
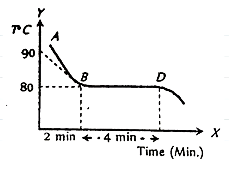
The figure given below shows the cooling curve of pure wax material after heating, it cools from A to B and solidifies along BD. If L and C are respective values of latent heat and the specific heat of the liquid wax, the ratio \[\dfrac{L}{C}\] is
A. 40
B. 80
C. 100
D. 20

Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint: We know that \[Q = ms\Delta t\] here m is representing the mass of the wax material and \[\Delta t\] is representing the change in temperature of the wax material during cooling. We will find the value of Q for curve AB and BD respectively and equate them to get the ratio of \[\dfrac{L}{C}\].
Complete Answer: It is given in the question that in the given figure the curve is showing the cooling of nature of pure wax material after cooling for 2 minutes from \[{90^{\rm O}}C\] to \[{80^{\rm O}}C\] the wax material solidifies for next 4 minutes. The cooling of the wax material is shown by the curve AB and the solidification of wax material is shown by the curve BD. The specific of the wax material is represented by C and the latent heat of the wax material is represented by L, then we have to find the ratio of latent heat and specific heat of the wax material, i.e., \[\dfrac{L}{C}\].
Let us assume that the rate of cooling of the given wax material be Q. Please Note that the rate of cooling is constant for the whole process.
We know that \[Q = ms\Delta t\] here m is representing the mass of the wax material and \[\Delta t\] is representing the change in temperature of the wax material during cooling.
The curve AB is representing the cooling of wax material, the specific heat of the cooling of wax material is given by C, and temperature change \[\Delta t\] is given by \[{90^{\rm O}}C - {80^{\rm O}}C\] . On putting all the values, we get-
\[Q = mC\left( {90 - 80} \right)\] for 2 minutes … (1)
Similarly, we know that the curve BD is representing the latent heat of fusion during the solidification of wax material for the next \[4\]minutes. It is represented by \[Q = mL\] … (2)
Before equating the equation (1) and (2) we will multiply the equation (1) by 2 because the process of solidification takes twice as long as the cooling process. We get-
\[Q = 2mC\left( {90 - 80} \right)\] … (3)
On comparing equation (2) and (3) we get-
\[2mC\left( {90 - 80} \right) = mL\]
On cancelling the similar terms from both sides, we get-
\[2C\left( {90 - 80} \right) = L\]
\[2C\left( {10} \right) = L\]
\[20C = L\]
On dividing both the sides with C we get-
\[\dfrac{L}{C} = 20\].
Thus, the ratio of \[\dfrac{L}{C}\] is equal to 20.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note: One can make a mistake by assuming the change in temperature during solidification as \[{0^{\rm O}}C\] and writing the value of Q for curve BD \[Q = mL\left( 0 \right)\] . It is Noted that the c = change in temperature is constant during solidification and it is not taken as zero for the calculation of Q for the curve BD.
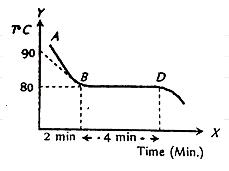
Complete Answer: It is given in the question that in the given figure the curve is showing the cooling of nature of pure wax material after cooling for 2 minutes from \[{90^{\rm O}}C\] to \[{80^{\rm O}}C\] the wax material solidifies for next 4 minutes. The cooling of the wax material is shown by the curve AB and the solidification of wax material is shown by the curve BD. The specific of the wax material is represented by C and the latent heat of the wax material is represented by L, then we have to find the ratio of latent heat and specific heat of the wax material, i.e., \[\dfrac{L}{C}\].

Let us assume that the rate of cooling of the given wax material be Q. Please Note that the rate of cooling is constant for the whole process.
We know that \[Q = ms\Delta t\] here m is representing the mass of the wax material and \[\Delta t\] is representing the change in temperature of the wax material during cooling.
The curve AB is representing the cooling of wax material, the specific heat of the cooling of wax material is given by C, and temperature change \[\Delta t\] is given by \[{90^{\rm O}}C - {80^{\rm O}}C\] . On putting all the values, we get-
\[Q = mC\left( {90 - 80} \right)\] for 2 minutes … (1)
Similarly, we know that the curve BD is representing the latent heat of fusion during the solidification of wax material for the next \[4\]minutes. It is represented by \[Q = mL\] … (2)
Before equating the equation (1) and (2) we will multiply the equation (1) by 2 because the process of solidification takes twice as long as the cooling process. We get-
\[Q = 2mC\left( {90 - 80} \right)\] … (3)
On comparing equation (2) and (3) we get-
\[2mC\left( {90 - 80} \right) = mL\]
On cancelling the similar terms from both sides, we get-
\[2C\left( {90 - 80} \right) = L\]
\[2C\left( {10} \right) = L\]
\[20C = L\]
On dividing both the sides with C we get-
\[\dfrac{L}{C} = 20\].
Thus, the ratio of \[\dfrac{L}{C}\] is equal to 20.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note: One can make a mistake by assuming the change in temperature during solidification as \[{0^{\rm O}}C\] and writing the value of Q for curve BD \[Q = mL\left( 0 \right)\] . It is Noted that the c = change in temperature is constant during solidification and it is not taken as zero for the calculation of Q for the curve BD.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




