
The function of mesosome in prokaryotes is -
(a)Aerobic respiration
(b)Cell wall formation
(c)Both (a) and (b)
(d)${ N }_{ 2 }$ fixation
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint The mesosome is an inward fold of the cell plasma membrane. It has been observed to have functions similar to that of organelles involved in cell wall formation and those that are present in mitochondria.
Complete answer:
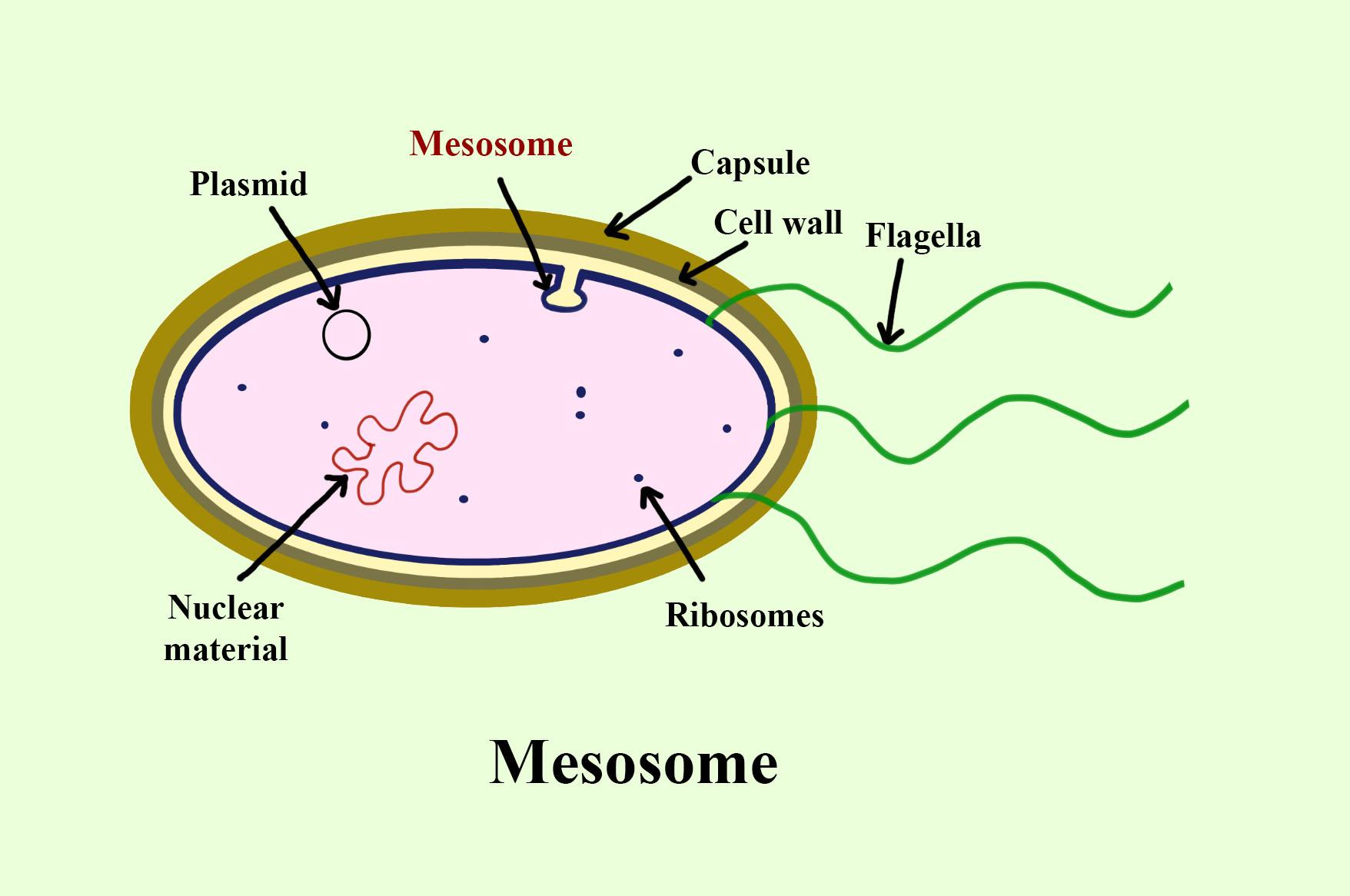
- The mesosome is an inward-folding extension or an invagination of the plasma membrane into the cytoplasm in prokaryotes. The extensions exist as vesicles, tubules, and lamellae.
- The mesosome has roles in aerobic respiration and cell wall formation in prokaryotes. They are also known as chondroid.
- The main function of the mesosome is to increase the surface area of the cell, thus helping in aerobic respiration. It also serves as a site for chromosome replication and oxidative photophosphorylation. These functions can be considered analogous to the cristae in the mitochondria.
- The mesosome is found in Gram-positive bacteria.
Additional information: - The function of mesosomes has been debated in the last few decades, as data was found stating that mesosomes do not occur in living cells and are artifacts formed due to damage to the cell membrane during chemical fixation. This was further proven through cryo-electron microscopy.
- They have also been observed in bacteria that have been treated with some antibiotics.
- Due to these observations, the data about the function of mesosomes is still inconclusive.
So, the correct answer is ‘Both (a) and (b)’.
Note: - Mesosomes were previously referred to as peripheral bodies.
- Mesosomes are not found in eukaryotes.
- Other photosynthetic prokaryotes like cyanobacteria also have similar extensions called chromatophores that contain pigments.
Complete answer:
- The mesosome is an inward-folding extension or an invagination of the plasma membrane into the cytoplasm in prokaryotes. The extensions exist as vesicles, tubules, and lamellae.
- The mesosome has roles in aerobic respiration and cell wall formation in prokaryotes. They are also known as chondroid.
- The main function of the mesosome is to increase the surface area of the cell, thus helping in aerobic respiration. It also serves as a site for chromosome replication and oxidative photophosphorylation. These functions can be considered analogous to the cristae in the mitochondria.
- The mesosome is found in Gram-positive bacteria.
Additional information: - The function of mesosomes has been debated in the last few decades, as data was found stating that mesosomes do not occur in living cells and are artifacts formed due to damage to the cell membrane during chemical fixation. This was further proven through cryo-electron microscopy.
- They have also been observed in bacteria that have been treated with some antibiotics.
- Due to these observations, the data about the function of mesosomes is still inconclusive.

So, the correct answer is ‘Both (a) and (b)’.
Note: - Mesosomes were previously referred to as peripheral bodies.
- Mesosomes are not found in eukaryotes.
- Other photosynthetic prokaryotes like cyanobacteria also have similar extensions called chromatophores that contain pigments.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




