
The end product of the Krebs cycle is
(a)Pyruvic acid
(b)Citric acid
(c)Malic acid
(d)Lactic acid
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The final product of the Krebs cycle is a poor organic acid found in fruits such as oranges, lemons, etc. It is a natural preservative and is also used in foods and soft drinks to give an acidic (sour) flavor. It also serves as a washing agent that is environmentally benign and functions as an antioxidant.
Complete answer:
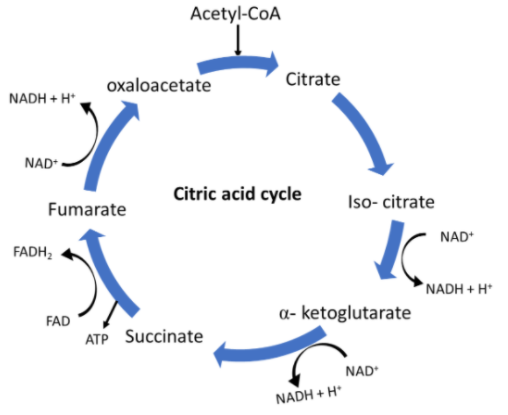
The Krebs cycle takes place in the cell's mitochondria, helps to generate energy, and takes place immediately after glycolysis. The cycle that begins with the pyruvic acid a 3-carbon molecule divides it into acetyl coenzyme A, which then combines further with oxalo acetic acid to form citric acid.
In a step-by-step process, the citric acid cycle collects the energy stored in acetyl CoA (processed glucose) chemical bonds, trapping it in the form of high-energy intermediate molecules. The trapped energy from the cycle of citric acid is then passed on to oxidative phosphorylation, where it is converted to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as a usable source of cellular energy.
The Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, starting by connecting acetyl CoA to citric acid forming oxaloacetic acid. The cycle continues in the presence of different enzymes through the production of different intermediates and the release of carbon dioxide and water as end products.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Citric acid’.
Note: The citric acid cycle is also referred to as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). It is a series of reactions used by all aerobic species to generate accumulated energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA obtained from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition, the cycle produces precursors of some amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in various other reactions.
Complete answer:
The Krebs cycle takes place in the cell's mitochondria, helps to generate energy, and takes place immediately after glycolysis. The cycle that begins with the pyruvic acid a 3-carbon molecule divides it into acetyl coenzyme A, which then combines further with oxalo acetic acid to form citric acid.
In a step-by-step process, the citric acid cycle collects the energy stored in acetyl CoA (processed glucose) chemical bonds, trapping it in the form of high-energy intermediate molecules. The trapped energy from the cycle of citric acid is then passed on to oxidative phosphorylation, where it is converted to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) as a usable source of cellular energy.
The Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix, starting by connecting acetyl CoA to citric acid forming oxaloacetic acid. The cycle continues in the presence of different enzymes through the production of different intermediates and the release of carbon dioxide and water as end products.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Citric acid’.
Note: The citric acid cycle is also referred to as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). It is a series of reactions used by all aerobic species to generate accumulated energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA obtained from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. In addition, the cycle produces precursors of some amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in various other reactions.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




