
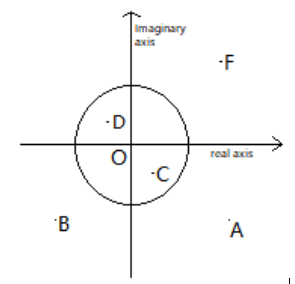
The diagram shows several numbers in the complex plane. The circle is the unit circle centred at the origin. One of these numbers is the reciprocal of $F$, which can be
1) $A$
2) $B$
3) $C$
4) $D$

Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Let the $F$ be the complex number given in the figure. The reciprocal of the complex number can be then determined by evaluating $\dfrac{1}{F}$. We shall then simplify the expression by rationalising the complex number and writing in the standard form. We can then compare different given points to find the answer.
Complete solution step by step:
To find the reciprocal of the $F$, we shall first let the complex number $F$ be $a + ib$, where the real part is represented by $a$ and the imaginary part is represented by $b$. Also, $a > 1$ and $b > 1$ because the point $F$ is given outside of the unit circle and is in the first quadrant.
The reciprocal of the complex number $F$ will be $\dfrac{1}{F}$, which can be represented by:
$\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{{a + ib}}$
To further simplify the complex number $\dfrac{1}{F}$, we will rationalise the complex number by multiplying the numerator and denominator by $a - ib$.
$\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{{a + ib}} \times \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{a - ib}}$
On simplifying, we get
$
\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{\left( {a + ib} \right)\left( {a - ib} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} - {{\left( {ib} \right)}^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
We will separate the real and imaginary part.
$
\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{a}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} - i\dfrac{b}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
$
\operatorname{Re} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right) = \dfrac{a}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
\operatorname{Im} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right) = \dfrac{{ - b}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
Since the real part is positive and the imaginary part is negative, the reciprocal of the point $F$lies in the fourth quadrant. Thus the possible solution is the points $C$ and $A$.
Also, we can conclude that the $\left| {\operatorname{Re} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right)} \right|$ and $\left| {\operatorname{Im} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right)} \right|$ will be less than 1 as \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > a\] and \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > b\].
Thus the complex point $\dfrac{1}{F}$ will lie inside the unit circle as the modulus of the real and complex part is less than 1.
Therefore, the complex point $C$ will be the solution.
Hence, C is the correct option.
Note: It is important to remember that the square of every number is greater than 0. Hence, \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > a\] and \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > b\], this will help in eliminating the wrong point. For this question, one must also know about how to plot complex numbers on the cartesian plane to identify the correct point from the given condition.
Complete solution step by step:
To find the reciprocal of the $F$, we shall first let the complex number $F$ be $a + ib$, where the real part is represented by $a$ and the imaginary part is represented by $b$. Also, $a > 1$ and $b > 1$ because the point $F$ is given outside of the unit circle and is in the first quadrant.
The reciprocal of the complex number $F$ will be $\dfrac{1}{F}$, which can be represented by:
$\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{{a + ib}}$
To further simplify the complex number $\dfrac{1}{F}$, we will rationalise the complex number by multiplying the numerator and denominator by $a - ib$.
$\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{{a + ib}} \times \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{a - ib}}$
On simplifying, we get
$
\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{\left( {a + ib} \right)\left( {a - ib} \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} - {{\left( {ib} \right)}^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
We will separate the real and imaginary part.
$
\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{{a - ib}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{a}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} - i\dfrac{b}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
$
\operatorname{Re} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right) = \dfrac{a}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
\operatorname{Im} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right) = \dfrac{{ - b}}{{{a^2} + {b^2}}} \\
$
Since the real part is positive and the imaginary part is negative, the reciprocal of the point $F$lies in the fourth quadrant. Thus the possible solution is the points $C$ and $A$.
Also, we can conclude that the $\left| {\operatorname{Re} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right)} \right|$ and $\left| {\operatorname{Im} \left( {\dfrac{1}{F}} \right)} \right|$ will be less than 1 as \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > a\] and \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > b\].
Thus the complex point $\dfrac{1}{F}$ will lie inside the unit circle as the modulus of the real and complex part is less than 1.
Therefore, the complex point $C$ will be the solution.
Hence, C is the correct option.
Note: It is important to remember that the square of every number is greater than 0. Hence, \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > a\] and \[\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} > b\], this will help in eliminating the wrong point. For this question, one must also know about how to plot complex numbers on the cartesian plane to identify the correct point from the given condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




