
The final electron acceptor during the electron transport chain in respiration is
(a) Hydrogen.
(b) Oxygen.
(c) FMN.
(d) Ubiquinone.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: The final electron acceptor during the electron transport chain in respiration is a gas very crucial for inspiration in human beings. It is a chemical element with the symbol ‘O’ and an atomic number eight.
Complete answer:
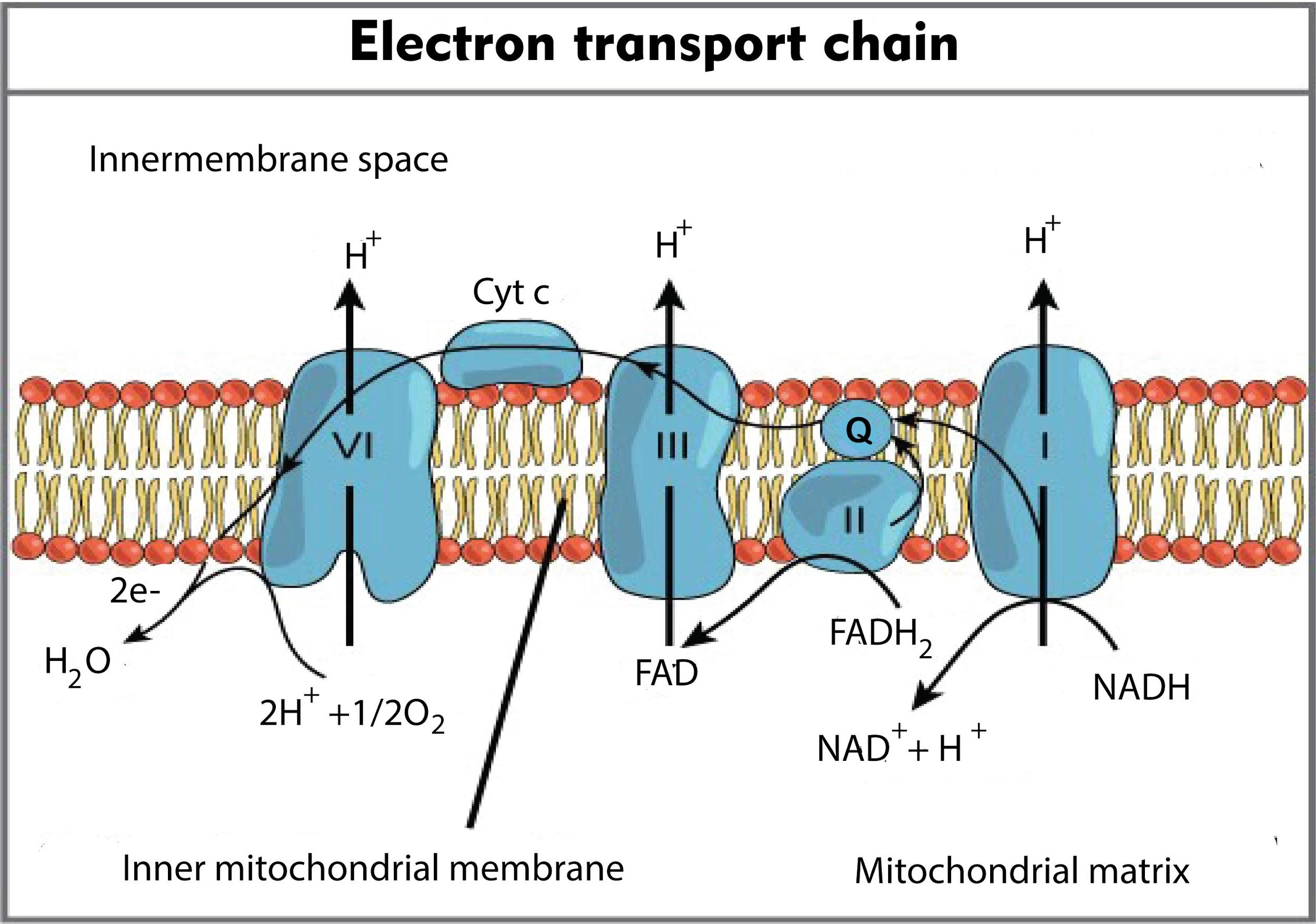
The final electron acceptor during the electron transport chain in respiration is oxygen. We know that there are two pathways in cellular respiration called glycolysis and citric acid cycle that generate ATP. However, most of the ATP generated during the catabolic breakdown of glucose is not directly from these pathways. Instead, it is derived from a process that involves moving of electrons through a series of electron transporters that undergo redox reactions: the electron transport chain(ETC/ETS).
Now let's study briefly about the electron transport chain.
This is the last stage of cellular respiration. It takes place within the molecules embedded in the mitochondrial membrane. The protons and electrons generated from the products of Krebs cycle are taken up by the first molecule of the electron transport chain. The electrons are then passed from molecule to molecule to finally let them react with oxygen and protons giving rise to water. The final reaction can not take place without oxygen and in the absence of this step ATP cannot be generated.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Oxygen.’
Note:
- The complex one, in the electron transport chain, is composed of flavin mononucleotide (FMN). It is a derivative of Vitamin B2, also called riboflavin.
- In the fourth complex of the electron transport chain, the reduced oxygen takes up hydrogen ions from the surrounding medium to give rise to water.
- Ubiquinone is a lipid- soluble substance that accepts electrons from complex one and two.
Complete answer:
The final electron acceptor during the electron transport chain in respiration is oxygen. We know that there are two pathways in cellular respiration called glycolysis and citric acid cycle that generate ATP. However, most of the ATP generated during the catabolic breakdown of glucose is not directly from these pathways. Instead, it is derived from a process that involves moving of electrons through a series of electron transporters that undergo redox reactions: the electron transport chain(ETC/ETS).
Now let's study briefly about the electron transport chain.
This is the last stage of cellular respiration. It takes place within the molecules embedded in the mitochondrial membrane. The protons and electrons generated from the products of Krebs cycle are taken up by the first molecule of the electron transport chain. The electrons are then passed from molecule to molecule to finally let them react with oxygen and protons giving rise to water. The final reaction can not take place without oxygen and in the absence of this step ATP cannot be generated.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Oxygen.’
Note:
- The complex one, in the electron transport chain, is composed of flavin mononucleotide (FMN). It is a derivative of Vitamin B2, also called riboflavin.
- In the fourth complex of the electron transport chain, the reduced oxygen takes up hydrogen ions from the surrounding medium to give rise to water.
- Ubiquinone is a lipid- soluble substance that accepts electrons from complex one and two.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




