
The function of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is
(a)Translation
(b)Transcription
(c)DNA amplification
(d)None of the above
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: A technique to make many copies of a specific region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism) is known as Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is a revolutionary method that was developed by Karry Mullis in the 1980s.
Complete step-by-step answer:
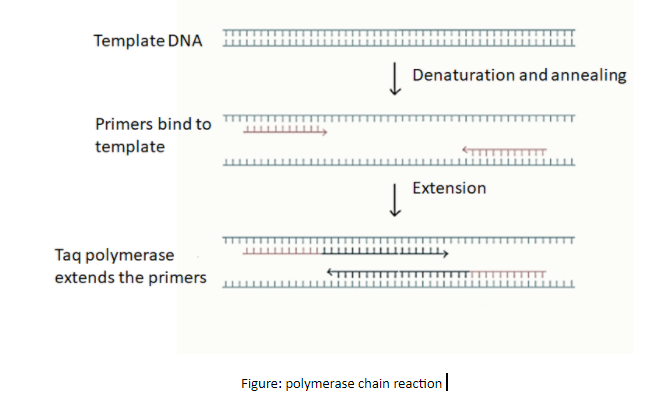
The function of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is DNA amplification. PCR is a technique to amplify the gene of interest is usually three steps:
Denaturation: Thermal cycle to separate or denature the DNA strands, this provides a single-stranded template for the next step.
Annealing: Cool the reaction so the primers (a short nucleic acid sequence that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis) can bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded template DNA.
Polymerization: An extension of primer into a complete DNA strand complementary to the template strand.
PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, and DNA primers. PCR practical applications and is routinely used in DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
So, the correct answer is ‘DNA amplification’.
Note: The three basic steps in PCR usually repeat 20 to 40 times in a typical PCR reaction, which generally takes a few hours or within an hour depending on certain high-speed machines. If the reaction is efficient, the target region can go from just one or a few copies to millions.
Translation- The process of synthesis of protein using mRNA nucleotide sequence as the template is known as translation and it occurs in the cytoplasm.
Transcription- The process of mRNA synthesis using DNA coding strand as the template is known as transcription and it occurs in the nucleus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The function of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is DNA amplification. PCR is a technique to amplify the gene of interest is usually three steps:
Denaturation: Thermal cycle to separate or denature the DNA strands, this provides a single-stranded template for the next step.
Annealing: Cool the reaction so the primers (a short nucleic acid sequence that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis) can bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded template DNA.
Polymerization: An extension of primer into a complete DNA strand complementary to the template strand.
PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, and DNA primers. PCR practical applications and is routinely used in DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
So, the correct answer is ‘DNA amplification’.

Note: The three basic steps in PCR usually repeat 20 to 40 times in a typical PCR reaction, which generally takes a few hours or within an hour depending on certain high-speed machines. If the reaction is efficient, the target region can go from just one or a few copies to millions.
Translation- The process of synthesis of protein using mRNA nucleotide sequence as the template is known as translation and it occurs in the cytoplasm.
Transcription- The process of mRNA synthesis using DNA coding strand as the template is known as transcription and it occurs in the nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




