
The correct order of hybridization of the central atom in the following species is:
\[N{{H}_{3}}\],\[{{[PtC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}\],\[PC{{l}_{5}}\]and\[BC{{l}_{3}}\]
a.) \[ds{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{3}}s{{p}^{2}},s{{p}^{3}}\]
b.) \[s{{p}^{3}},ds{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{3}},s{{p}^{2}}\]
c.) \[ds{{p}^{2}},s{{p}^{2}},s{{p}^{3}},ds{{p}^{3}}\]
d.) \[ds{{p}^{2}},s{{p}^{3}},s{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{3}}\]
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: Hybridization of an atom depends on the number of atoms from which the central atom is attached and number of lone pairs attached to it.
Complete step by step solution:
In shortcut form we can calculate hybridization as:
First we have to look at the atom of which we have to calculate hybridization, and count the number of atoms connected to it, not bonds.
And count the number of lone pairs attached to it. And add them both.
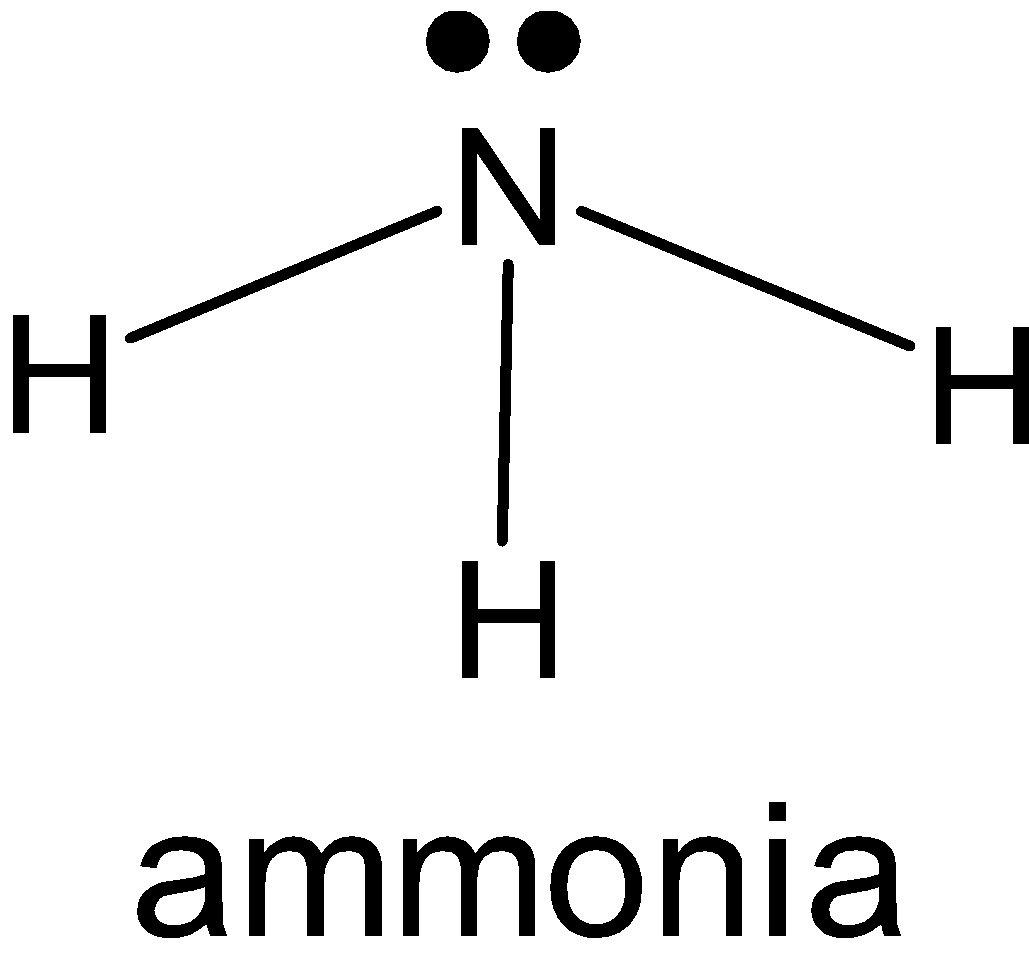
\[N{{H}_{3}}\]: Nitrogen has 5 electrons in a valence shell from which it makes 3 single bonds with hydrogen and it has one lone pair on it. And \[N{{H}_{3}}\]has a tetrahedral shape. So, the hybridization of nitrogen is \[s{{p}^{3}}\]. 3 bond pairs in p-orbital and one lone pair from s-orbital.
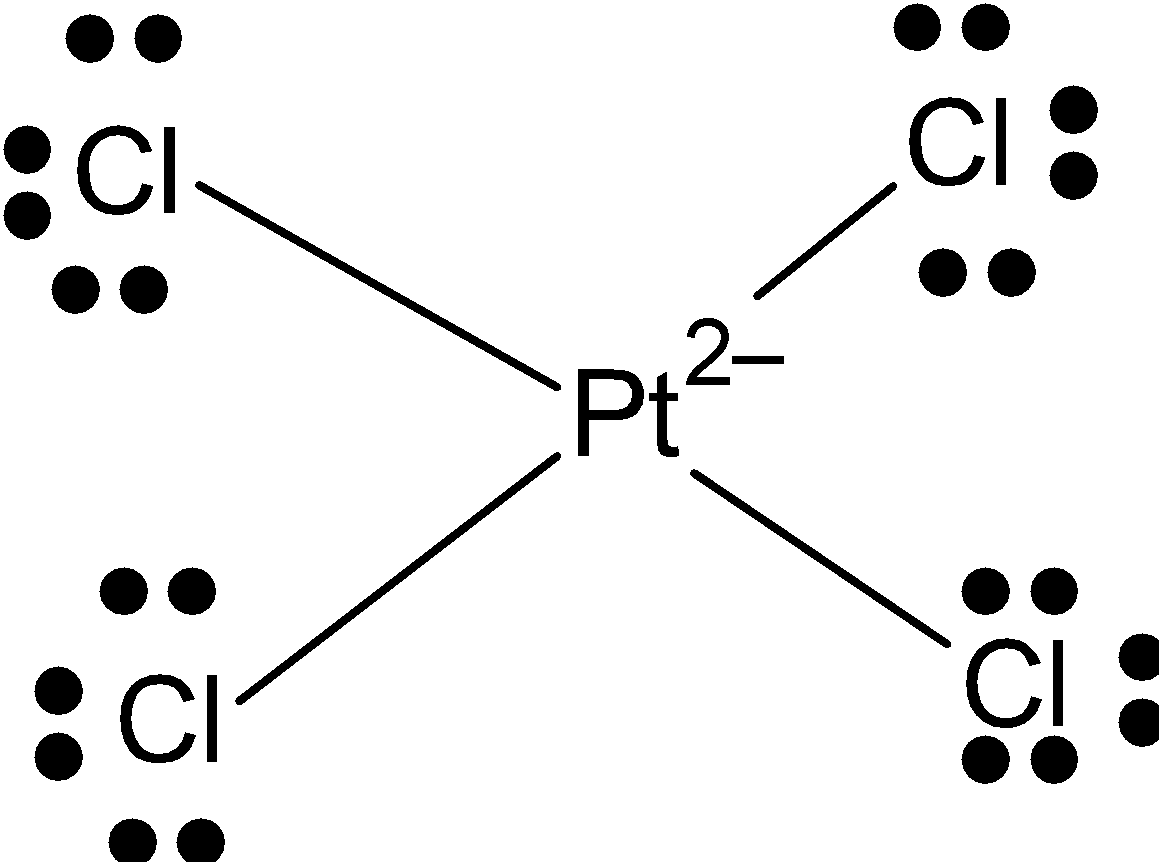
\[{{[PtC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}\]: \[Pt\] has 8 valence electrons in valence shell from which it makes 4 bonds with chlorine. And it has a square planar shape. So, the hybridization of \[P{{t}^{+2}}\]is\[ds{{p}^{2}}\]. Because one d-orbital is vacant.
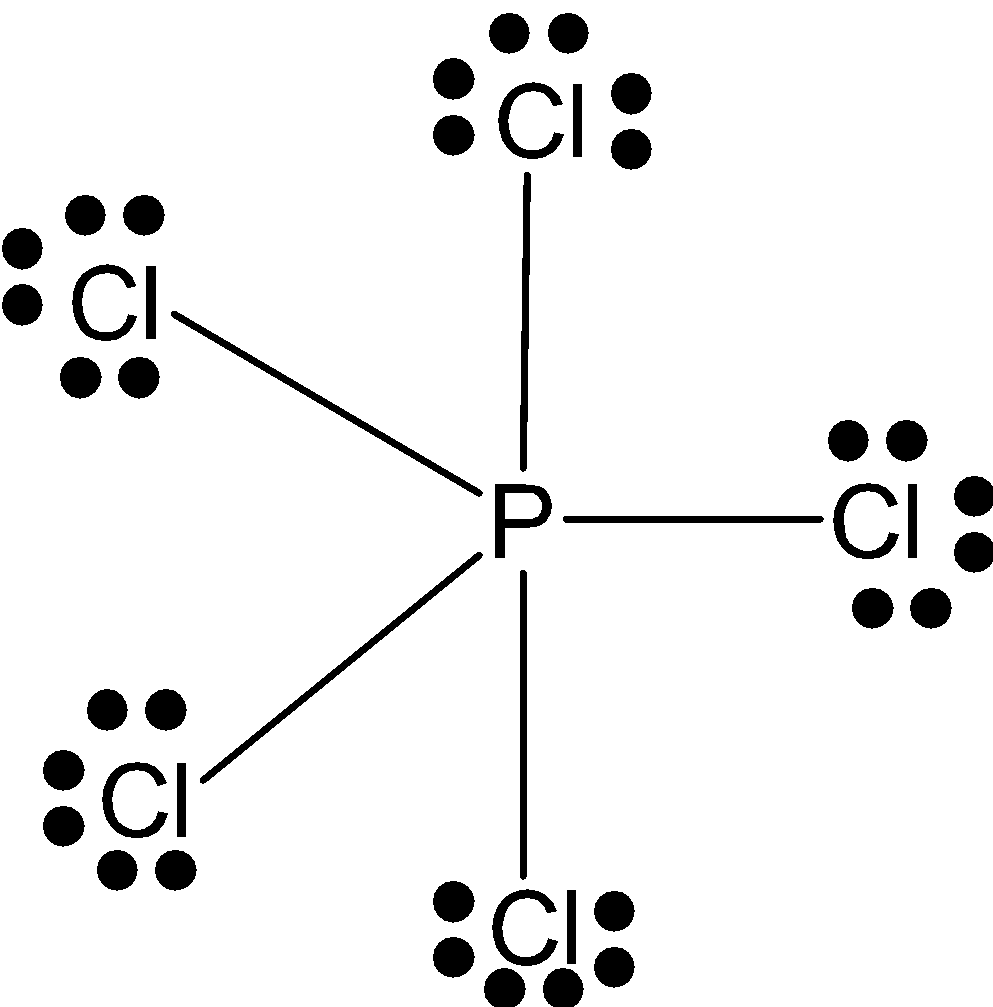
\[PC{{l}_{5}}\]: \[P\] has 5 valence electrons with which it makes 5 bonds with chlorines. And these electron pairs by bonding are filled in one s-orbital 3 in d-orbital and one pair in d-orbital. So, it has \[s{{p}^{3}}d\]configuration and triangular bipyramidal shape.
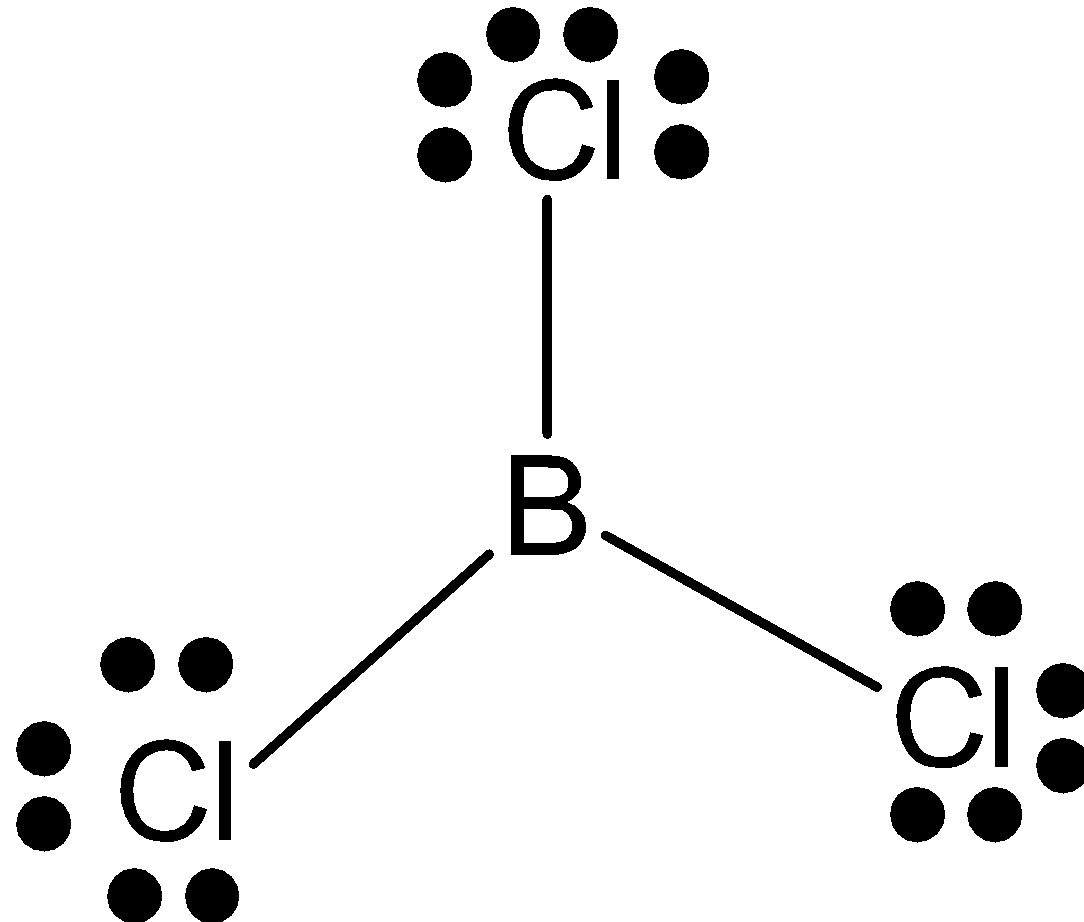
\[BC{{l}_{3}}\]: \[B\] has 3 valence electrons and it makes 3 bonds with chlorine. So, it has hybridization \[s{{p}^{2}}\] and triangular shape.
So, the correct answer is “B(\[s{{p}^{3}},ds{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{3}},s{{p}^{2}}\])”.
Note: \[{{[PtC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}\] is an exception because it has 5d-orbital and here chlorine acts as strong electrons. So, two unpaired electrons of d-orbital get paired so one d-orbital is vacant. But in case of \[N{{H}_{3}}\], nitrogen does not have d orbital so all electrons get filled in p orbital.
Complete step by step solution:
In shortcut form we can calculate hybridization as:
First we have to look at the atom of which we have to calculate hybridization, and count the number of atoms connected to it, not bonds.
And count the number of lone pairs attached to it. And add them both.
\[N{{H}_{3}}\]: Nitrogen has 5 electrons in a valence shell from which it makes 3 single bonds with hydrogen and it has one lone pair on it. And \[N{{H}_{3}}\]has a tetrahedral shape. So, the hybridization of nitrogen is \[s{{p}^{3}}\]. 3 bond pairs in p-orbital and one lone pair from s-orbital.

\[{{[PtC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}\]: \[Pt\] has 8 valence electrons in valence shell from which it makes 4 bonds with chlorine. And it has a square planar shape. So, the hybridization of \[P{{t}^{+2}}\]is\[ds{{p}^{2}}\]. Because one d-orbital is vacant.

\[PC{{l}_{5}}\]: \[P\] has 5 valence electrons with which it makes 5 bonds with chlorines. And these electron pairs by bonding are filled in one s-orbital 3 in d-orbital and one pair in d-orbital. So, it has \[s{{p}^{3}}d\]configuration and triangular bipyramidal shape.

\[BC{{l}_{3}}\]: \[B\] has 3 valence electrons and it makes 3 bonds with chlorine. So, it has hybridization \[s{{p}^{2}}\] and triangular shape.

So, the correct answer is “B(\[s{{p}^{3}},ds{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{3}},s{{p}^{2}}\])”.
Note: \[{{[PtC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}\] is an exception because it has 5d-orbital and here chlorine acts as strong electrons. So, two unpaired electrons of d-orbital get paired so one d-orbital is vacant. But in case of \[N{{H}_{3}}\], nitrogen does not have d orbital so all electrons get filled in p orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




