
The compound which as one isopropyl group is:
(A) 2, 2, 3, 3- tetramethyl pentane
(B) 2,2- dimethyl pentane
(C) 2, 2, 3 –trimethylpentane
(D) 2-methyl pentane
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: The nomenclature is a very important part of organic chemistry. This nomenclature is not only for compounds but also for carbon atoms that make this compound. For nomenclature of carbon atoms, use the terms primary, secondary, and tertiary to refer to the substitution level that carbon has in a molecule. based on the classification of carbon atoms useful to determine the stability and predict the products in organic reaction mechanisms.
Complete step by step solution:
Classifications of carbon atoms based on nomenclature are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. To describe how many other carbons are attached to given carbon. This classification applied to only saturated carbons and its substitution compounds like alcohols, amines, etc.
The terminology of carbon-containing functional groups:
Primary carbons: a hydrogen atom on a carbon atom attached to one other carbon atom
Secondary carbons: hydrogen on a carbon attached to only two other carbon atoms
Tertiary carbons: hydrogen on a carbon attached to three other carbon atoms
Quaternary carbons: carbon attached to four other carbon atoms.
If any carbon atom is a tertiary carbon with this structure will be

Let us check the IUPAC names of the compounds given,
(A) 2, 2, 3, 3- tetramethyl pentane – there is no isopropyl carbon atom in the parent chain.
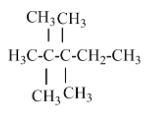
(B) 2,2- dimethyl pentane – there is no isopropyl group in this structure
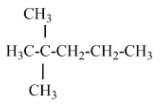
(C) 2, 2, 3 –trimethyl pentane - there is no isopropyl group in this structure
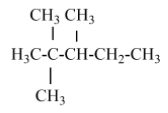
(D) 2-methyl pentane- contains one isopropyl group and Option D is the correct answer.
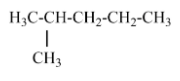
Hence, the answer is option (D).
Note: For carbocations, if carbons with more carbons attached which is tertiary carbocation tend to be less electron deficient due to hyperconjugation from nearby C-H bonds. So, tertiary carbon cations are more stable compared to secondary, primary, and methyl cations respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Classifications of carbon atoms based on nomenclature are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. To describe how many other carbons are attached to given carbon. This classification applied to only saturated carbons and its substitution compounds like alcohols, amines, etc.
The terminology of carbon-containing functional groups:
Primary carbons: a hydrogen atom on a carbon atom attached to one other carbon atom
Secondary carbons: hydrogen on a carbon attached to only two other carbon atoms
Tertiary carbons: hydrogen on a carbon attached to three other carbon atoms
Quaternary carbons: carbon attached to four other carbon atoms.
If any carbon atom is a tertiary carbon with this structure will be

Let us check the IUPAC names of the compounds given,
(A) 2, 2, 3, 3- tetramethyl pentane – there is no isopropyl carbon atom in the parent chain.
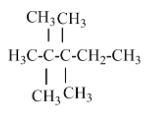
(B) 2,2- dimethyl pentane – there is no isopropyl group in this structure
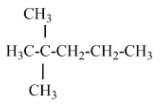
(C) 2, 2, 3 –trimethyl pentane - there is no isopropyl group in this structure
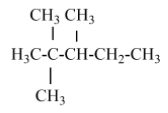
(D) 2-methyl pentane- contains one isopropyl group and Option D is the correct answer.
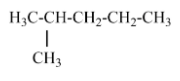
Hence, the answer is option (D).
Note: For carbocations, if carbons with more carbons attached which is tertiary carbocation tend to be less electron deficient due to hyperconjugation from nearby C-H bonds. So, tertiary carbon cations are more stable compared to secondary, primary, and methyl cations respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




