
The figure shows a circuit
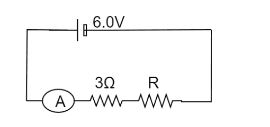
When the circuit is switched on the ammeter reads $0.5A$
(a) Calculate the value of an unknown resistor $R$.
(b) Calculate the charge passing through the $3 \Omega$ resistor in $120\,s$.
(c) Calculate the power dissipated in the $3 \Omega $ resistor.

Answer
479.4k+ views
Hint: for solving part (a) we will use ohm’s law. and for resistors in series total resistance in the circuit is the sum of the resistance produced by all the resistors . for part (b) using the current and charge relation we will find the charge. for part (c) use the formula for power dissipation.
Formula used:
$V = IR$ (ohm’s law)
Where $V$ is the voltage $I$ is current and $R$ is the resistance of the circuit.
$I = \dfrac{q}{t}$
Where $q$ is the charge and $t$ is the time
$P = {I^2}R$
Where $P$ is the power dissipated
Complete step by step answer:
(a) We have been given ammeter reading so current $I = 0.5A$ and $V = 6V$. According to ohm's law, the current in a conductor between two points is proportional to the voltage across these two points.
$V = IR'$..........( here $R'$ is the total resistance)
$ \Rightarrow 6 = 0.5 + R$
$ \Rightarrow R = 12\Omega $
In the given circuit the resistor let ${R_1} = 3\Omega $ and unknown resistance be $R$ . as they are in series
So, $R' = {R_1} + R$
$ \Rightarrow 12\Omega = 3\Omega + R$
$ \therefore R = 9\Omega $
(b) We have been given time $t = 120\,s$ so current will be given as,
$I = \dfrac{q}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.5\,A = \dfrac{q}{{120\,s}}$
$ \therefore q = 6\,C$
(c) For the resistance of $3\Omega $ power dissipated will be
$P = {I^2}R$
$ \Rightarrow P = {\left( {0.5} \right)^2}(3)$
$ \therefore P = 0.75\,watt$
Note: if the resistors are in parallel total resistance is found out as $\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$. We can see in part B that the charge flowing through both the resistors is the same because in series combination current flowing through the different resistors is the same. if there was a parallel combination of resistors we have to find the charge flowing through different resistors separately.
Formula used:
$V = IR$ (ohm’s law)
Where $V$ is the voltage $I$ is current and $R$ is the resistance of the circuit.
$I = \dfrac{q}{t}$
Where $q$ is the charge and $t$ is the time
$P = {I^2}R$
Where $P$ is the power dissipated
Complete step by step answer:
(a) We have been given ammeter reading so current $I = 0.5A$ and $V = 6V$. According to ohm's law, the current in a conductor between two points is proportional to the voltage across these two points.
$V = IR'$..........( here $R'$ is the total resistance)
$ \Rightarrow 6 = 0.5 + R$
$ \Rightarrow R = 12\Omega $
In the given circuit the resistor let ${R_1} = 3\Omega $ and unknown resistance be $R$ . as they are in series
So, $R' = {R_1} + R$
$ \Rightarrow 12\Omega = 3\Omega + R$
$ \therefore R = 9\Omega $
(b) We have been given time $t = 120\,s$ so current will be given as,
$I = \dfrac{q}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.5\,A = \dfrac{q}{{120\,s}}$
$ \therefore q = 6\,C$
(c) For the resistance of $3\Omega $ power dissipated will be
$P = {I^2}R$
$ \Rightarrow P = {\left( {0.5} \right)^2}(3)$
$ \therefore P = 0.75\,watt$
Note: if the resistors are in parallel total resistance is found out as $\dfrac{1}{R} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$. We can see in part B that the charge flowing through both the resistors is the same because in series combination current flowing through the different resistors is the same. if there was a parallel combination of resistors we have to find the charge flowing through different resistors separately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




