
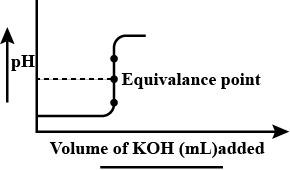
The following curve represents the titration curve of HCL against KOH. The pH at equivalence point is
Examine the titration curve below and answer the question
(A) 3
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8

Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: The process of titration is a chemical analysis which is used to find out the concentration of unknown solution by adding a solution of known concentration. The known solution is known as titrant and the unknown solution is known as analyte. Equivalent point is the point where the concentration of the acid and base is equivalent. Strong acids and bases neutralize each other completely at equivalence points.
Complete Step By Step Solution
HCl is known as hydrochloric acid which is a strong acid i.e. it dissociates completely into its ions. It is being titrated against KOH which is a strong base so it will also dissociate completely into its ions.
Dissociation of HCl: $ \text{HCl}\rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^{+}}+\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}} $
And dissociation of KOH is as- $ \text{KOH}\rightleftharpoons {{\text{K}}^{+}}+\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}} $
Acids release hydrogen ions and bases release hydroxyl ions. At equivalence point the concentration of acids and bases is the same i.e. equivalent as the name indicates. Strong acids and strong bases undergo complete neutralization reaction at equivalence point. The pH for a completely neutral reaction is 7. So, the titration curve given above represents the pH value 7 at the equivalence point. Therefore, the correct choice is (C).
The neutralization reaction of HCl and KOH is given as $ \text{HCl}+\text{KOH}\rightleftharpoons \text{KCl}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O} $
The end products of a neutralization reaction are always salt and water.
Additional Information
Equivalent Point is that point at which the concentration of titrant being added is enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution. Indicator is added to know the equivalent point for the titration. The indicator shows a color change according to its properties and thus the equivalent point is determined. Indicator helps in determining the pH of the solution. It is quite useful in the titration of strong acids and weak bases or weak acids and strong bases which do not completely dissociate into their ions due to which the solution is either acidic or basic. But in the titration of HCl against KOH, one is strong acid and the other is strong base due to which complete neutralization occurs and the solution becomes neutral i.e. neither acidic nor basic that’s why the pH of the resulting solution becomes 7.
Note
The pH value tells us about the power of hydrogen or simply the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. The range of the pH scale is from 0-14, the scale shows less than 7 in acidic medium and greater than 7 in basic medium and 7 for neutral medium. At an equivalence point, only salt and water are present in the solution. Potassium chloride (KCl) is the salt formed in the titration of HCl and KOH.
Complete Step By Step Solution
HCl is known as hydrochloric acid which is a strong acid i.e. it dissociates completely into its ions. It is being titrated against KOH which is a strong base so it will also dissociate completely into its ions.
Dissociation of HCl: $ \text{HCl}\rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^{+}}+\text{C}{{\text{l}}^{-}} $
And dissociation of KOH is as- $ \text{KOH}\rightleftharpoons {{\text{K}}^{+}}+\text{O}{{\text{H}}^{-}} $
Acids release hydrogen ions and bases release hydroxyl ions. At equivalence point the concentration of acids and bases is the same i.e. equivalent as the name indicates. Strong acids and strong bases undergo complete neutralization reaction at equivalence point. The pH for a completely neutral reaction is 7. So, the titration curve given above represents the pH value 7 at the equivalence point. Therefore, the correct choice is (C).
The neutralization reaction of HCl and KOH is given as $ \text{HCl}+\text{KOH}\rightleftharpoons \text{KCl}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O} $
The end products of a neutralization reaction are always salt and water.
Additional Information
Equivalent Point is that point at which the concentration of titrant being added is enough to completely neutralize the analyte solution. Indicator is added to know the equivalent point for the titration. The indicator shows a color change according to its properties and thus the equivalent point is determined. Indicator helps in determining the pH of the solution. It is quite useful in the titration of strong acids and weak bases or weak acids and strong bases which do not completely dissociate into their ions due to which the solution is either acidic or basic. But in the titration of HCl against KOH, one is strong acid and the other is strong base due to which complete neutralization occurs and the solution becomes neutral i.e. neither acidic nor basic that’s why the pH of the resulting solution becomes 7.
Note
The pH value tells us about the power of hydrogen or simply the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution. The range of the pH scale is from 0-14, the scale shows less than 7 in acidic medium and greater than 7 in basic medium and 7 for neutral medium. At an equivalence point, only salt and water are present in the solution. Potassium chloride (KCl) is the salt formed in the titration of HCl and KOH.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




