The roots (also called as zeros, y = 0) of the quadratic equation $ a{{x}^{2}} $ + bx + c = 0 are given by x = $ \dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ . The quantity $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac is called the discriminant of the equation and determines the nature of its roots.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac ≥ 0, the roots are real.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac = 0, the roots are real and equal.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac < 0, the roots are complex and conjugates of each other.
Locate the position of the roots of the parabola. Are real roots real or imaginary (no real roots)? What does it tell about the value of the discriminant $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac?
Complete step-by-step answer:
It should be observed that the value of $ {{x}^{2}} $ is always positive and greater than the terms bx and c for large magnitudes of x. Therefore, the sign of the multiplier a in the term $ a{{x}^{2}} $ , decides whether the value of y will move in the positive or negative direction for an increase in the magnitude of x in either direction. This is illustrated in the following graphs:




Since the given graph has two real roots and it opens upwards in the positive direction, we can conclude that a > 0 and $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac > 0 (see Note below).
The correct answer is A. $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac > 0.
Note: The roots (also called as zeros, y = 0) of the quadratic equation $ a{{x}^{2}} $ + bx + c = 0 are given by x = $ \dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a} $ . The quantity $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac is called the discriminant of the equation and determines the nature of its roots.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac ≥ 0, the roots are real.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac = 0, the roots are real and equal.
If $ {{b}^{2}} $ − 4ac < 0, the roots are complex and conjugates of each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Which are the three major ports of Tamil Nadu A Chennai class 10 social science CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE




