
The compound \[M{X_4}\] is tetrahedral. The number of \[\angle XMX\] angles in the compound is:
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The number of bonds gives the information regarding the bond angles in the compound. For this label all the bonded atoms and check for the number of bond pairs and lone pairs.
Complete step by step answer: The compound \[M{X_4}\] is tetrahedral. That means it resembles methane \[C{H_4}\] which also has four hydrogen atoms bonded to the central carbon atom.
In order to determine the number of \[\angle XMX\] bond angles the four bonded atoms \[X\] are labeled as A, B, C and D. As the compound is tetrahedral all the bond angles in the compound are at an angle of\[109^\circ 28'\].
Let us draw the labeled diagram of the compound \[M{X_4}\].
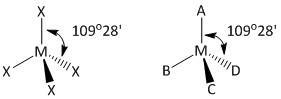
In the tetrahedral model the top \[X\] atom is labeled as A, the bottom three are labeled as B, C and D. The atom C is above the plane and the atom D is inside the plane.
The bond angle indicates that the \[\angle AMD\] angle is \[109^\circ 28'\] which is the same as that for \[\angle XMX\] angle. Thus the bond angles in \[M{X_4}\] are written as
$\angle AMB$
$\angle AMC$
$\angle AMD$
$\angle BMC$
$\angle BMD$
$\angle CMD$
Hence the number of \[\angle XMX\] bond angles in \[M{X_4}\] is six
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The bond angle of tetrahedral compound is with the help of VSEPR theory. VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. It assumes the number of valence electrons around the central atom plus the number of bonded atoms. In tetrahedral geometry the bond pair- bond pair repulsion leads to the bond angle of \[109^\circ 28'\]. If a lone pair is present in spite of a bonded atom the bond angle changes along with the geometry due to greater repulsion between lone pair and bond pair.
Complete step by step answer: The compound \[M{X_4}\] is tetrahedral. That means it resembles methane \[C{H_4}\] which also has four hydrogen atoms bonded to the central carbon atom.
In order to determine the number of \[\angle XMX\] bond angles the four bonded atoms \[X\] are labeled as A, B, C and D. As the compound is tetrahedral all the bond angles in the compound are at an angle of\[109^\circ 28'\].
Let us draw the labeled diagram of the compound \[M{X_4}\].

In the tetrahedral model the top \[X\] atom is labeled as A, the bottom three are labeled as B, C and D. The atom C is above the plane and the atom D is inside the plane.
The bond angle indicates that the \[\angle AMD\] angle is \[109^\circ 28'\] which is the same as that for \[\angle XMX\] angle. Thus the bond angles in \[M{X_4}\] are written as
$\angle AMB$
$\angle AMC$
$\angle AMD$
$\angle BMC$
$\angle BMD$
$\angle CMD$
Hence the number of \[\angle XMX\] bond angles in \[M{X_4}\] is six
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The bond angle of tetrahedral compound is with the help of VSEPR theory. VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. It assumes the number of valence electrons around the central atom plus the number of bonded atoms. In tetrahedral geometry the bond pair- bond pair repulsion leads to the bond angle of \[109^\circ 28'\]. If a lone pair is present in spite of a bonded atom the bond angle changes along with the geometry due to greater repulsion between lone pair and bond pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




