
The ganglia of the sympathetic and the central nervous system in frog develops from the
A. Neural cell
B. Notochordal cells
C. Neural plate cells
D. Neural crest cells
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The ganglia of the sympathetic and the central nervous system in the frog develop from the neural crest cells. The neural crest also gives rise to CNS (brain and spinal cord) and PNS (Peripheral Nervous System).
Complete answer:
- Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells that are present only in vertebrates. These cells arise from the embryonic ectoderm cell layer.
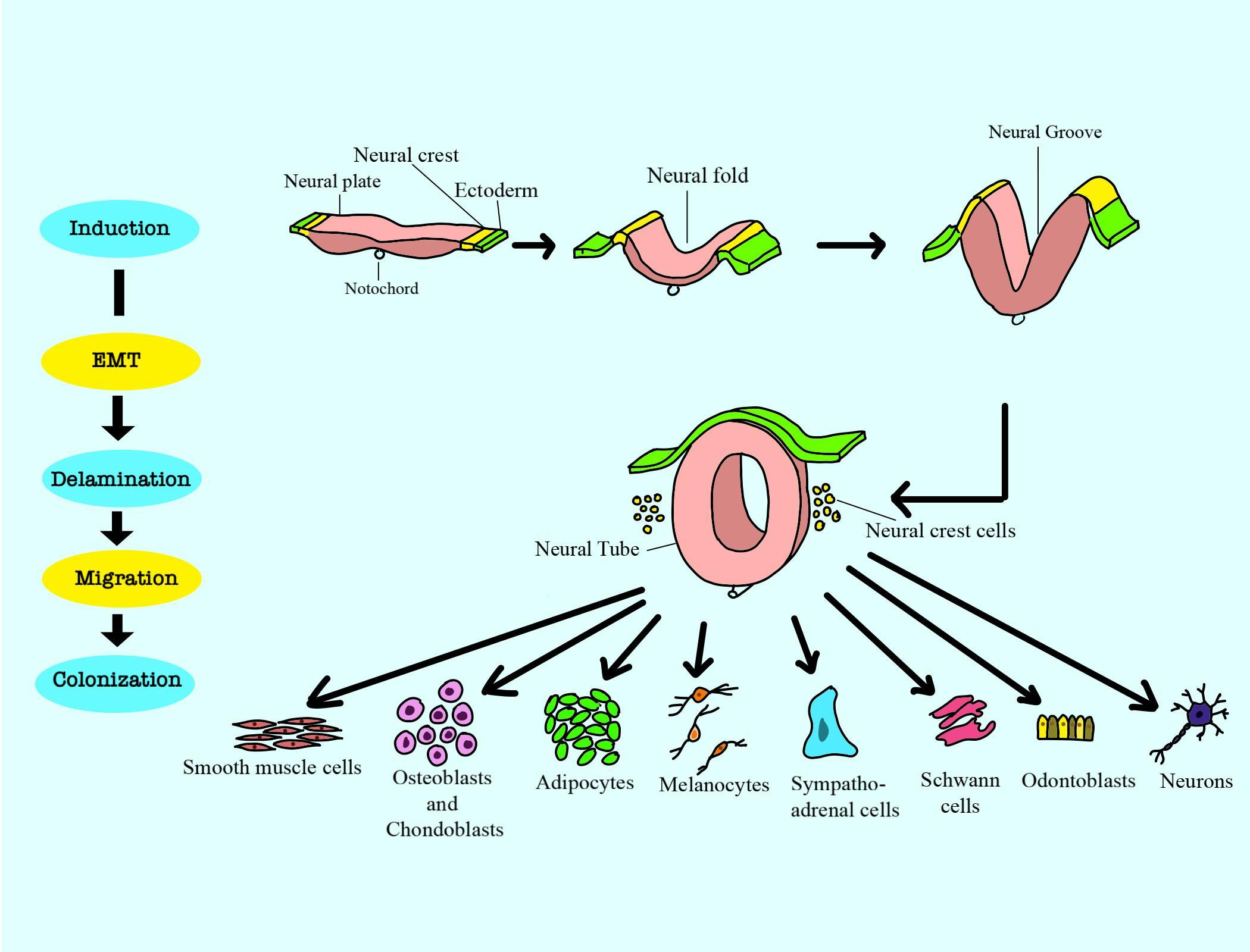
- These cells are a transient embryonic progenitor population that emerges from the dorsal neural tube during early development.
- Ectoderm cells can give rise to diverse cells including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage, bone, smooth muscle, neurons, both peripheral and enteric.
- These cells that migrate through the rostral half of somites differentiate into sensory and sympathetic neurons of the peripheral nervous system. They would then differentiate into pigment cells of the dermis.
- They contribute to key vertebrate- specific features.
Additional information:
- Nervous system of a frog includes two olfactory lobes, two cerebral hemispheres, a pineal body, two optic lobes, a cerebellum, and a medulla oblongata.
- One of the notable features of frogs is that they possess spines and spinal cord just like humans.
- Frogs are capable of drinking water through the skin.
- Frogs have the largest brain to body ratio among all other amphibians.
So the answer is ‘D. Neural crest cells’.
Note: Sympathetic ganglia play an important role in delivering information to the body about stress and impending danger and they are responsible for the familiar fight or flight response. Neural plate formation is the first step of neurulation and it is specified to become a neural ectoderm.
Complete answer:
- Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells that are present only in vertebrates. These cells arise from the embryonic ectoderm cell layer.

- These cells are a transient embryonic progenitor population that emerges from the dorsal neural tube during early development.
- Ectoderm cells can give rise to diverse cells including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage, bone, smooth muscle, neurons, both peripheral and enteric.
- These cells that migrate through the rostral half of somites differentiate into sensory and sympathetic neurons of the peripheral nervous system. They would then differentiate into pigment cells of the dermis.
- They contribute to key vertebrate- specific features.
Additional information:
- Nervous system of a frog includes two olfactory lobes, two cerebral hemispheres, a pineal body, two optic lobes, a cerebellum, and a medulla oblongata.
- One of the notable features of frogs is that they possess spines and spinal cord just like humans.
- Frogs are capable of drinking water through the skin.
- Frogs have the largest brain to body ratio among all other amphibians.
So the answer is ‘D. Neural crest cells’.
Note: Sympathetic ganglia play an important role in delivering information to the body about stress and impending danger and they are responsible for the familiar fight or flight response. Neural plate formation is the first step of neurulation and it is specified to become a neural ectoderm.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




