
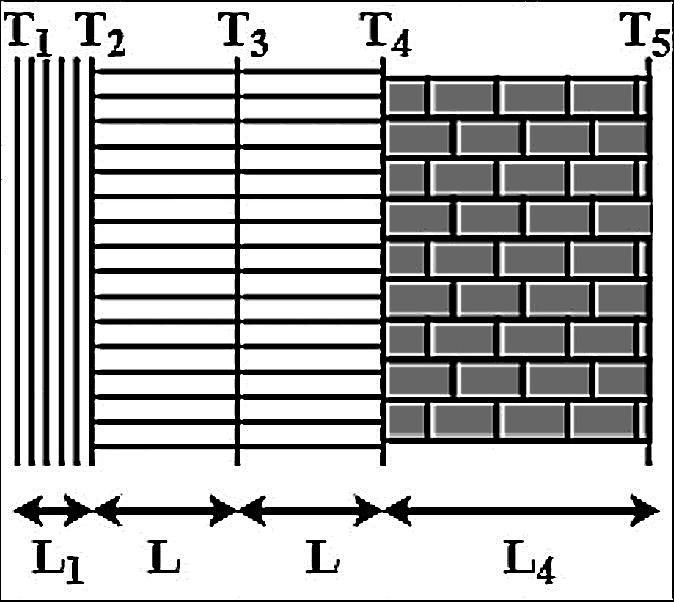
The figure shows the cross - section of the outer wall of a house built in a hill - resort to keep the house insulated from the freezing temperature of outside. The wall consists of teak wood of thickness ${L}_{1}$ and brick of thickness ($L=5{ L }_{ 1 }$). sandwiching two layers of an unknown material with identical thermal conductivities and thickness. The thermal conductivity of teak wood is ${K}_{1}$ and that of brick is (${ K }_{ 4 }=5K$). Heat conduction through the wall has reached a steady state with the temperature of three surfaces being known. (${ T }_{ 1 }=25°C$, ${ T }_{ 2 }=20°C$ and ${ T }_{ 5 }=-20°C$). Find the interface temperature ${ T }_{ 4 }$ and ${ T }_{ 3 }$.

Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for thermal resistance. Using the formula, find the thermal resistance of wood and brick walls. You will get resistance throughout to be the same. So, use the formula for thermal current. Equate the thermal current of each section. Substitute the given values and find the unknown interface temperatures i.e. ${ T }_{ 4 }$ and ${ T }_{ 3 }$.
Complete answer:
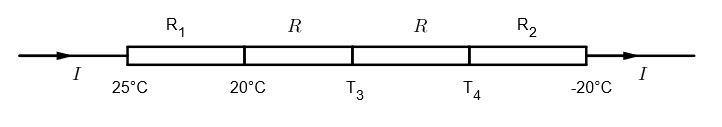
Let the area of interface be A.
Thermal Resistance is given by,
$R=\dfrac { L }{ KA }$
Thus, Thermal Resistance of wood is
${ R }_{ 1 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 1 } }{ { K }_{ 1 }A }$ …(1)
And, thermal resistance of brick wall is
${ R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 4 } }{ { K }_{ 4 }A }$ …(2)
But, the thickness of brick is 5 times the thickness of wood and thermal conductivity of brick is 5 times the thermal conductivity of wood.
Thus, equation. (2) becomes,
${ R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { 5L }_{ 1 } }{ { 5K }_{ 1 }A }$
${ \Rightarrow R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 1 } }{ { K }_{ 1 }A }$ …(3)
From the equation. (1) and equation. (3),
${ R }_{ 1 }={ R }_{ 2 }$
Let the thermal resistance between each sandwich layer be R. As the resistance thought is same, thermal current through each wall is also the same.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac { 25-20 }{ { R }_{ 1 } } =\dfrac { 20-{ T }_{ 3 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 4 }+20 }{ { R }_{ 1 } }$
$\Rightarrow 25-20={ T }_{ 4 }+20$
$\Rightarrow { T }_{ 4 }=25-20-20$
$\Rightarrow { T }_{ 4 }=-15°C$ …(4)
Also, $ \dfrac { 20-{ T }_{ 3 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 } }{ R }$
$ \Rightarrow 20-{ T }_{ 3 }={ T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 }$
$ \Rightarrow { T }_{ 3 }=\cfrac { 25+{ T }_{ 4 } }{ 2 }$ …(5)
Substituting equation. (4) in equation. (5) we get,
$ \Rightarrow { T }_{ 3 }=\cfrac { 20-15 }{ 2 }$
$ { T }_{ 3 }=2.5°C$
Hence, the interface temperature ${ T }_{ 4 }$ and ${ T }_{ 3 }$ are $-15°C$ and $2.5°C$ respectively.
Note:
Thermal Conductivity denoted by K is the property of the material indicating its ability to conduct heat. Thermal conductivity is reciprocal of thermal resistivity. Heat transfer in materials of low thermal conductivity occurs at a lower rate as compared to the materials of high thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity is an intrinsic property of the materials. It does not depend on the dimensions of the material. It depends on the temperature, density and moisture content of the material.
Complete answer:

Let the area of interface be A.
Thermal Resistance is given by,
$R=\dfrac { L }{ KA }$
Thus, Thermal Resistance of wood is
${ R }_{ 1 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 1 } }{ { K }_{ 1 }A }$ …(1)
And, thermal resistance of brick wall is
${ R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 4 } }{ { K }_{ 4 }A }$ …(2)
But, the thickness of brick is 5 times the thickness of wood and thermal conductivity of brick is 5 times the thermal conductivity of wood.
Thus, equation. (2) becomes,
${ R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { 5L }_{ 1 } }{ { 5K }_{ 1 }A }$
${ \Rightarrow R }_{ 2 }=\dfrac { { L }_{ 1 } }{ { K }_{ 1 }A }$ …(3)
From the equation. (1) and equation. (3),
${ R }_{ 1 }={ R }_{ 2 }$
Let the thermal resistance between each sandwich layer be R. As the resistance thought is same, thermal current through each wall is also the same.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac { 25-20 }{ { R }_{ 1 } } =\dfrac { 20-{ T }_{ 3 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 4 }+20 }{ { R }_{ 1 } }$
$\Rightarrow 25-20={ T }_{ 4 }+20$
$\Rightarrow { T }_{ 4 }=25-20-20$
$\Rightarrow { T }_{ 4 }=-15°C$ …(4)
Also, $ \dfrac { 20-{ T }_{ 3 } }{ R } =\dfrac { { T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 } }{ R }$
$ \Rightarrow 20-{ T }_{ 3 }={ T }_{ 3 }-{ T }_{ 4 }$
$ \Rightarrow { T }_{ 3 }=\cfrac { 25+{ T }_{ 4 } }{ 2 }$ …(5)
Substituting equation. (4) in equation. (5) we get,
$ \Rightarrow { T }_{ 3 }=\cfrac { 20-15 }{ 2 }$
$ { T }_{ 3 }=2.5°C$
Hence, the interface temperature ${ T }_{ 4 }$ and ${ T }_{ 3 }$ are $-15°C$ and $2.5°C$ respectively.
Note:
Thermal Conductivity denoted by K is the property of the material indicating its ability to conduct heat. Thermal conductivity is reciprocal of thermal resistivity. Heat transfer in materials of low thermal conductivity occurs at a lower rate as compared to the materials of high thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity is an intrinsic property of the materials. It does not depend on the dimensions of the material. It depends on the temperature, density and moisture content of the material.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




