
The equations of the tangents drawn from the origin to the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} + 2rx - 2hy + {h^2} = 0$ are-
A) $x = 0$
B) $y = 0$
C) $\left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x - 2rhy = 0$
D) $\left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x + 2rhy = 0$
Answer
612.3k+ views
Hint- First, we will convert the given equation of the circle into the basic equation of the circle i.e. ${\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$. Then we will solve it further with the help of a diagram mentioned in the solution below.
Complete step-by-step answer:
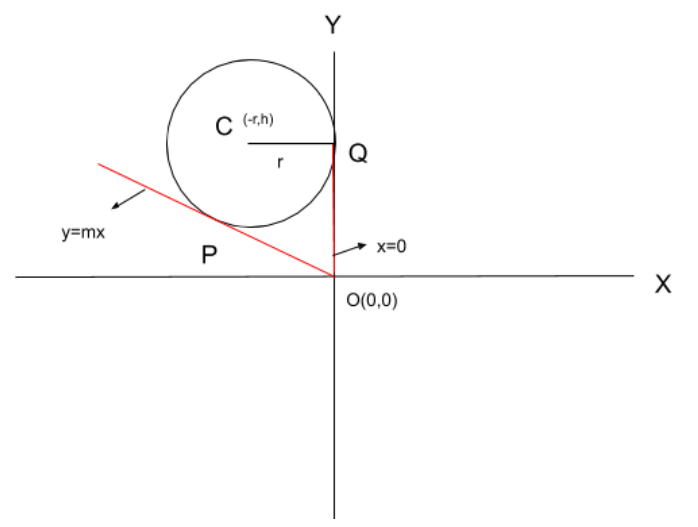
The given equation by the question of the circle is ${x^2} + {y^2} + 2rx - 2hy + {h^2} = 0$. We will convert it into the basic form of the equation of a circle. In order to do so, we will add ${r^2}$ to both the sides of the equation. We will get-
$ \to {x^2} + {y^2} + 2rx - 2hy + {h^2} = 0$
Adding ${r^2}$ on both the sides-
$
\to \left( {{x^2} + 2rx + {r^2}} \right) + \left( {{y^2} - 2hy + {h^2}} \right) = {r^2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - \left( { - r} \right)} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - h} \right)^2} = {r^2} \\
$
Thus, we get the equation of the circle in its basic form.
As we can see from the above equation. The centre of the circle is $\left( { - r,h} \right)$ . The X coordinate of the centre of the circle is r and the radius of the circle is also r. With this information we can say that the circle will touch the Y axis. Which means that the equation of the first tangent from the origin to the circle will be $x = 0$.
Now, let the equation of the second tangent be $y = mx$.
The perpendicular distance from $C\left( { - r,h} \right)$ to the second tangent drawn from the origin to the circle $y = mx$ is-
$ \to r = \left| {\dfrac{{ - mr - h}}{{\sqrt {{m^2} + 1} }}} \right|$
After squaring both sides, we get-
$
\Rightarrow {r^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( { - mr - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{m^2} + 1}} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {m^2}{r^2} + 2mrh + {h^2} = {m^2}{r^2} + {r^2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{{r^2} - {h^2}}}{{2rh}} \\
$
Taking minus common in the above equation, we get-
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)}}{{2rh}}$
Putting this value of m into the equation of the second tangent $y = mx$, we get-
$
\Rightarrow y = mx \\
\\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ - \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)}}{{2rh}}x \\
\\
\Rightarrow \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x + 2rhy = 0 \\
$
Hence, the equation of the first tangent is $y = mx$, and the second tangent is $\left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x + 2rhy = 0$.
Thus, the correct options are A and D.
Note: In such a question, taking help of a figure is necessary as it makes the question a bit easier to understand and doesn’t mess things up at all. Remember to always convert the equation of the circle given by the question to its basic form. It will be easier to solve the answer then.
Complete step-by-step answer:

The given equation by the question of the circle is ${x^2} + {y^2} + 2rx - 2hy + {h^2} = 0$. We will convert it into the basic form of the equation of a circle. In order to do so, we will add ${r^2}$ to both the sides of the equation. We will get-
$ \to {x^2} + {y^2} + 2rx - 2hy + {h^2} = 0$
Adding ${r^2}$ on both the sides-
$
\to \left( {{x^2} + 2rx + {r^2}} \right) + \left( {{y^2} - 2hy + {h^2}} \right) = {r^2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - \left( { - r} \right)} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - h} \right)^2} = {r^2} \\
$
Thus, we get the equation of the circle in its basic form.
As we can see from the above equation. The centre of the circle is $\left( { - r,h} \right)$ . The X coordinate of the centre of the circle is r and the radius of the circle is also r. With this information we can say that the circle will touch the Y axis. Which means that the equation of the first tangent from the origin to the circle will be $x = 0$.
Now, let the equation of the second tangent be $y = mx$.
The perpendicular distance from $C\left( { - r,h} \right)$ to the second tangent drawn from the origin to the circle $y = mx$ is-
$ \to r = \left| {\dfrac{{ - mr - h}}{{\sqrt {{m^2} + 1} }}} \right|$
After squaring both sides, we get-
$
\Rightarrow {r^2} = \dfrac{{{{\left( { - mr - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{m^2} + 1}} \\
\\
\Rightarrow {m^2}{r^2} + 2mrh + {h^2} = {m^2}{r^2} + {r^2} \\
\\
\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{{r^2} - {h^2}}}{{2rh}} \\
$
Taking minus common in the above equation, we get-
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{ - \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)}}{{2rh}}$
Putting this value of m into the equation of the second tangent $y = mx$, we get-
$
\Rightarrow y = mx \\
\\
\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{ - \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)}}{{2rh}}x \\
\\
\Rightarrow \left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x + 2rhy = 0 \\
$
Hence, the equation of the first tangent is $y = mx$, and the second tangent is $\left( {{h^2} - {r^2}} \right)x + 2rhy = 0$.
Thus, the correct options are A and D.
Note: In such a question, taking help of a figure is necessary as it makes the question a bit easier to understand and doesn’t mess things up at all. Remember to always convert the equation of the circle given by the question to its basic form. It will be easier to solve the answer then.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




