
The equipotential surface of an electric dipole is
A. Sphere whose centre coincides with the centre of the electric dipole
B. A plane surface inclined at an angle of 45° with the axis of the electric dipole
C. A plane surface passing through the centre of the electric dipole and perpendicular to the axis of the electric dipole
D. Any plane surface parallels the axis of the electric dipole.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The equipotential surface of an electric dipole is an imaginary surface around a point charge of an electric dipole, which has equal potential at every point.
Complete step by step answer:
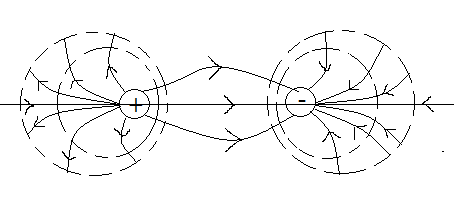
The equipotential surfaces of an electric dipole are shown in the figure since the distance of each point on a plane passing through the centre of the axis of the electric dipole is equal to the potential throughout the plane is zero. Hence it is over one possible equipotential surface.
Figure: (Dotted lines are representing the equipotential surface
Some of the points to be remembered regarding the equipotential surface are as follows:
• Potential energy U = constant for point charge q on Equipotential surface.
• The surface of a conductor at equilibrium is at the equipotential surface.
• Electric field vectors (tangents to field lines) are perpendicular to an equipotential surface.
• Electrostatic force does zero work on point Charge q moving on the equipotential surface.
• The electric field exerts a force on a positive (negative) point charge q in the direction of steepest Potential drop (rise).
• When a positive (negative) point charge q moves from a region of high potential to a region of low potential, the Electric field does positive (negative) work on it. In the process, the potential energy decreases (increases).
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
An equipotential surface is a surface over which the potential due to any charge configuration is the same throughout. The equipotential surfaces are three-dimensional imaginary surfaces.
Complete step by step answer:
The equipotential surfaces of an electric dipole are shown in the figure since the distance of each point on a plane passing through the centre of the axis of the electric dipole is equal to the potential throughout the plane is zero. Hence it is over one possible equipotential surface.
Figure: (Dotted lines are representing the equipotential surface

Some of the points to be remembered regarding the equipotential surface are as follows:
• Potential energy U = constant for point charge q on Equipotential surface.
• The surface of a conductor at equilibrium is at the equipotential surface.
• Electric field vectors (tangents to field lines) are perpendicular to an equipotential surface.
• Electrostatic force does zero work on point Charge q moving on the equipotential surface.
• The electric field exerts a force on a positive (negative) point charge q in the direction of steepest Potential drop (rise).
• When a positive (negative) point charge q moves from a region of high potential to a region of low potential, the Electric field does positive (negative) work on it. In the process, the potential energy decreases (increases).
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
An equipotential surface is a surface over which the potential due to any charge configuration is the same throughout. The equipotential surfaces are three-dimensional imaginary surfaces.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




