
The formation of diethyl ether from ethanol is catalysed by:
(A) \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]
(B) \[{\rm{Al}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
(C) \[{\rm{Cu}}\]
(D) \[{\rm{Ni}}\]
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Diethyl ether can be found if we replace one hydrogen atom of ethanol. This hydrogen atom should be ionizable or replaceable. We also know that alcohol and ether are functional isomers.
Step by step answer:Diethyl ether is formed by the nucleophilic substitution reaction. When ethanol is treated with a second mole of ethanol in the presence of sulphuric acid, diethyl ether is formed by the dehydration process of one of the ethanol molecules.
The reaction occurs as shown below.
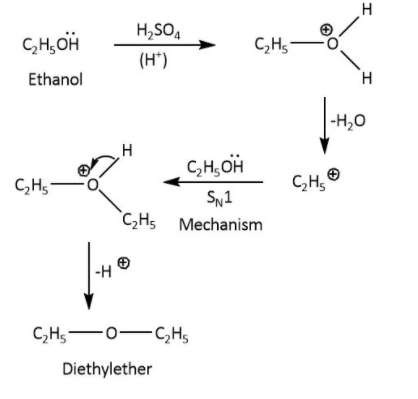
In this reaction, the mechanism is followed by the dehydration of ethanol molecules followed by unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. First, the ethanol is treated in the presence of any acid (\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) which can give proton. So the water molecule is eliminated from ethanol and carbocation is generated. Now, the second molecule of ethanol will act as a nucleophile and attacks at the electrophilic carbon this process is known as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution. After this step we will get our final product as diethyl ether as shown in the above mechanism.
Therefore, the correct option is option (A).
Note: The above reaction is very sensitive for temperature. If the temperature is \[{\rm{150}}{\;^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\] or less then only our product will be ether. If the temperature is more than \[{\rm{150}}{\;^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\] then ethylene will be the product.
Diethyl ether can also be produced by Williamson ether synthesis in which ethanol is treated with any base and then the ethoxide is formed. In this case ethoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at ethyl chloride. So, the diethyl ether is formed.
Step by step answer:Diethyl ether is formed by the nucleophilic substitution reaction. When ethanol is treated with a second mole of ethanol in the presence of sulphuric acid, diethyl ether is formed by the dehydration process of one of the ethanol molecules.
The reaction occurs as shown below.

In this reaction, the mechanism is followed by the dehydration of ethanol molecules followed by unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. First, the ethanol is treated in the presence of any acid (\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]) which can give proton. So the water molecule is eliminated from ethanol and carbocation is generated. Now, the second molecule of ethanol will act as a nucleophile and attacks at the electrophilic carbon this process is known as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution. After this step we will get our final product as diethyl ether as shown in the above mechanism.
Therefore, the correct option is option (A).
Note: The above reaction is very sensitive for temperature. If the temperature is \[{\rm{150}}{\;^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\] or less then only our product will be ether. If the temperature is more than \[{\rm{150}}{\;^{\rm{o}}}{\rm{C}}\] then ethylene will be the product.
Diethyl ether can also be produced by Williamson ether synthesis in which ethanol is treated with any base and then the ethoxide is formed. In this case ethoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at ethyl chloride. So, the diethyl ether is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




