
The d-orbital involved in \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization is:
A. \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\]
B. \[{d_{xy}}\]
C. \[{d_{{z^2}}}\]
D. \[{d_{zz}}\]
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: To determine the hybridization of any compound, we must know the structure of that compound. Hybridization is defined as a concept of mixing two atomic orbitals having the same energy levels to give new degenerate orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
The formula to calculate the hybridization of the central atom of the molecule is, \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\] . where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom, C is the total cationic charge and A is the total anionic charge, H is the hybridization.
For, \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization, the hybridization number (H) should be 5. These five orbitals are degenerate, that is their energies are the same but configurations are different.
In this \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization there are a total of 5 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital takes part in this hybridization.
So, the correct answer is C.
Additional information:
For, \[\;S{F_4}\] the hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6 + 4 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {10} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = 5 \\
\]
For \[H = 5\] , the hybridization would be \[s{p^3}d\] , so the geometry of \[\;S{F_4}\] is Trigonal bipyramidal. In this case, the central atom chlorine has 4 bond pairs and 1 lone pair, therefore, the shape is a see-saw. Due to this shape, it has a permanent dipole moment. The structure is shown below,
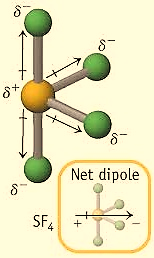
Remember that when a lone pair is present, then the molecular geometry will be the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms without the lone pair. If there is no lone pair only bond pairs then the number of bond pairs can be equal to the hybridization number.
Note:In the case of \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization there are a total of 6 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals take part in this hybridization. In the case of \[s{p^3}{d^3}\] hybridization there is a total of 7 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] , \[{d_{xy}}\] and \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals take part in this hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
The formula to calculate the hybridization of the central atom of the molecule is, \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\] . where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom, C is the total cationic charge and A is the total anionic charge, H is the hybridization.
| Hybridization number(H) | Hybridization | geometry |
| 2 | Sp | linear |
| 3 | \[s{p^2}\] | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | \[s{p^3}\] | tetrahedral |
| 5 | \[s{p^3}d\] | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] | octahedral |
| 7 | \[s{p^3}{d^3}\] | Pentagonal bipyramidal |
For, \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization, the hybridization number (H) should be 5. These five orbitals are degenerate, that is their energies are the same but configurations are different.
In this \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization there are a total of 5 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] orbital takes part in this hybridization.
So, the correct answer is C.
Additional information:
For, \[\;S{F_4}\] the hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6 + 4 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {10} \right] \\
\Rightarrow H = 5 \\
\]
For \[H = 5\] , the hybridization would be \[s{p^3}d\] , so the geometry of \[\;S{F_4}\] is Trigonal bipyramidal. In this case, the central atom chlorine has 4 bond pairs and 1 lone pair, therefore, the shape is a see-saw. Due to this shape, it has a permanent dipole moment. The structure is shown below,

Remember that when a lone pair is present, then the molecular geometry will be the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms without the lone pair. If there is no lone pair only bond pairs then the number of bond pairs can be equal to the hybridization number.
Note:In the case of \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization there are a total of 6 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] and \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals take part in this hybridization. In the case of \[s{p^3}{d^3}\] hybridization there is a total of 7 orbitals which are, s, \[{P_x}\] , \[{P_y}\] , and \[{P_z}\] . In the case of d subshell, the \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] , \[{d_{xy}}\] and \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] orbitals take part in this hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




