
The development of Funaria gametophyte always initiated from:
(a) Antheridium
(b) Protonema
(c) Archegonia
(d) Capsule
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: The spores liberated germinate into a creeping, green, branched, chlorophyll and frequently filamentous stage which marked the development of gametophyte in Funaria.
Complete answer:
The predominant stage of the life cycle of a Funaria is the gametophyte which consists of protonema and leafy stages. It is commonly found in the life cycle of Hornworts and Liverworts.
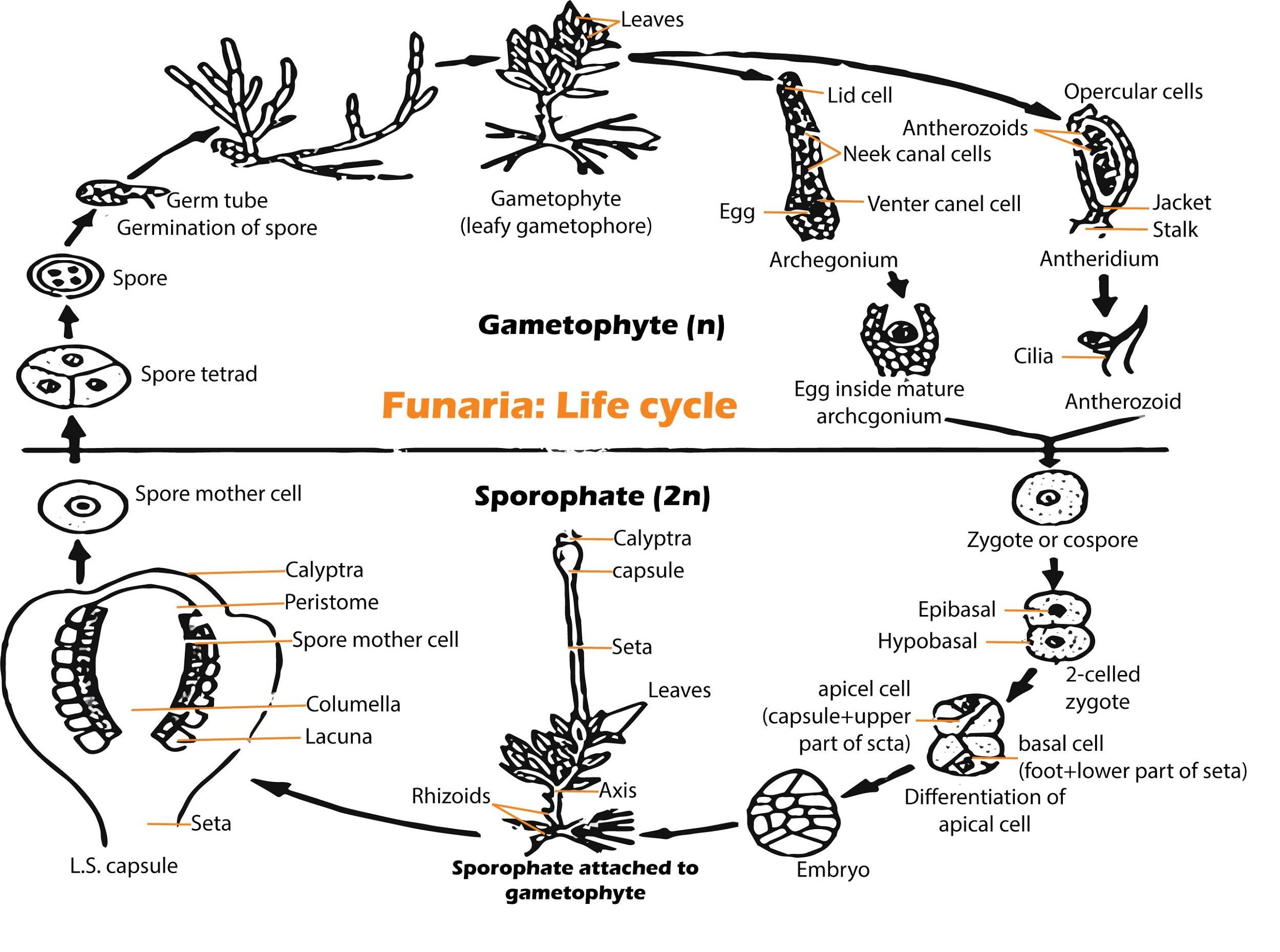
Additional Information: - The plant body is a leafy gametophyte which has multicellular and branched rhizoids.
- They contain upright, slender, axis bearing, spirally arranged leaves. This stage bears the sex organ. - In sexual reproduction, the sex organs antheridia and archegonia are produced at the apex of the leafy shoot.
- The sex organs are present on the same plant but different branches.
- Each antheridium produces several biflagellate antherozoids. Each archegonium produces a fertile egg. - The fusion of gametes with the help of water leads to the formation of zygote. The zygote develops into a sporophyte which is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule. - The capsule encloses two spore sacs where spores are formed through meiosis. - The spore on liberation germinates into a creeping green branched and frequently filamentous stage called protonema (juvenile phase) .
- In the case of mosses, protonema consists of two types of cell chromonemata and caulonema.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Protonema.’
Note: Vegetative reproduction also occurs in Funaria. Fragmentation and budding occur in secondary protonema. In secondary protonema, a lateral bud is produced which develops into a leafy stage. Funaria is an amphibious plant and sexual reproduction takes place through the water. They show alternation of generation i.e. gametophyte alternates with sporophytes.
Complete answer:
The predominant stage of the life cycle of a Funaria is the gametophyte which consists of protonema and leafy stages. It is commonly found in the life cycle of Hornworts and Liverworts.

Additional Information: - The plant body is a leafy gametophyte which has multicellular and branched rhizoids.
- They contain upright, slender, axis bearing, spirally arranged leaves. This stage bears the sex organ. - In sexual reproduction, the sex organs antheridia and archegonia are produced at the apex of the leafy shoot.
- The sex organs are present on the same plant but different branches.
- Each antheridium produces several biflagellate antherozoids. Each archegonium produces a fertile egg. - The fusion of gametes with the help of water leads to the formation of zygote. The zygote develops into a sporophyte which is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule. - The capsule encloses two spore sacs where spores are formed through meiosis. - The spore on liberation germinates into a creeping green branched and frequently filamentous stage called protonema (juvenile phase) .
- In the case of mosses, protonema consists of two types of cell chromonemata and caulonema.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Protonema.’
Note: Vegetative reproduction also occurs in Funaria. Fragmentation and budding occur in secondary protonema. In secondary protonema, a lateral bud is produced which develops into a leafy stage. Funaria is an amphibious plant and sexual reproduction takes place through the water. They show alternation of generation i.e. gametophyte alternates with sporophytes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




