
The crystal with metal deficiency defect is:
A.NaCl
B.FeO
C.KCl
D.ZnO
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: If an ion(cation/anion) is missing from the lattice point of a crystal structure of the solid, or the cation is misplaced from its position to an interstitial position then it is called point defects.as a result of these point defects the arrangement of the lattice is getting distorted. Point defects of solids are mainly two types, stoichiometric defect, and non-stoichiometric defect.
Complete step by step answer:
When the stoichiometry of the cation and anion in lattice remain constant after the defect is called a stoichiometric defect. But when stoichiometry of the cation and anion in the lattice is changed or disturbed then this is a non-stoichiometric defect.
A)the stoichiometric defect can also be divided into two parts
1.Schottky defect: When an equal number of cation and anion is missing from its lattice point of the crystal then it is called Schottky defect.
2.Frenkel defect: When the cation misplaced its position from its lattice point to an interstitial position of the crystal lattice, then it is called Frenkel defect.
B)The non –stoichiometric defect is of two types:
1.Metal Excess Defect
2.Metal Deficiency defect
The non-stoichiometric defects disturb the stoichiometry of the compounds. These defects are either due to the presence of excess metal ions or deficiency of metal ions.
a)In a metal deficiency defect, a cation is missing from its lattice site. To maintain electrical neutrality, one of the nearest metal ions acquires an extra positive charge.
b)This type of defect occurs in compounds where the metal exhibit variable valency e.g. Transition metal complexes like NiO, FeO, FeS, etc.
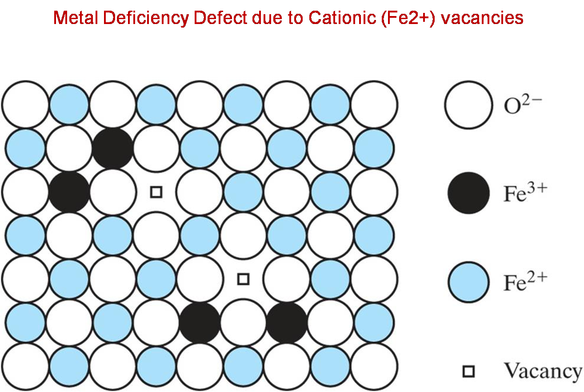
Therefore, the correct answer is, B.
Note:The free electrons can be excited to higher energy levels giving absorption spectra and as a consequence, their compounds are colored.
The metal excess defect is caused due to anionic vacancies and by the presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites. Interstitial sites are the position between the regular positions in an array of atoms or ions that can be occupied by other atoms or ions.
When alkali metal halides are heated in an atmosphere of vapor of the alkali metal, anion vacancies are created
The crystals with metal excess defects are generally colored due to the presence of free electrons in them. The crystals with this defect conduct electricity due to the presence of free electrons and are semiconductors.
Complete step by step answer:
When the stoichiometry of the cation and anion in lattice remain constant after the defect is called a stoichiometric defect. But when stoichiometry of the cation and anion in the lattice is changed or disturbed then this is a non-stoichiometric defect.
A)the stoichiometric defect can also be divided into two parts
1.Schottky defect: When an equal number of cation and anion is missing from its lattice point of the crystal then it is called Schottky defect.
2.Frenkel defect: When the cation misplaced its position from its lattice point to an interstitial position of the crystal lattice, then it is called Frenkel defect.
B)The non –stoichiometric defect is of two types:
1.Metal Excess Defect
2.Metal Deficiency defect
The non-stoichiometric defects disturb the stoichiometry of the compounds. These defects are either due to the presence of excess metal ions or deficiency of metal ions.
a)In a metal deficiency defect, a cation is missing from its lattice site. To maintain electrical neutrality, one of the nearest metal ions acquires an extra positive charge.
b)This type of defect occurs in compounds where the metal exhibit variable valency e.g. Transition metal complexes like NiO, FeO, FeS, etc.

Therefore, the correct answer is, B.
Note:The free electrons can be excited to higher energy levels giving absorption spectra and as a consequence, their compounds are colored.
The metal excess defect is caused due to anionic vacancies and by the presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites. Interstitial sites are the position between the regular positions in an array of atoms or ions that can be occupied by other atoms or ions.
When alkali metal halides are heated in an atmosphere of vapor of the alkali metal, anion vacancies are created
The crystals with metal excess defects are generally colored due to the presence of free electrons in them. The crystals with this defect conduct electricity due to the presence of free electrons and are semiconductors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




