
The diagram shows part of the xylem vessel. What is the substance X that prevents the collapse of the xylem vessel?
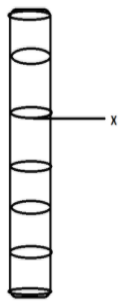
A) Lignin walls
B) Companion cells
C) End Wall
D) None of the above

Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint: The structure of the roots, stems, and leaves of plants enables the transport of water, nutrients, and photosynthates throughout the plant. The principal tissues responsible for this movement are the phloem and xylem. Due to the rigidity of the xylem cells that sustain the plant, vascular plants are able to grow taller than other plants.
Complete answer:
The xylem is the vascular tissue that is responsible for water and nutrient upward conduction from the roots. Water and nutrients are transferred by the xylem tissue to different areas of the plant, such as shoots and leaves. Its key components include xylem parenchyma, tracheid, xylem vessels, and xylem fibres. One of the two cell forms of tracheal components is the xylem vessel; the other is the tracheid. In vascular plants, these two are the water conducting components. However,
The cells adapted for conducting water from root to leaves and shoots have a mechanical role in young plants, mostly in addition to the epidermis. The xylem vessels and tracheid are elongated cells, these cells have thickened walls that help prevent their collapse by pulling the transpiration stream when water in them is under tension. The drying effect on the leaf surface facilitates the flow of water from the roots into the body of the plant. The xylem's first shaped conducting cells consist of very thin-walled, elongated cells that have to expand with the development of the stem length. Their collapse during the time they are needed to function is prevented by special thickening in their walls. The inner walls of the xylem vessels are strengthened by the deposits of a substance called Lignin. Lignin is a tough and rigid substance; it prevents the vessel from collapsing.
Companion cells- These cells are found inside the phloem of angiosperms.
End wall- It is absent in xylem.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘A’ Lignin walls.
Note: Plants are giant hydraulic engineers.For moving water to leaves so that photosynthesis can take place, water capacity is important. Only tracheids are present in Pteridophytes and most Gymnosperms. There are both xylem vessels and tracheids in most angiosperms, but the xylem vessels act as the main conducting part.
Complete answer:
The xylem is the vascular tissue that is responsible for water and nutrient upward conduction from the roots. Water and nutrients are transferred by the xylem tissue to different areas of the plant, such as shoots and leaves. Its key components include xylem parenchyma, tracheid, xylem vessels, and xylem fibres. One of the two cell forms of tracheal components is the xylem vessel; the other is the tracheid. In vascular plants, these two are the water conducting components. However,
The cells adapted for conducting water from root to leaves and shoots have a mechanical role in young plants, mostly in addition to the epidermis. The xylem vessels and tracheid are elongated cells, these cells have thickened walls that help prevent their collapse by pulling the transpiration stream when water in them is under tension. The drying effect on the leaf surface facilitates the flow of water from the roots into the body of the plant. The xylem's first shaped conducting cells consist of very thin-walled, elongated cells that have to expand with the development of the stem length. Their collapse during the time they are needed to function is prevented by special thickening in their walls. The inner walls of the xylem vessels are strengthened by the deposits of a substance called Lignin. Lignin is a tough and rigid substance; it prevents the vessel from collapsing.
Companion cells- These cells are found inside the phloem of angiosperms.
End wall- It is absent in xylem.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘A’ Lignin walls.
Note: Plants are giant hydraulic engineers.For moving water to leaves so that photosynthesis can take place, water capacity is important. Only tracheids are present in Pteridophytes and most Gymnosperms. There are both xylem vessels and tracheids in most angiosperms, but the xylem vessels act as the main conducting part.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




