
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. If resonance energy of benzene is $ - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$, its enthalpy of hydrogenation would be
A) $ - 508.9{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
B) $ - 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
C) $ - 269.9{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
D) $ - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We know that benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ contains three double bonds. To break these three bonds and convert benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ to cyclohexane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ three molecules of hydrogen $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ will be required. To calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given compound we must add resonance energy to the total enthalpy of the reaction.
Complete solution:
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane.
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane. The hydrogenation reaction of benzene is as follows:
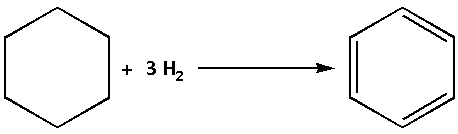
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. Thus, the enthalpy for hydrogenation of benzene is,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = 3 \times \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = 3 \times - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$.
We know that benzene is a resonating structure. Thus, benzene possesses resonance energy. The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. Thus,
${\text{Resonance energy}} = \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}}$
We are given that the resonance energy of benzene is $ - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. Thus,
$ - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} = - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}}$
$ - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} + 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$ - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = - 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$.
Thus, the correct option is (C) 8.87.
Note:The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. The resonance energy is the measure of extra stability of a conjugated system compared to the number of isolated double bonds.
Complete solution:
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane.
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane. The hydrogenation reaction of benzene is as follows:
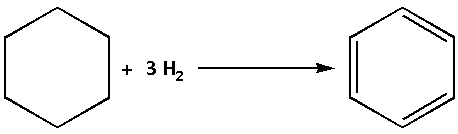
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is $ - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. Thus, the enthalpy for hydrogenation of benzene is,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = 3 \times \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = 3 \times - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} = - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$.
We know that benzene is a resonating structure. Thus, benzene possesses resonance energy. The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. Thus,
${\text{Resonance energy}} = \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}}$
We are given that the resonance energy of benzene is $ - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$. Thus,
$ - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} = - 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}}$
$ - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = - 150.4{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}} + 358.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$ - \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene (actual)}}}} = - 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is $ - 208.1{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}$.
Thus, the correct option is (C) 8.87.
Note:The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. The resonance energy is the measure of extra stability of a conjugated system compared to the number of isolated double bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




