
The correct statements about squaric acid are?
A.It is a stronger acid than phenol.
B.It can form two conjugate bases.
C.It can liberate $C{O_2}$ from $NaHC{O_3}$
D.The conjugate base of squaric acid has all C-C bond lengths equal.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:First of all, we will determine its hydrogen ion losing capacity . From this we will determine the acidic strength and how many conjugate bases it forms. And if the squaric acid is a stronger acid than carbonic acid, it will liberate carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step answer:
3,4-Dihydroxy Cyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione is commonly known as squaric acid.
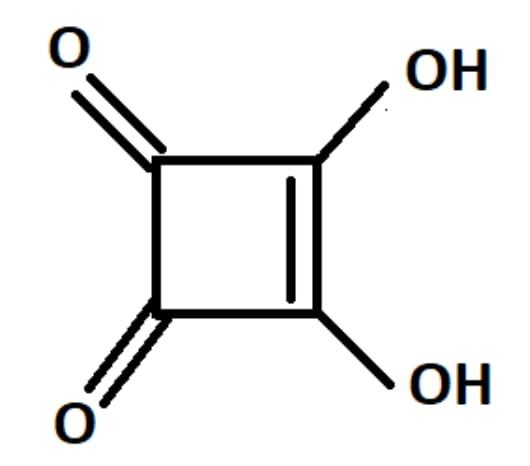
Its structure resembles the structure of a square and hence it is called squaric acid.
Any compound’s acidic strength depends upon the ease of the removal of \[{H^ + }\] ions . It ionises completely and can furnish two hydrogen ions in the solution. The conjugate base of squaric acid is hydrogen squared anion –: $C_4HO_4$ ( It has only one conjugate anion). The conjugate base is highly stable and forms many resonating structures( 4 equivalent and one aromatic ). “Stronger the conjugate base , stronger will be the acid “. Here , the anion is resonance stabilized and hence more stable( the negative charge is dispersed over the oxygen atoms ).
The acidity of phenol is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion( its stability is due to resonance of delocalised electrons).
The conjugate base of squaric acid is more stable than phenoxide ion and hence it is more stable than phenol.
It has only one conjugate base.
It is a stronger acid than carbonic acid and hence it can give effervescence of carbon dioxide.i.e. it can liberate $C{O_2}$ from $NaHC{O_3}$
It is not actually a square and hence its bond lengths are not equal . It just resembles the structure of a square.
Hence, the correct options are (A) and (C) .
Note: The presence of a deactivating group on any atom increases its acidity. While the presence of the activating group may or may not do so.
Complete step by step answer:
3,4-Dihydroxy Cyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione is commonly known as squaric acid.

Its structure resembles the structure of a square and hence it is called squaric acid.
Any compound’s acidic strength depends upon the ease of the removal of \[{H^ + }\] ions . It ionises completely and can furnish two hydrogen ions in the solution. The conjugate base of squaric acid is hydrogen squared anion –: $C_4HO_4$ ( It has only one conjugate anion). The conjugate base is highly stable and forms many resonating structures( 4 equivalent and one aromatic ). “Stronger the conjugate base , stronger will be the acid “. Here , the anion is resonance stabilized and hence more stable( the negative charge is dispersed over the oxygen atoms ).
The acidity of phenol is due to the stability of the phenoxide ion( its stability is due to resonance of delocalised electrons).
The conjugate base of squaric acid is more stable than phenoxide ion and hence it is more stable than phenol.
It has only one conjugate base.
It is a stronger acid than carbonic acid and hence it can give effervescence of carbon dioxide.i.e. it can liberate $C{O_2}$ from $NaHC{O_3}$
It is not actually a square and hence its bond lengths are not equal . It just resembles the structure of a square.
Hence, the correct options are (A) and (C) .
Note: The presence of a deactivating group on any atom increases its acidity. While the presence of the activating group may or may not do so.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




