
The diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point O such that $\dfrac{{AO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CO}}{{DO}}$. Show that ABCD is a trapezium.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: In this particular question first draw the pictorial representation of the given problem it will give us a clear picture of what we have to find out then make a construction in the figure, draw a line OE parallel to AB such that it cuts the line BC at point E, so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
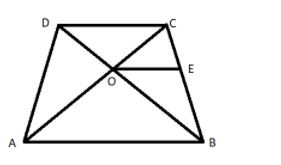
Given data:
The diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point O, such that,
$\dfrac{{AO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CO}}{{DO}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}}$....... (1).
Now we have to prove that ABCD is a trapezium.
As we know that in a trapezium any two opposite sides are parallel, the rest of the two opposite sides are not parallel to each other.
If we prove that AB parallel to CD i.e. AB||CD then ABCD is trapezium.
Proof –
So for this draw a line OE parallel to AB such that it cuts the line BC at point E, as shown in the figure.
So, OE||AB.................... (2)
Now in triangle ABC, according to basic proportionality theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$.................... (3), (this is only possible if and only if OE||AB)
Now from equation (1) and (3) we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$
Hence by converse of basic proportionality theorem the above relation is only possible if and only if OE||DC............... (4)
So from equation (2) and (4)
AB||OE||DC
Hence ABCD is trapezium.
Hence Proved.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that in a triangle if we draw a line parallel to the base of the triangle and cuts the other two sides of the triangle then according to the basic proportionality theorem the ratio of the respective sides of upper half and the lower half are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given data:
The diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point O, such that,
$\dfrac{{AO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CO}}{{DO}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}}$....... (1).
Now we have to prove that ABCD is a trapezium.
As we know that in a trapezium any two opposite sides are parallel, the rest of the two opposite sides are not parallel to each other.
If we prove that AB parallel to CD i.e. AB||CD then ABCD is trapezium.
Proof –
So for this draw a line OE parallel to AB such that it cuts the line BC at point E, as shown in the figure.
So, OE||AB.................... (2)
Now in triangle ABC, according to basic proportionality theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$.................... (3), (this is only possible if and only if OE||AB)
Now from equation (1) and (3) we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CO}}{{AO}} = \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{DO}}{{BO}} = \dfrac{{CE}}{{BE}}$
Hence by converse of basic proportionality theorem the above relation is only possible if and only if OE||DC............... (4)
So from equation (2) and (4)
AB||OE||DC
Hence ABCD is trapezium.
Hence Proved.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that in a triangle if we draw a line parallel to the base of the triangle and cuts the other two sides of the triangle then according to the basic proportionality theorem the ratio of the respective sides of upper half and the lower half are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




