
The electric field in a region is given by \[\overrightarrow{E}=\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j}\] with \[{{E}_{0}}=2\times {{10}^{3}}N{{C}^{-1}}\]. Find the flux of this field through a rectangular surface of area \[0.2{{m}^{2}}\] parallel to the Y-Z plane.
A. \[320N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}\]
B. \[240N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}\]
C. \[400N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-1}}\]
D. None of these
Answer
614.4k+ views
Hint: Apply Gauss’s law. In GAUSS’S law the direction of the area-vector is along the normal to the corresponding surface, so find the direction of area vector( x, y or z direction) then use \[\hat{j}\cdot \hat{i}=0\].
Complete step by step answer:
Apply Gauss’s law
\[\phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]
Where, \[\phi \]= flux of electric field through chosen surface
\[\overrightarrow{E}\]= electric field
\[\overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]= area vector
Given data
\[{{E}_{0}}=2\times {{10}^{3}}N{{C}^{-1}}\]
\[\overrightarrow{E}=\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j}\]
Rectangle surface of area \[0.2{{m}^{2}}\] parallel to the Y-Z plane
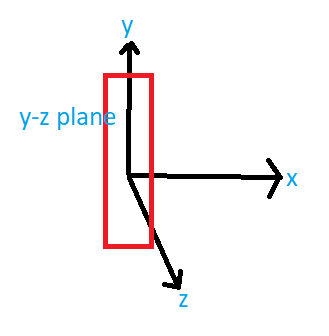
Area vector is in x direction because area vector is perpendicular to given plane and x is perpendicular to y-z plane
\[\overrightarrow{\Delta S}=0.2\hat{i}\]
\[\phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S} \\
& \overrightarrow{E}=\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j} \\
& \phi =\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j}\cdot 0.2\hat{i} \\
& (\hat{j}\cdot \hat{i}=0) \\
& \phi =0 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: Remember the direction of the area-vector is always along the normal to the corresponding surface. If the electric field is perpendicular to the surface, it is parallel to the area vector. If the electric field is parallel to the surface, the area vector is perpendicular to the electric field.
Complete step by step answer:
Apply Gauss’s law
\[\phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]
Where, \[\phi \]= flux of electric field through chosen surface
\[\overrightarrow{E}\]= electric field
\[\overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]= area vector
Given data
\[{{E}_{0}}=2\times {{10}^{3}}N{{C}^{-1}}\]
\[\overrightarrow{E}=\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j}\]
Rectangle surface of area \[0.2{{m}^{2}}\] parallel to the Y-Z plane

Area vector is in x direction because area vector is perpendicular to given plane and x is perpendicular to y-z plane
\[\overrightarrow{\Delta S}=0.2\hat{i}\]
\[\phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \phi =\overrightarrow{E}\cdot \overrightarrow{\Delta S} \\
& \overrightarrow{E}=\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j} \\
& \phi =\dfrac{3}{5}{{E}_{0}}\hat{j}\cdot 0.2\hat{i} \\
& (\hat{j}\cdot \hat{i}=0) \\
& \phi =0 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: Remember the direction of the area-vector is always along the normal to the corresponding surface. If the electric field is perpendicular to the surface, it is parallel to the area vector. If the electric field is parallel to the surface, the area vector is perpendicular to the electric field.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




