
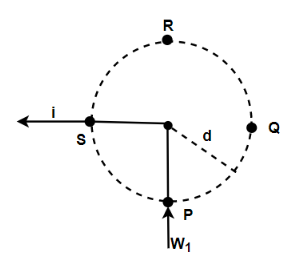
The figure shows a long wire bent at the middle to form a right angle. Show that the magnitudes of the magnetic fields at the points $P,Q,R{\text{ and S}}$ are equal and find this magnitude.

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: So in this question, we have to show the magnetic fields at each point should be equal. And the formula for the magnetic field for the semi finite will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$ . Also, the wires in this will be treated as the semi-infinite straight current-carrying conductor. So by using this relation we will answer this question.
Formula used
Magnetic field formula for the semi finite wire is given by,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field, ${\mu _ \circ }$ is the permeability of the free space, $d$ is the distance, $i$ is the current.
Complete step by step answer:
So firstly we will find the magnetic field at the point $P$ and is represented by ${B_P}$ since the first wire is at the point $P$ . Since all the points lie along a circle having the radius $d$ . Hence, $R\& Q$ both will lie at a distance $d$ from the wire. So the magnetic field at $B$ will be the same in magnitude.
So there will not be any magnetic field for this. But for the second wire at the point, $P$ the magnetic field will be $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Now we will check the magnetic field at $Q$ , since the magnetic field due to the second wire is zero as the point lies on the wire.
So, the magnetic field due to the first wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Similarly, the magnetic field at $R$ a point due to the first wire will be zero.
So, the magnetic field due to the second wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Now we will check at point $S$
The magnetic field at $S$ a point due to the second wire will be zero.
So, the magnetic field due to the first wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
So now we have to find the magnitude,
Since we can see that the magnetic field is the same at all the points due to the two-wire.
Hence, the magnitude will also be the same.
Note:
The magnitude of any vector will be calculated by taking the square root of the number. So whenever we have to find the magnitude of any number of vectors then we will first take the square root of the number and if the number is more than one then the addition is done first and then we can solve it.
Formula used
Magnetic field formula for the semi finite wire is given by,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field, ${\mu _ \circ }$ is the permeability of the free space, $d$ is the distance, $i$ is the current.
Complete step by step answer:
So firstly we will find the magnetic field at the point $P$ and is represented by ${B_P}$ since the first wire is at the point $P$ . Since all the points lie along a circle having the radius $d$ . Hence, $R\& Q$ both will lie at a distance $d$ from the wire. So the magnetic field at $B$ will be the same in magnitude.
So there will not be any magnetic field for this. But for the second wire at the point, $P$ the magnetic field will be $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Now we will check the magnetic field at $Q$ , since the magnetic field due to the second wire is zero as the point lies on the wire.
So, the magnetic field due to the first wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Similarly, the magnetic field at $R$ a point due to the first wire will be zero.
So, the magnetic field due to the second wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
Now we will check at point $S$
The magnetic field at $S$ a point due to the second wire will be zero.
So, the magnetic field due to the first wire in the case of semi-infinite it will be given by $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }i}}{{4\pi d}}$
So now we have to find the magnitude,
Since we can see that the magnetic field is the same at all the points due to the two-wire.
Hence, the magnitude will also be the same.
Note:
The magnitude of any vector will be calculated by taking the square root of the number. So whenever we have to find the magnitude of any number of vectors then we will first take the square root of the number and if the number is more than one then the addition is done first and then we can solve it.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




